Final ID: MDP87
Detection and Quantification of Myocardial Infarct with Four Different Histological Staining Techniques
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Precise quantification of myocardial infarct size in therapeutic studies is a key prerequisite to ensure reliable and demonstrative results, and supports the rapid translation of findings into clinical practice. However, current quantification methods are often highly dependent on hand tracing and pose challenges that may impact accuracy, user ease, cost, and timeliness of image analysis. Here, we developed a semi-automatic color-based algorithm capable of infarct region detection and quantification with four different histological staining techniques.
Methods: This model consists of an algorithm based on the unique digital color differences between normal and scarred regions of histological tissue. Typically, multicolored images contain pixels that consist of three colors: red, green and blue. We observed a pattern in the computational color code proportions between unscarred and scarred regions of cardiac tissues in various staining approaches. Therefore, with the aid of MATLAB software, employing a color threshold to these color combinations can potentially identify and isolate the infarct region. In this study, mouse cardiac tissue images from four histological staining methods (masson’s trichrome (MTS), hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) and picrosirius red (PSR)) were included to demonstrate the performance of our algorithm.
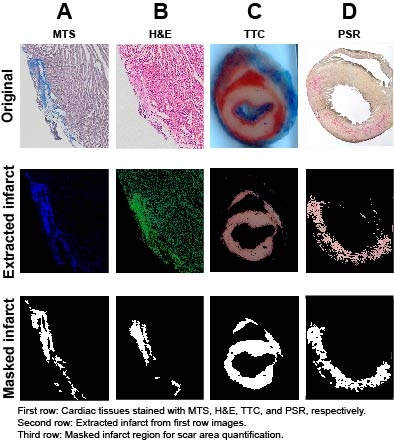
Results: The algorithm effectively identified and produced a clear visualization of scar tissue for the four staining techniques (Figure). Notably, using the MTS image as a reference (panel A), the algorithm could detect the infarct region in a similar heart structure on the H&E image (panel B), which is infrequently used for fibrotic tissue assessment. The infarct region was also successfully extracted and masked. Further, we developed a user-friendly graphic interface to quantify the infarct area and potential volume if the entire heart is sectioned for analysis.
Conclusion: In conclusion, we demonstrate that our algorithm is capable of accurately identifying and isolating cardiac infarct regions using color-based methods, as well as quantifying area and volumetric data from necrotic tissue.
Methods: This model consists of an algorithm based on the unique digital color differences between normal and scarred regions of histological tissue. Typically, multicolored images contain pixels that consist of three colors: red, green and blue. We observed a pattern in the computational color code proportions between unscarred and scarred regions of cardiac tissues in various staining approaches. Therefore, with the aid of MATLAB software, employing a color threshold to these color combinations can potentially identify and isolate the infarct region. In this study, mouse cardiac tissue images from four histological staining methods (masson’s trichrome (MTS), hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) and picrosirius red (PSR)) were included to demonstrate the performance of our algorithm.
Results: The algorithm effectively identified and produced a clear visualization of scar tissue for the four staining techniques (Figure). Notably, using the MTS image as a reference (panel A), the algorithm could detect the infarct region in a similar heart structure on the H&E image (panel B), which is infrequently used for fibrotic tissue assessment. The infarct region was also successfully extracted and masked. Further, we developed a user-friendly graphic interface to quantify the infarct area and potential volume if the entire heart is sectioned for analysis.
Conclusion: In conclusion, we demonstrate that our algorithm is capable of accurately identifying and isolating cardiac infarct regions using color-based methods, as well as quantifying area and volumetric data from necrotic tissue.
More abstracts on this topic:
Artificial-Intelligence Based Tracking of Atrial Fibrillation Waves that Exit Pulmonary Veins Predicts Response to Ablation
Anbazhakan Suhaas, Abad Juan Ricardo Carlos, Ruiperez-campillo Samuel, Rodrigo Miguel, Narayan Sanjiv
A Novel Cardioprotective Mechanism in Myocardial Reperfusion Injury: Dual Neutrophil Modulation and ROS/HOCl Scavenging by an Atypical ChemokineZwissler Leon, Bernhagen Juergen, Cabrera-fuentes Hector Alejandro, Hernandez Resendiz Sauri, Yap En Ping, Schindler Lisa, Zhang Zhishen, Dickerhof Nina, Hampton Mark, Liehn Elisa, Hausenloy Derek