Final ID: Mo4160
Body Mass Index and Waist-Hip Ratio -- Risk Factors for Aortic Valve Disease: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Aortic valve disease (AVD) is common among older adults. Although body mass index (BMI) has been reported to be a risk factor for aortic valve stenosis (AS), it is unknown whether BMI or waist-hip ratio (WHR) is associated with aortic valve insufficiency (AI). Additionally, it is unknown whether there is a stronger association between BMI/WHR with AVD among Blacks compared with Whites.
Hypothesis: Higher BMI/WHR is associated with an increased incidence of AS and AI in the ARIC study, a community-based cohort of Black and White adults.
Methods: The analysis involved ARIC participants with echocardiograms at visit 5 (2011-2013) and visit 7 (2018-2019). BMI and WHR were ascertained from visit 5 and standardized by standard deviation (SD). Incident AVD between visits 5 and 7 was classified as aortic valve sclerosis, isolated AI, and AS regardless of AI, according to AHA guidelines. A multinomial regression model adjusted for multiple potential confounding variables, including age, sex, race, education, smoking status, drinking, diabetes, systolic blood pressure, antihypertensive medications, coronary heart disease, HDL-C LDL-C, and eGFR.
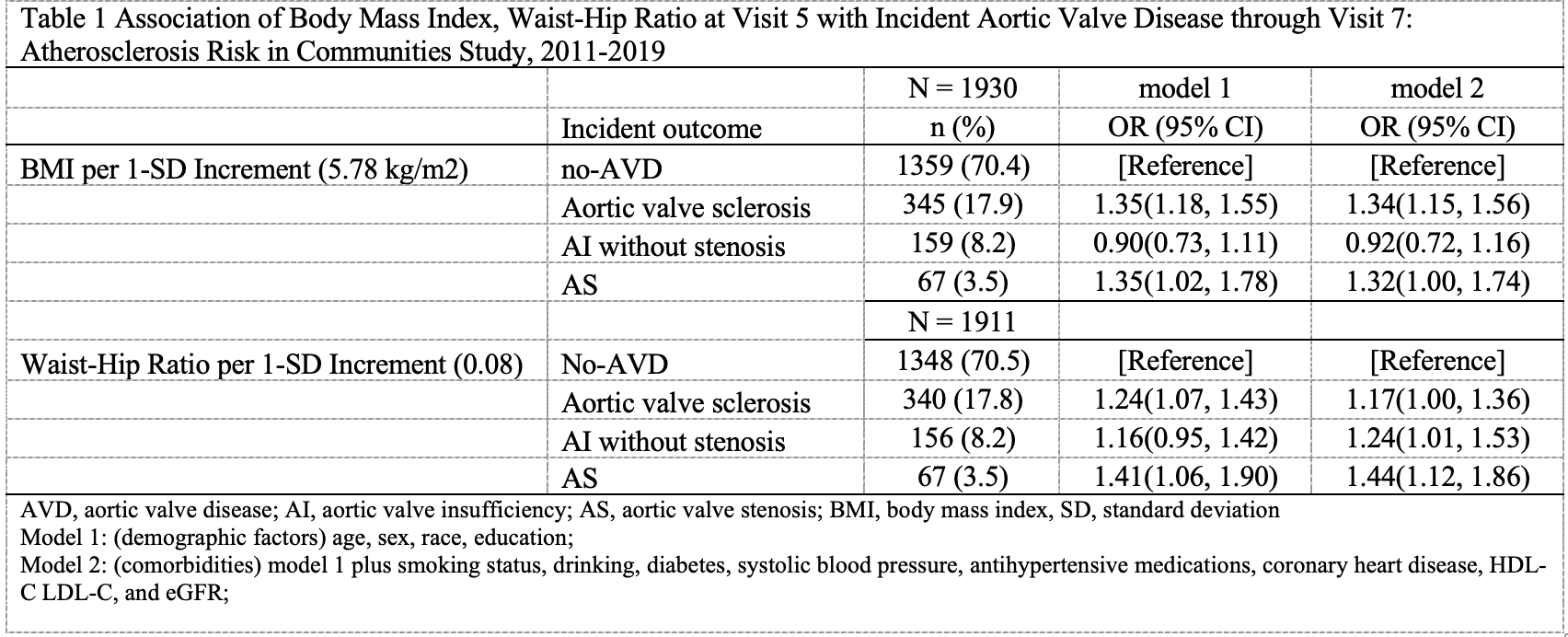
Results: Of 1931 participants included in the analysis (mean age of 73.5 ± 4.1 years, 59.7% female, and 23.2% Black), 572 participants (29.6%) had incident AVD (n = 345 sclerosis, 159 pure AI, 68 AS). Higher BMI at visit 5 was associated with a greater incidence of aortic valve sclerosis (OR: 1.34 per 1-SD (5.78 kg/m2), 95% CI: 1.15-1.56) and AS (OR: 1.32, 95% CI: 1.00-1.74) but was not associated with AI. Higher WHR was associated positively with aortic valve sclerosis (OR: 1.17 per 1-SD (0.08 unit), 95% CI: 1.00-1.36), AS (OR: 1.44, 95% CI: 1.12-1.86), and also AI (OR: 1.24, 95% CI: 1.01-1.53) (Table 1). There were no race-by-obesity interactions in all analyses.
Conclusion: A higher BMI is associated with a higher risk of AS, but not AI. By contrast, increased WHR is a risk factor for both AS and AI. Further research is warranted to replicate this novel finding and define potential underlying mechanisms.
Hypothesis: Higher BMI/WHR is associated with an increased incidence of AS and AI in the ARIC study, a community-based cohort of Black and White adults.
Methods: The analysis involved ARIC participants with echocardiograms at visit 5 (2011-2013) and visit 7 (2018-2019). BMI and WHR were ascertained from visit 5 and standardized by standard deviation (SD). Incident AVD between visits 5 and 7 was classified as aortic valve sclerosis, isolated AI, and AS regardless of AI, according to AHA guidelines. A multinomial regression model adjusted for multiple potential confounding variables, including age, sex, race, education, smoking status, drinking, diabetes, systolic blood pressure, antihypertensive medications, coronary heart disease, HDL-C LDL-C, and eGFR.
Results: Of 1931 participants included in the analysis (mean age of 73.5 ± 4.1 years, 59.7% female, and 23.2% Black), 572 participants (29.6%) had incident AVD (n = 345 sclerosis, 159 pure AI, 68 AS). Higher BMI at visit 5 was associated with a greater incidence of aortic valve sclerosis (OR: 1.34 per 1-SD (5.78 kg/m2), 95% CI: 1.15-1.56) and AS (OR: 1.32, 95% CI: 1.00-1.74) but was not associated with AI. Higher WHR was associated positively with aortic valve sclerosis (OR: 1.17 per 1-SD (0.08 unit), 95% CI: 1.00-1.36), AS (OR: 1.44, 95% CI: 1.12-1.86), and also AI (OR: 1.24, 95% CI: 1.01-1.53) (Table 1). There were no race-by-obesity interactions in all analyses.
Conclusion: A higher BMI is associated with a higher risk of AS, but not AI. By contrast, increased WHR is a risk factor for both AS and AI. Further research is warranted to replicate this novel finding and define potential underlying mechanisms.
More abstracts on this topic:
Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosing Low-Gradient Aortic Stenosis Using Echocardiographic Imaging.
Wrzosek Michal
A drug target Mendelian randomization study of triglyceride lowering therapies for aortic stenosisCiofani Jonathan, Han Daniel, Gill Dipender, Rao Karan, Allahwala Usaid, Bhindi Ravinay