Final ID: Sa4104
Machine learning models based on hyperspectral images accurately diagnose coronary artery disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) can be used for high-precision classification, offering high spectral resolution, wide spectral coverage, and high data dimensionality. Patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) possess distinctive body surface image characteristics. However, value of HSI for the diagnosis of CAD remains unclear
Hypothesis CAD patients exhibit characteristic spectral signatures on surface, which can be used for diagnostic identification of CAD.
Methods This is a cross-sectional observational study. Clinical baseline characteristics, results of coronary artery angiography (CAG) and tongue dorsum hyperspectral images (spectral range:688-951nm) were collected from the subjects. In this study, 3650 hyperspectral images were included. These images are divided into training sets(N=2555) and validation sets(N=1095). Machine learning algorithms were used to selection of features in hyperspectral images and construction of CAD diagnosis models (including Gaussian process (GP), random forest (RF), support vector machine (SVM), gradient boosting (GB), TheilSen etc). Model fusion was achieved by forward selection strategies to improve model performance. The screened features are further used to generate new clinical markers through band math. Predictive performance of the models was assessed based on the results from CAG.
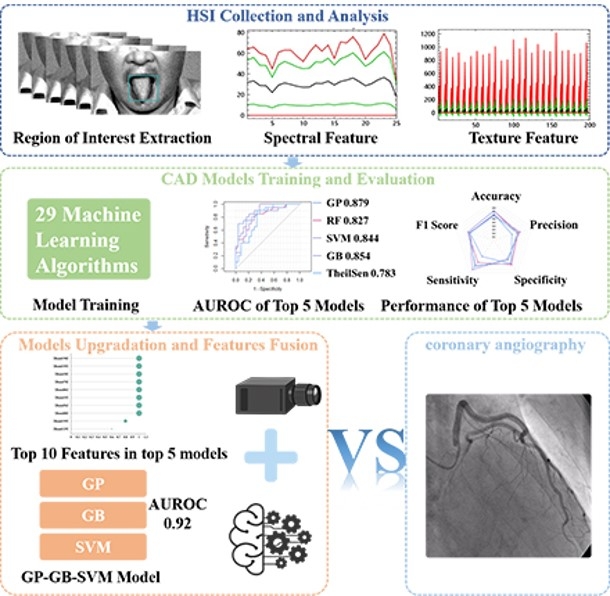
Results The model performance was evaluated through area under receiver operating characteristics (AUROC), decision curve analysis (DCA), calibration curve, accuracy, precision, sensitivity, specificity, and F1 score. (1) The top 5 performance models were selected from 29 models, including GP, RF, SVM, GB, and TheilSen. The corresponding AUROC for top 5 models were 0.879, 0.827, 0.844, 0.854 and 0.783.(2) Based on forward selection strategy, GP, GB and SVM models were selected to develop fusion model (GP-GB-SVM model). Model performance of GP-GB-SVM model was upgraded and AUROC of GP-GB-SVM was 0.92. (3) The top 10 features were recognized from top 5 models. Combination of 10 features through band math generated new clinical marker (Hyper-CAD), which can effectively predict risk of CAD.
Conclusion The present study suggests that patients with CAD exhibit characteristic HSI alterations on the surface. Patients with CAD can be effectively diagnosed and identified based on these alterations.
Hypothesis CAD patients exhibit characteristic spectral signatures on surface, which can be used for diagnostic identification of CAD.
Methods This is a cross-sectional observational study. Clinical baseline characteristics, results of coronary artery angiography (CAG) and tongue dorsum hyperspectral images (spectral range:688-951nm) were collected from the subjects. In this study, 3650 hyperspectral images were included. These images are divided into training sets(N=2555) and validation sets(N=1095). Machine learning algorithms were used to selection of features in hyperspectral images and construction of CAD diagnosis models (including Gaussian process (GP), random forest (RF), support vector machine (SVM), gradient boosting (GB), TheilSen etc). Model fusion was achieved by forward selection strategies to improve model performance. The screened features are further used to generate new clinical markers through band math. Predictive performance of the models was assessed based on the results from CAG.
Results The model performance was evaluated through area under receiver operating characteristics (AUROC), decision curve analysis (DCA), calibration curve, accuracy, precision, sensitivity, specificity, and F1 score. (1) The top 5 performance models were selected from 29 models, including GP, RF, SVM, GB, and TheilSen. The corresponding AUROC for top 5 models were 0.879, 0.827, 0.844, 0.854 and 0.783.(2) Based on forward selection strategy, GP, GB and SVM models were selected to develop fusion model (GP-GB-SVM model). Model performance of GP-GB-SVM model was upgraded and AUROC of GP-GB-SVM was 0.92. (3) The top 10 features were recognized from top 5 models. Combination of 10 features through band math generated new clinical marker (Hyper-CAD), which can effectively predict risk of CAD.
Conclusion The present study suggests that patients with CAD exhibit characteristic HSI alterations on the surface. Patients with CAD can be effectively diagnosed and identified based on these alterations.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Machine Learning Readmission Risk Prediction Model for Cardiac Disease
Bailey Angela, Wang Wei, Shannon Clarence, Huling Jared, Tignanelli Christopher
4D Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Identifies Differences in Regional Strain Patterns Among Pediatric Heart Transplant Patients with Acute Rejection or Cardiac Allograft VasculopathyHenderson Christopher, Starnes Joseph, Samyn Margaret, Damon Bruce, Hernandez Lazaro, Goergen Craig, Soslow Jonathan, Prado Marco Aurélio, Earl Conner, Georgedurrett Kristen, Lee Simon, Nandi Deipanjan, Chan Kak-chen, Shugh Svetlana, Kikano Sandra