Final ID: MDP698
Artificial intelligence-based hyperspectral technique facilitates the diagnosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is an important type of heart failure. The diagnostic process for patients with HFpEF is complex. Hyperspectral cameras have the ability to acquire high-definition hyperspectral images and have a wide range of applications and advantages. Therefore, the development of a fast and non-invasive diagnostic model for HFpEF is innovative.
Hypothesis: The aim of this study is to construct a rapid diagnostic model for HFpEF patients based on hyperspectral image and artificial intelligence.
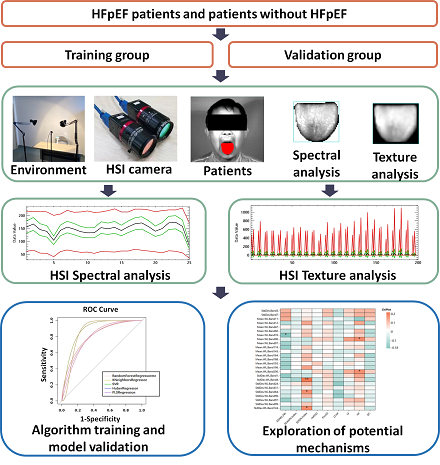
Methods: We enrolled 3500 hyperspectral images from HFpEF patients and control patients, and all data were randomly divided into training group (n=2625) and validation group (n=875). The characteristic spectral information and texture information were obtained using image segmentation software and image analysis software. We used various algorithms to identify the characteristic spectral bands that can be used to identify patients with HFpEF to screen out the best model, and compared the evaluation indexes of different algorithms. We compared the autonomic indexes and lipid metabolism indexes of HFpEF patients and non-HFpEF patients to explore the potential mechanism.
Results: More than 30 artificial intelligence algorithms were used to filter the spectrum that best reflects the HFpEF patients, among which random forest algorithm was the best performing model. The accuracy was 0.829, precision was 1.000, recall was 1.000, F1 Score was 0.750, specificity was 0.792, sensitivity was 0.909, and Joden index was 0.701, the area under the curve of the was 0.884. There were significant differences in autonomic indexes between the two group, as well as lipid levels and body mass index, suggesting that differences in autonomic functional activity and lipid metabolism are potential mechanisms.
Conclusions: An artificial intelligence HFpEF diagnostic model based on hyperspectral imaging was developed and validated. The model can quickly and efficiently help physicians to screen HFpEF patients, as well as help early self-identification of HFpEF patients to seek timely medical treatment, thus contributing to the early detection, early diagnosis, early treatment of HFpEF patients.
Hypothesis: The aim of this study is to construct a rapid diagnostic model for HFpEF patients based on hyperspectral image and artificial intelligence.
Methods: We enrolled 3500 hyperspectral images from HFpEF patients and control patients, and all data were randomly divided into training group (n=2625) and validation group (n=875). The characteristic spectral information and texture information were obtained using image segmentation software and image analysis software. We used various algorithms to identify the characteristic spectral bands that can be used to identify patients with HFpEF to screen out the best model, and compared the evaluation indexes of different algorithms. We compared the autonomic indexes and lipid metabolism indexes of HFpEF patients and non-HFpEF patients to explore the potential mechanism.
Results: More than 30 artificial intelligence algorithms were used to filter the spectrum that best reflects the HFpEF patients, among which random forest algorithm was the best performing model. The accuracy was 0.829, precision was 1.000, recall was 1.000, F1 Score was 0.750, specificity was 0.792, sensitivity was 0.909, and Joden index was 0.701, the area under the curve of the was 0.884. There were significant differences in autonomic indexes between the two group, as well as lipid levels and body mass index, suggesting that differences in autonomic functional activity and lipid metabolism are potential mechanisms.
Conclusions: An artificial intelligence HFpEF diagnostic model based on hyperspectral imaging was developed and validated. The model can quickly and efficiently help physicians to screen HFpEF patients, as well as help early self-identification of HFpEF patients to seek timely medical treatment, thus contributing to the early detection, early diagnosis, early treatment of HFpEF patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A DHX38 Spliceosomal Mutation Impairs MYC Signaling, Cardiac Transcriptome Splicing, and Leads to Diastolic Dysfunction
Iwanski Jessika, Sarvagalla Sailu, Methawasin Mei, Van Den Berg Marloes, Churko Jared
4D Flow MRI Allows for Enhanced Characterization of Aortic RegurgitationAvgousti Harris, Johnson Ethan, Berhane Haben, Thomas James, Allen Bradley, Markl Michael, Appadurai Vinesh