Final ID: MDP1577
Prediabetes Subphenotypes Show Different Associations with Time to Type 2 Diabetes in the Diabetes Prevention Program
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): INTRODUCTION
Prediabetes is a prominent risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). The clinical phenotype of individuals with prediabetes, however, is diverse, and characterization of subphenotypes may identify differing underlying physiology and outcomes. This study aimed to examine associations among prediabetes clusters and time to T2D development.
METHODS
We performed k-means cluster analyses in a subset of individuals with prediabetes (n=994) from the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP). Clusters were based on 7 clinically measurable variables (age, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol (HDL-C), fasting glucose (FG), and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)). Differences in time to T2D between clusters, overall and by treatment arm, were assessed via Kaplan-Meier survival estimates with post-hoc tests adjusted for multiple comparisons via a Bonferroni correction. Cox proportional Hazard models adjusted for treatment, sex, and race and ethnicity were used to determine T2D hazard ratios (HR) by cluster.
RESULTS
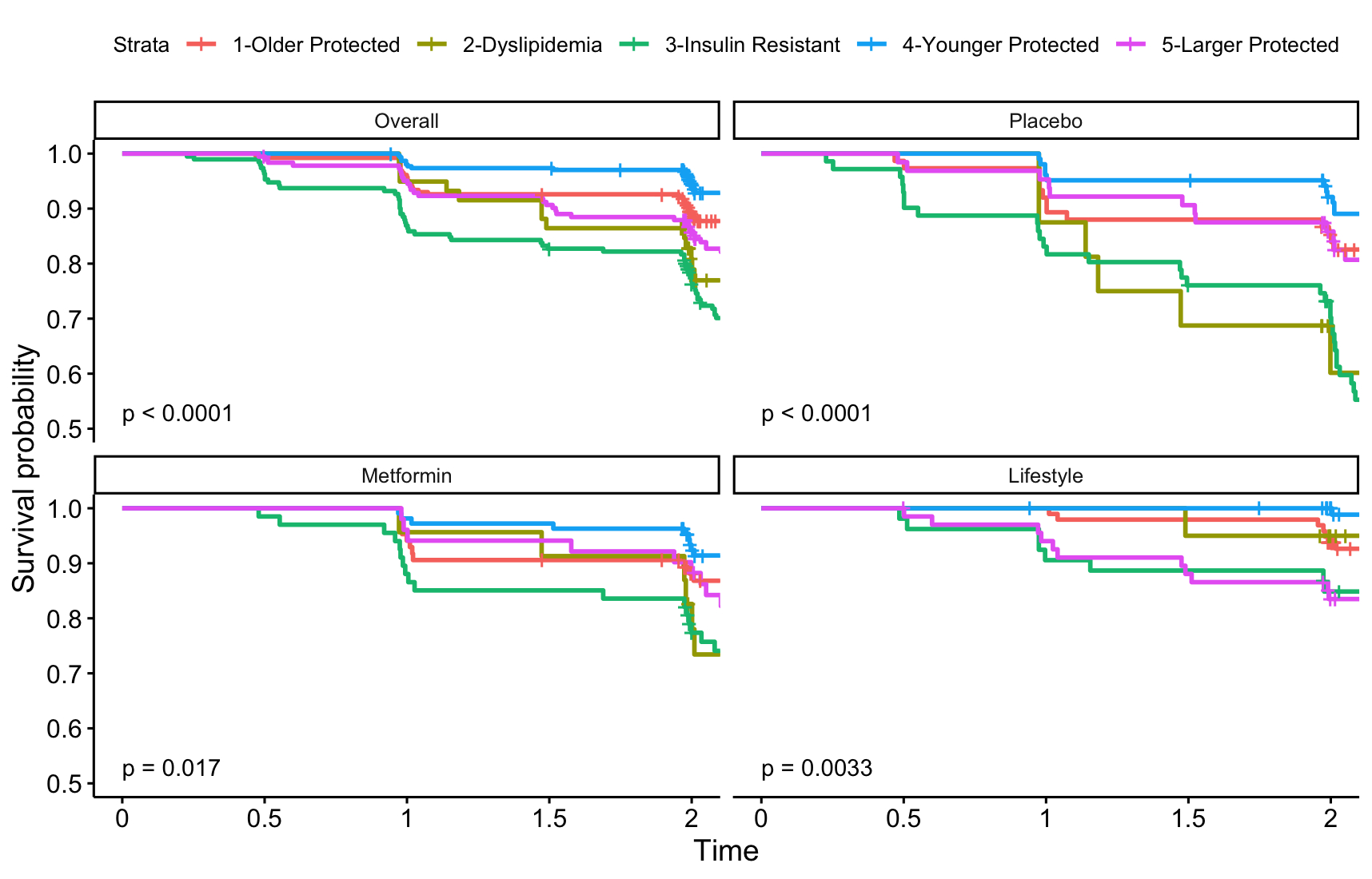
Five distinct clusters were identified. 1: “older protected” (highest age and HDL-C, lowest BMI and triglycerides); 2: “dyslipidemia” (highest triglycerides, lowest HDL-C); 3: “insulin resistant” (highest FG and HbA1c); 4: “younger protected” (lowest age, FG and HbA1c, lower BMI and waist circumference); and 5: “larger protected (highest BMI and waist circumference, lower triglycerides). Clusters differed significantly in gender and race and ethnicity. Time to diabetes differed between clusters overall and by DPP treatment arm (fig. 1). Post-hoc tests indicated significantly lower time to T2D, both overall and in placebo, in cluster 3 vs. 1, cluster 2 vs. 4, and cluster 3 vs. 5. Time to T2D was also significantly lower in cluster 5 vs. 4 overall and in lifestyle, and in cluster 3 vs. 4 overall and in all treatment arms (corrected p<0.05). Adjusted Cox models indicate that the HR (95% CI) for T2D vs. cluster 4 in cluster 1 is 1.92 (1.10, 3.36), 3.77 (1.88, 7.59) in cluster 2, 4.93 (2.96, 8.23) in cluster 3, and 2.74 (1.57, 4.81) in cluster 5.
CONCLUSIONS
Clinical variables were used to identify 5 distinct subphenotypes of individuals with prediabetes, each demonstrating different rates of T2D development, with treatment-adjusted differences. This study highlights potential heterogeneity in individuals with prediabetes and potential clinically relevant clusters with increased risk of progression to T2D.
Prediabetes is a prominent risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). The clinical phenotype of individuals with prediabetes, however, is diverse, and characterization of subphenotypes may identify differing underlying physiology and outcomes. This study aimed to examine associations among prediabetes clusters and time to T2D development.
METHODS
We performed k-means cluster analyses in a subset of individuals with prediabetes (n=994) from the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP). Clusters were based on 7 clinically measurable variables (age, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol (HDL-C), fasting glucose (FG), and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)). Differences in time to T2D between clusters, overall and by treatment arm, were assessed via Kaplan-Meier survival estimates with post-hoc tests adjusted for multiple comparisons via a Bonferroni correction. Cox proportional Hazard models adjusted for treatment, sex, and race and ethnicity were used to determine T2D hazard ratios (HR) by cluster.
RESULTS
Five distinct clusters were identified. 1: “older protected” (highest age and HDL-C, lowest BMI and triglycerides); 2: “dyslipidemia” (highest triglycerides, lowest HDL-C); 3: “insulin resistant” (highest FG and HbA1c); 4: “younger protected” (lowest age, FG and HbA1c, lower BMI and waist circumference); and 5: “larger protected (highest BMI and waist circumference, lower triglycerides). Clusters differed significantly in gender and race and ethnicity. Time to diabetes differed between clusters overall and by DPP treatment arm (fig. 1). Post-hoc tests indicated significantly lower time to T2D, both overall and in placebo, in cluster 3 vs. 1, cluster 2 vs. 4, and cluster 3 vs. 5. Time to T2D was also significantly lower in cluster 5 vs. 4 overall and in lifestyle, and in cluster 3 vs. 4 overall and in all treatment arms (corrected p<0.05). Adjusted Cox models indicate that the HR (95% CI) for T2D vs. cluster 4 in cluster 1 is 1.92 (1.10, 3.36), 3.77 (1.88, 7.59) in cluster 2, 4.93 (2.96, 8.23) in cluster 3, and 2.74 (1.57, 4.81) in cluster 5.
CONCLUSIONS
Clinical variables were used to identify 5 distinct subphenotypes of individuals with prediabetes, each demonstrating different rates of T2D development, with treatment-adjusted differences. This study highlights potential heterogeneity in individuals with prediabetes and potential clinically relevant clusters with increased risk of progression to T2D.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Longitudinal 20-year Analysis Indicates Acceleration of Cardiometabolic Comorbidities on Dementia Risk
Lihua Huang, Danish Muhammad, Auyeung Tw, Jenny Lee, Kwok Timothy, Abrigo Jill, Wei Yingying, Lo Cecilia, Fung Erik
Glycemic Status Modifies the Prognostic Value of the Cardiometabolic Index for Cardiorenal Outcomes: Evidence From a Population-Based Cohort StudyXie Yingyi, Wang Ziyi, Song Yanjun, Guo Yuanlin, Song Weihua, Dou Kefei