Final ID: MDP1528
Fully Automatic Quantification of the Aortic Root in 4D Transesophageal Echocardiography
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Aortic root (AoR) morphology and dynamics are integral to understanding aortic valve function and planning patient-specific aortic interventions with transesophageal echocardiography (TEE). Modeling the AoR in time-varying 3D data is advantageous over conventional 2D cross-sectional analysis. However, manual segmentation of the AoR in 3D relies on a learning curve and takes up to 1.5 hours per volume. We hypothesize that the AoR can be rapidly and accurately segmented and quantified fully automatically with deep learning in pre-operative 4D TEE.
Methods: Pre-operative TEE from both bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) and tricuspid aortic valve (TAV) patients were semi-automatically segmented and manually verified. A nnU-Net model was trained, validated, and tested with 74 TEE time-series images (46 BAV, 28 TAV) consisting of 1971 individual 3D volumes (60/40% training/testing split) from 2 institutions. The Dice similarity coefficient and average mesh-to-mesh distances were compared to interobserver variability between multiple manual tracers. AoR volume and diameters were automatically computed. Quantification agreement between model-generated and semi-automatic segmentations was analyzed with the intraclass correlation coefficient and Student’s t-test.
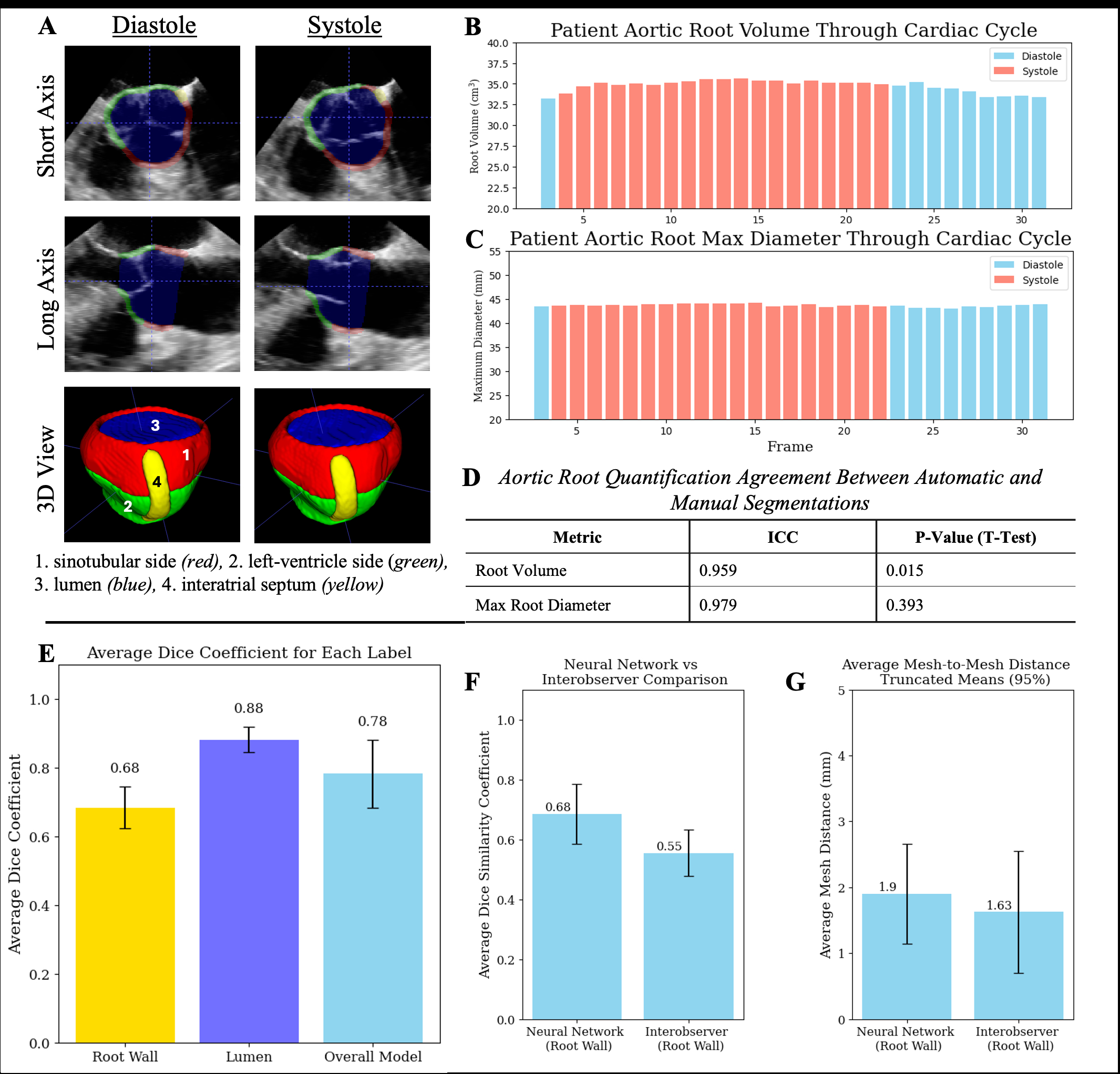
Results: A representative automatic segmentation and quantification of the AoR is shown in Figure 1a-c. Quantification agreement between automatic and manual segmentations for all test data are shown in Figure 1d. Measurements on automatic segmentations have strong agreement with measurements on manual segmentations (ICC > 0.95). Automatic segmentation results are insignificantly different from interobserver tracings (p > 0.01), suggesting that a reliable AoR segmentation can be produced in inference time as little as 1-2 seconds per 3D volume (Figure 1e-g).
Conclusions: The proposed deep learning method rapidly produces AoR segmentations and quantifications that are comparable to manual tracing. This framework can aid in population-based comparison of BAV and TAV roots and facilitate patient-specific AoR assessment for surgical planning. In the future, leaflet segmentations can be incorporated for analysis of the full aortic valve apparatus in TEE.
Methods: Pre-operative TEE from both bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) and tricuspid aortic valve (TAV) patients were semi-automatically segmented and manually verified. A nnU-Net model was trained, validated, and tested with 74 TEE time-series images (46 BAV, 28 TAV) consisting of 1971 individual 3D volumes (60/40% training/testing split) from 2 institutions. The Dice similarity coefficient and average mesh-to-mesh distances were compared to interobserver variability between multiple manual tracers. AoR volume and diameters were automatically computed. Quantification agreement between model-generated and semi-automatic segmentations was analyzed with the intraclass correlation coefficient and Student’s t-test.
Results: A representative automatic segmentation and quantification of the AoR is shown in Figure 1a-c. Quantification agreement between automatic and manual segmentations for all test data are shown in Figure 1d. Measurements on automatic segmentations have strong agreement with measurements on manual segmentations (ICC > 0.95). Automatic segmentation results are insignificantly different from interobserver tracings (p > 0.01), suggesting that a reliable AoR segmentation can be produced in inference time as little as 1-2 seconds per 3D volume (Figure 1e-g).
Conclusions: The proposed deep learning method rapidly produces AoR segmentations and quantifications that are comparable to manual tracing. This framework can aid in population-based comparison of BAV and TAV roots and facilitate patient-specific AoR assessment for surgical planning. In the future, leaflet segmentations can be incorporated for analysis of the full aortic valve apparatus in TEE.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Role for ANPEP in Osteogenic Signaling and Aortic Valve Calcification
Fan Jianing, Chen Qixin, Miao Jiaxin, Li Zhenzhen, Zhou Daxin, Ge Junbo
A Hemodynamic Warning Sign: Continuous Mitral Regurgitation and Normal Sinus RhythmMahi Ishani, Chowdhury Mahdi, Madan Hritik, Garg Vaani