Final ID: Mo3081
Deep Learning Quantification of Aortic Compliance from Parasternal Long-Axis Echocardiograms
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Aortic compliance is crucial for maintaining diastolic blood pressure and systemic perfusion throughout the cardiac cycle. Echocardiography is widely used for cardiovascular imaging but has limited precision in clinical phenotyping of aortic compliance.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that a deep learning approach can quantify aortic compliance by precision characterization of the aortic root in parasternal long-axis echocardiogram videos and that this deep learning measured aortic compliance would correlate with aspects of thoracic aortic repair.
Aims
Develop a high precision deep learning model for quantifying aortic compliance from echocardiogram videos and explore associations with surgical repair.
Methods
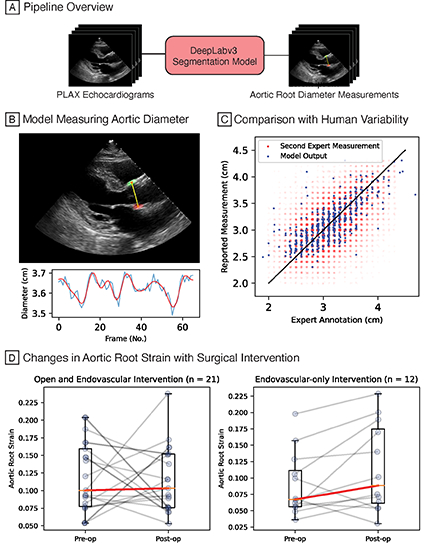
We used 51730 PLAX echocardiogram videos from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, divided into training (46188), validation (5035), and test (507) cohorts. The DeepLabv3 architecture with a 50-layer residual network backbone was used for frame-level segmentation of the aortic root. Strain was obtained by dividing the change in root diameter by the minimum diameter during each cardiac cycle. Evaluation of measurements was performed on a separate cohort of 33 patients who underwent endovascular repair of the thoracic aorta.
Results
The model accurately measured aortic root diameter with a mean absolute error (MAE) of 2.5mm comparing favorably with clinical inter-observer variability (MAE of 2.9mm, p=0.010). Exploratory data analysis showed increasing aortic root strain after endovascular repair (n=12, p=0.084) but no clear trends after combined endovascular and open repair (n=21, p=0.852). Aortic strain was lower in patients with prior abdominal surgery (n=12, p=0.001) and dissection that underwent repair (n=14, p=0.099), and postoperative aortic strains were lower in patients requiring surgery within 30 days (n=7, p=0.024).
Conclusion
A deep learning workflow can measure aortic root diameter and identify changes in aortic compliance with higher precision than human assessment. Trends in preoperative and postoperative aortic strain in patients undergoing endovascular repair suggest utility of aortic strain phenotyping for prognosticating clinical outcomes.
Aortic compliance is crucial for maintaining diastolic blood pressure and systemic perfusion throughout the cardiac cycle. Echocardiography is widely used for cardiovascular imaging but has limited precision in clinical phenotyping of aortic compliance.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that a deep learning approach can quantify aortic compliance by precision characterization of the aortic root in parasternal long-axis echocardiogram videos and that this deep learning measured aortic compliance would correlate with aspects of thoracic aortic repair.
Aims
Develop a high precision deep learning model for quantifying aortic compliance from echocardiogram videos and explore associations with surgical repair.
Methods
We used 51730 PLAX echocardiogram videos from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, divided into training (46188), validation (5035), and test (507) cohorts. The DeepLabv3 architecture with a 50-layer residual network backbone was used for frame-level segmentation of the aortic root. Strain was obtained by dividing the change in root diameter by the minimum diameter during each cardiac cycle. Evaluation of measurements was performed on a separate cohort of 33 patients who underwent endovascular repair of the thoracic aorta.
Results
The model accurately measured aortic root diameter with a mean absolute error (MAE) of 2.5mm comparing favorably with clinical inter-observer variability (MAE of 2.9mm, p=0.010). Exploratory data analysis showed increasing aortic root strain after endovascular repair (n=12, p=0.084) but no clear trends after combined endovascular and open repair (n=21, p=0.852). Aortic strain was lower in patients with prior abdominal surgery (n=12, p=0.001) and dissection that underwent repair (n=14, p=0.099), and postoperative aortic strains were lower in patients requiring surgery within 30 days (n=7, p=0.024).
Conclusion
A deep learning workflow can measure aortic root diameter and identify changes in aortic compliance with higher precision than human assessment. Trends in preoperative and postoperative aortic strain in patients undergoing endovascular repair suggest utility of aortic strain phenotyping for prognosticating clinical outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
12-lead electrocardiograms predict adverse cardiovascular outcomes of emergency department patients
Haimovich Julian, Kolossvary Marton, Alam Ridwan, Padros I Valls Raimon, Lu Michael, Aguirre Aaron
A Deep Learning Digital Biomarker for Mitral Valve Prolapse using Echocardiogram VideosAl-alusi Mostafa, Khurshid Shaan, Sanborn Danita, Picard Michael, Ho Jennifer, Maddah Mahnaz, Ellinor Patrick, Lau Emily, Small Aeron, Reeder Christopher, Shnitzer Dery Tal, Andrews Carl, Kany Shinwan, Ramo Joel, Haimovich Julian