Final ID: Su4008
Complete Versus Culprit Only Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients with Chronic Total Occlusion in Non-Infarct Related Artery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Multivessel coronary artery disease has a higher risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes. Although patients presenting with STEMI usually undergo revascularization of the infarct-related artery only (i.e. cuplrit only percutaneous coronary intervention or CO-PCI), recent trials suggest improved outcomes with complete PCI of all arteries with chronic total occlusion (CTO).
Aim: To meta-analyze data from randomized controlled trials comparing the impact of complete versus CO-PCI in STEMI patients with CTO in the non-infarct related artery (non-IRA).
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search of Medline, EMBASE, and Scopus up till May 2024, to identify studies comparing the clinical outcomes between CO-PCI versus complete PCI in patients with STEMI accompanied by CTO in the non-IRA. Effect estimates were pooled using a random-effects model and reported as risk ratios (RR) along with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs), with a significant p value < 0.05. Outcomes of interest include all-cause and cardiac mortality, myocardial infarction and stroke.
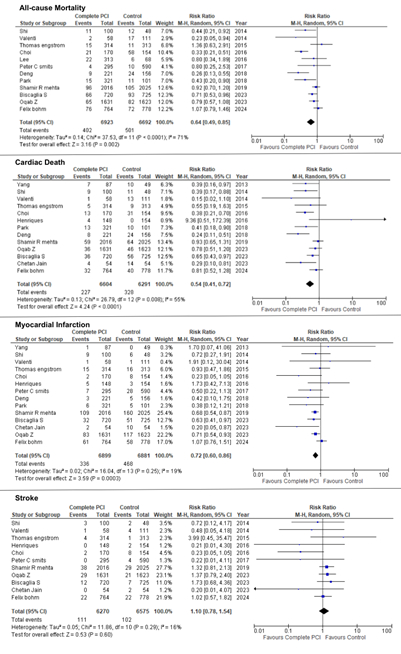
Results: Our search strategy yielded 16 eligible studies (complete PCI, n= 7,982; CO-PCI, n= 7,753). Complete PCI significantly reduced all-cause mortality in comparison to CO-PCI (RR=0.64 [0.49, 0.84]; p=0.002). Complete PCI was also associated with a significant reduction in cardiac death (RR: 0.54 [0.41 - 0.72]; p<0.0001), and myocardial infarction (RR=0.72 [0.60 - 0.86]; p=0.0003), compared with CO-PCI. However, there was no significant difference in stroke risk 1.10 [0.78-1.54; p=0.60]. The forest plots are illustrated in Figure 1.
Conclusion: In STEMI patients with chronic total occlusion in the non-infarct related artery, complete PCI may yield superior outcomes compared with CO-PCI.
Aim: To meta-analyze data from randomized controlled trials comparing the impact of complete versus CO-PCI in STEMI patients with CTO in the non-infarct related artery (non-IRA).
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search of Medline, EMBASE, and Scopus up till May 2024, to identify studies comparing the clinical outcomes between CO-PCI versus complete PCI in patients with STEMI accompanied by CTO in the non-IRA. Effect estimates were pooled using a random-effects model and reported as risk ratios (RR) along with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs), with a significant p value < 0.05. Outcomes of interest include all-cause and cardiac mortality, myocardial infarction and stroke.
Results: Our search strategy yielded 16 eligible studies (complete PCI, n= 7,982; CO-PCI, n= 7,753). Complete PCI significantly reduced all-cause mortality in comparison to CO-PCI (RR=0.64 [0.49, 0.84]; p=0.002). Complete PCI was also associated with a significant reduction in cardiac death (RR: 0.54 [0.41 - 0.72]; p<0.0001), and myocardial infarction (RR=0.72 [0.60 - 0.86]; p=0.0003), compared with CO-PCI. However, there was no significant difference in stroke risk 1.10 [0.78-1.54; p=0.60]. The forest plots are illustrated in Figure 1.
Conclusion: In STEMI patients with chronic total occlusion in the non-infarct related artery, complete PCI may yield superior outcomes compared with CO-PCI.
More abstracts on this topic:
Abbreviated Ticagrelor-Based Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Harmouch Wissam, Elbadawi Ayman, Thakker Ravi, Khalid Umair, Khalife Wissam, Kleiman Neal, Rangasetty Umamahesh, Kayani Waleed, Jneid Hani, Al Hemyari Bashar
2-Deoxyuridine Associates with Recurrent Coronary EventsPistritu Dan, Castano David, Liehn Elisa, Koh Cho Yeow, Gerszten Robert, Singaraja Roshni, Chan Mark, Shah Svati