Final ID: 4141751
Exercise-Induced Improvements in Capillary Density are Influenced by Sex, Hormone Replacement Therapy, and Exercise Intensity
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background While cardiometabolic disease (CMD) is the top cause of death for US women, age at onset is 10-20 years after that of men largely due to menopausal estrogen loss. Along with premenopausal estrogen, exercise decreases CMD risk in part by increasing capillary density (CD). To better understand CMD risk in postmenopausal women, we investigated the impact of sex, hormone replacement therapy (HRT), and exercise amount/intensity on CD. We hypothesized that compared to women not using HRT and independent of exercise amount/intensity, women using HRT and men would display greater exercise improvements in CD and lesser declines during a detraining period.
Methods Previously sedentary adults with overweight/obesity (n=228) were randomized to an inactive control or one of three 6-mo exercise groups: 1) low-amount/moderate-intensity (LAMI); 2) low-amount/vigorous-intensity (LAVI); or 3) high-amount/vigorous-intensity (HAVI). Biopsy-derived skeletal muscle CD was measured at baseline, 24-h-, 4-days-, and 14-days post-intervention (detraining period). Change scores were calculated by subtracting baseline from post-intervention CDs and analyzed using one-way ANOVA and post-hoc by two-tailed two-sample t-tests. The effects of sex, HRT, and exercise group on CD over time were assessed by linear mixed models.
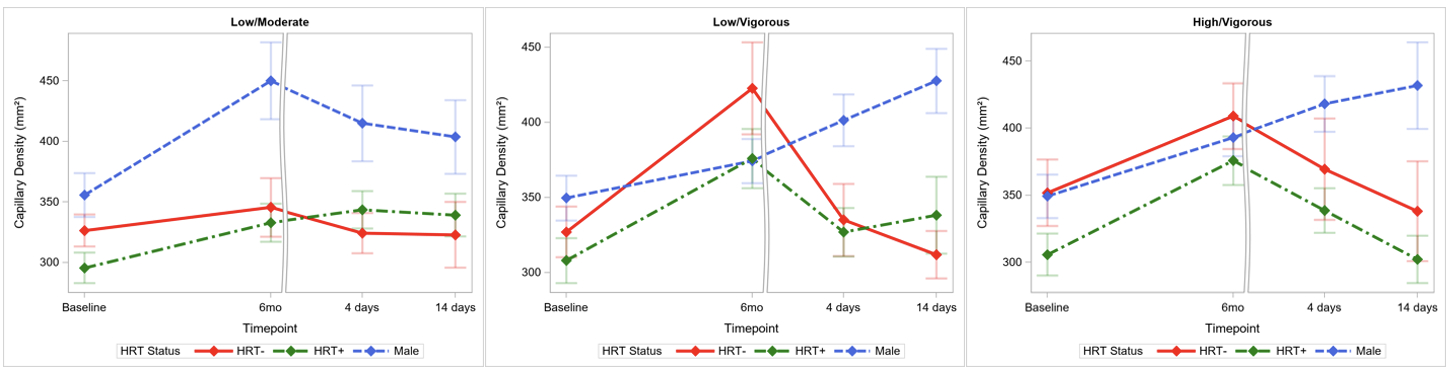
Results Exercise significantly increased CD in all groups except LAMI women not using HRT and LAVI men. In vigorous-intensity groups, men increased CD through detraining while women rapidly returned to baseline. With LAMI exercise, CD in women not using HRT and men returned to baseline with detraining. Women using HRT with LAMI, but not vigorous-intensity exercise, sustained CD improvements through detraining.
Conclusions Sex, HRT, and exercise intensity impacted CD responses to exercise and detraining. Men and women performing vigorous-intensity exercise display disparate detraining responses, indicating women require continued training to maintain exercise-induced CD improvements. HRT sustained CD improvements through detraining in women performing LAMI but not vigorous-intensity exercise. These findings influence recommended exercise frequency and intensity by sex and HRT use to decrease postmenopausal CMD risk.
Methods Previously sedentary adults with overweight/obesity (n=228) were randomized to an inactive control or one of three 6-mo exercise groups: 1) low-amount/moderate-intensity (LAMI); 2) low-amount/vigorous-intensity (LAVI); or 3) high-amount/vigorous-intensity (HAVI). Biopsy-derived skeletal muscle CD was measured at baseline, 24-h-, 4-days-, and 14-days post-intervention (detraining period). Change scores were calculated by subtracting baseline from post-intervention CDs and analyzed using one-way ANOVA and post-hoc by two-tailed two-sample t-tests. The effects of sex, HRT, and exercise group on CD over time were assessed by linear mixed models.
Results Exercise significantly increased CD in all groups except LAMI women not using HRT and LAVI men. In vigorous-intensity groups, men increased CD through detraining while women rapidly returned to baseline. With LAMI exercise, CD in women not using HRT and men returned to baseline with detraining. Women using HRT with LAMI, but not vigorous-intensity exercise, sustained CD improvements through detraining.
Conclusions Sex, HRT, and exercise intensity impacted CD responses to exercise and detraining. Men and women performing vigorous-intensity exercise display disparate detraining responses, indicating women require continued training to maintain exercise-induced CD improvements. HRT sustained CD improvements through detraining in women performing LAMI but not vigorous-intensity exercise. These findings influence recommended exercise frequency and intensity by sex and HRT use to decrease postmenopausal CMD risk.
More abstracts on this topic:
AI-Derived Retinal Vasculature Features Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Insights from the CRIC Study
Dhamdhere Rohan, Modanwal Gourav, Rahman Mahboob, Al-kindi Sadeer, Madabhushi Anant
Association between Age at Menarche and Age at Onset of Angina Pectoris: An Analysis of NHANES Data from 2017-2020Nuchpramool Prachawanee, Prasitsumrit Vitchapong, Kulthamrongsri Kritpong, Thiravetyan Ben, Suenghataiphorn Thanathip, Wannaphut Chalothorn, Srikulmontri Thitiphan, Tantisattamo Ekamol, Kulthamrongsri Narathorn, Wanichwecharungruang Nisha, Suriyathumrongkul Napat, Yinadsawaphan Thanaboon, Wattanachayakul Phuuwadith, Kookanok Chutawat, Saowapa Sakditad, Kanthajan Tatchaya