Final ID: 4131622
Opportunistic Screening of Chronic Liver Disease With Deep Learning Enhanced Echocardiography
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Chronic liver disease affects more than 1.5 billion adults worldwide, but the majority of cases are asymptomatic and undiagnosed. Echocardiography is broadly performed and visualizes the liver; however, this information is not diagnostically leveraged.
Hypothesis and Aims
We hypothesized that a deep-learning algorithm can detect chronic liver diseases using subcostal echocardiography images that contains hepatic tissue. To develop and evaluate a deep learning algorithm on subcostal echocardiography videos to enable opportunistic screening for chronic liver disease.
Methods
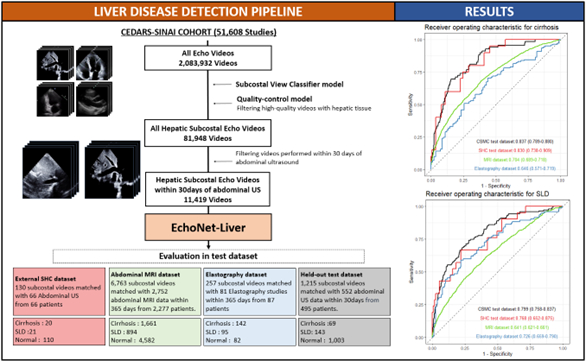
We identified adult patients who received echocardiography and abdominal imaging (either abdominal ultrasound or abdominal magnetic resonance imaging) with ≤30 days between tests. A convolutional neural network pipeline was developed to predict the presence of cirrhosis or steatotic liver disease (SLD) using echocardiogram images. The model performance was evaluated in a held-out test dataset, dataset in which diagnosis was made by magnetic resonance imaging, and external dataset.
Results
A total of 2,083,932 echocardiography videos (51,608 studies) from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center (CSMC) were used to develop EchoNet-Liver, an automated pipeline that identifies high quality subcostal images from echocardiogram studies and detects presence of cirrhosis or SLD. In a total of 11,419 quality-controlled subcostal videos from 4,849 patients, a chronic liver disease detection model was able to detect the presence of cirrhosis with an AUC of 0.837 (0.789 - 0.880) and SLD with an AUC of 0.799 (0.758 - 0.837). In a separate test cohort with paired abdominal MRIs, cirrhosis was detected with an AUC of 0.726 (0.659-0.790) compared to MR elastography and SLD was detected with an AUC of 0.704 (0.689-0.718). In the external test cohort of 66 patients (n = 130 videos), the model detected cirrhosis with an AUC of 0.830 (0.738 - 0.909) and SLD with an AUC of 0.768 (0.652 – 0.875).
Conclusions:
Deep learning assessment of clinically indicated echocardiography enables opportunistic screening of SLD and cirrhosis. Application of this algorithm may identify patients who may benefit from further diagnostic testing and treatment for hepatic disease.
Chronic liver disease affects more than 1.5 billion adults worldwide, but the majority of cases are asymptomatic and undiagnosed. Echocardiography is broadly performed and visualizes the liver; however, this information is not diagnostically leveraged.
Hypothesis and Aims
We hypothesized that a deep-learning algorithm can detect chronic liver diseases using subcostal echocardiography images that contains hepatic tissue. To develop and evaluate a deep learning algorithm on subcostal echocardiography videos to enable opportunistic screening for chronic liver disease.
Methods
We identified adult patients who received echocardiography and abdominal imaging (either abdominal ultrasound or abdominal magnetic resonance imaging) with ≤30 days between tests. A convolutional neural network pipeline was developed to predict the presence of cirrhosis or steatotic liver disease (SLD) using echocardiogram images. The model performance was evaluated in a held-out test dataset, dataset in which diagnosis was made by magnetic resonance imaging, and external dataset.
Results
A total of 2,083,932 echocardiography videos (51,608 studies) from Cedars-Sinai Medical Center (CSMC) were used to develop EchoNet-Liver, an automated pipeline that identifies high quality subcostal images from echocardiogram studies and detects presence of cirrhosis or SLD. In a total of 11,419 quality-controlled subcostal videos from 4,849 patients, a chronic liver disease detection model was able to detect the presence of cirrhosis with an AUC of 0.837 (0.789 - 0.880) and SLD with an AUC of 0.799 (0.758 - 0.837). In a separate test cohort with paired abdominal MRIs, cirrhosis was detected with an AUC of 0.726 (0.659-0.790) compared to MR elastography and SLD was detected with an AUC of 0.704 (0.689-0.718). In the external test cohort of 66 patients (n = 130 videos), the model detected cirrhosis with an AUC of 0.830 (0.738 - 0.909) and SLD with an AUC of 0.768 (0.652 – 0.875).
Conclusions:
Deep learning assessment of clinically indicated echocardiography enables opportunistic screening of SLD and cirrhosis. Application of this algorithm may identify patients who may benefit from further diagnostic testing and treatment for hepatic disease.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Diagnosis Dilemma of Positional Hypoxia: Scoliosis-Mediated Platypnea-Orthodeoxia Syndrome
Ademuwagun Christianah, Arjoon Roy, Seth Paula, Chang Gene, Ibe Oby
A Novel Echocardiography Risk Score Predicted Mortality In Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.Iwakura Katsuomi, Yoshio Yasumura, Hikoso Shungo, Okada Katsuki, Nakatani Daisaku, Sotomi Yohei, Sakata Yasushi, Tanaka Nobuaki, Okada Masato, Okamura Atsunori, Heitaro Watanabe, Seo Masahiro, Hayashi Takaharu, Yano Masamichi, Yamada Takahisa