Final ID: 4141630
Development of a Model for MEPPC Using hiPSC-HPCs and Bioprinted Purkinje Networks
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Multifocal Ectopic Purkinje-related Premature Contractions (MEPPCs) is marked by early and frequent spontaneous membrane depolarization of the His-Purkinje cells (HPCs), which can trigger life-threatening arrhythmias and sudden death. It has been postulated that MEPPC-associated variants in SCN5A result in increased sodium influx leading to early depolarization and triggered arrhythmias.
Hypothesis: Our central hypothesis is that MEPPC is caused by a gain-of-function in INAV that leads to spontaneous HPC automaticity and triggered arrhythmogenesis originating from the CCS, which propagates into the surrounding myocardial tissue.
Aims: The goals of this study are to develop a rigorous method to generate HPCs from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) and characterize he hiPSC-HPCs using IHC, qPCR and electrophysiology. A second objective of this study is to develop a method to bioengineer 3D Purkinje networks using state-of-the-art advances in laser based bioprinting.
Methods: To generate hiPSC-HPCs, 90% of confluent hiPSCs were transitioned to GSK-3 inhibitor CHIR99021 followed by Wnt inhibitor IWP2 to generate cardiac progenitor cells. Subsequently, hiPSCs were exposed to sodium nitroprusside on day 5, which led to spontaneous beating after 10 days, followed by a change in cell morphology, transitioning to large and cylindrical cells indicative of HPCs. To generate 3D Purkinje networks, we used a commercial laser based bioprinter, the Lumen X. We optimized our bioink formulation and selected 90% PEGDA as our base polymer, supplemented with 10% GELMA.
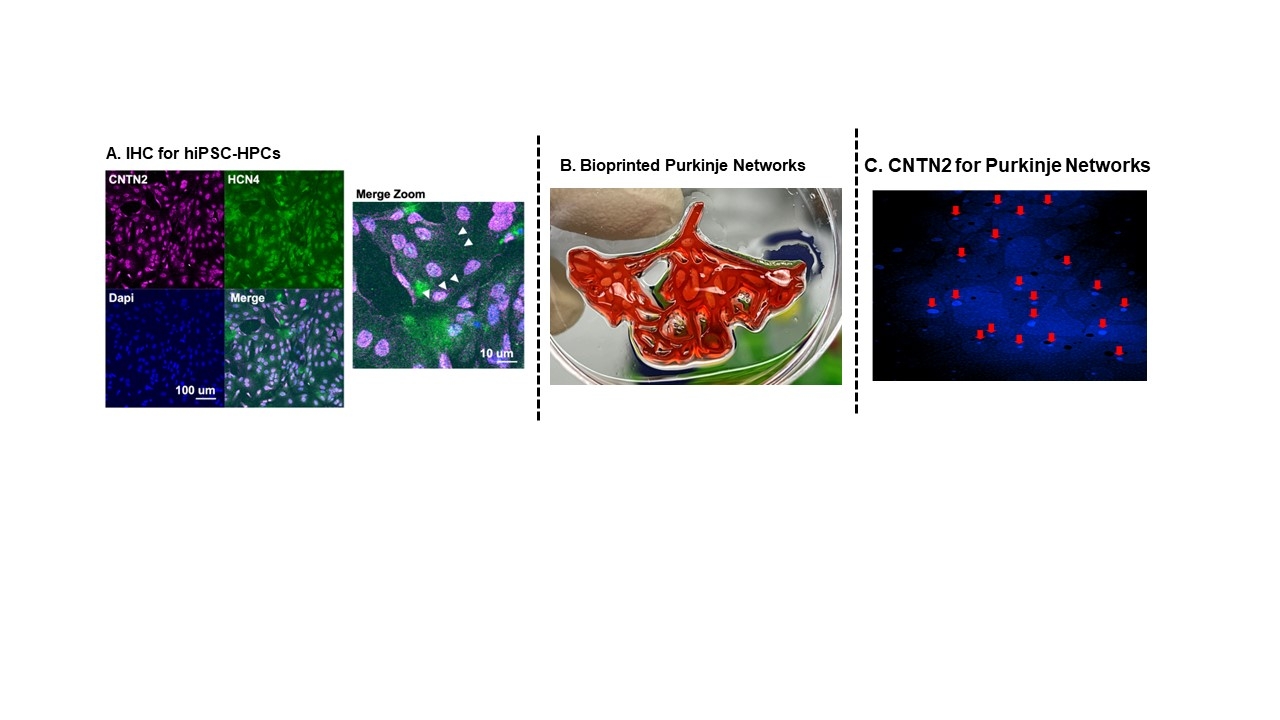
Results: Robust expression of both CNTN2, an HPC-specific marker, and HCN4, unique to cardiac nodal and conduction cells, was observed by IHC (Fig. 1A). We successfully bioprinted Purkinje networks (Fig. 1B) and cell viability was confirmed using a live/dead assay. Phenotype of hiPSC-HPCs within the bioprinted Purkinje networks was confirmed using CNTN2 staining (Fig. 1C), a marker specific for Purkinje cells.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate our ability to successfully reprogram hiPSCs to form HPCs and our ability to utilize these cells to bioprint human 3D Purkinje networks.
Hypothesis: Our central hypothesis is that MEPPC is caused by a gain-of-function in INAV that leads to spontaneous HPC automaticity and triggered arrhythmogenesis originating from the CCS, which propagates into the surrounding myocardial tissue.
Aims: The goals of this study are to develop a rigorous method to generate HPCs from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) and characterize he hiPSC-HPCs using IHC, qPCR and electrophysiology. A second objective of this study is to develop a method to bioengineer 3D Purkinje networks using state-of-the-art advances in laser based bioprinting.
Methods: To generate hiPSC-HPCs, 90% of confluent hiPSCs were transitioned to GSK-3 inhibitor CHIR99021 followed by Wnt inhibitor IWP2 to generate cardiac progenitor cells. Subsequently, hiPSCs were exposed to sodium nitroprusside on day 5, which led to spontaneous beating after 10 days, followed by a change in cell morphology, transitioning to large and cylindrical cells indicative of HPCs. To generate 3D Purkinje networks, we used a commercial laser based bioprinter, the Lumen X. We optimized our bioink formulation and selected 90% PEGDA as our base polymer, supplemented with 10% GELMA.
Results: Robust expression of both CNTN2, an HPC-specific marker, and HCN4, unique to cardiac nodal and conduction cells, was observed by IHC (Fig. 1A). We successfully bioprinted Purkinje networks (Fig. 1B) and cell viability was confirmed using a live/dead assay. Phenotype of hiPSC-HPCs within the bioprinted Purkinje networks was confirmed using CNTN2 staining (Fig. 1C), a marker specific for Purkinje cells.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate our ability to successfully reprogram hiPSCs to form HPCs and our ability to utilize these cells to bioprint human 3D Purkinje networks.
More abstracts on this topic:
Three-Dimensional Bioprinting of Cardiac Tissues: Innovations, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
Ponnada Sarath Chandra, Seth Sukriti, Patel Heena, Patel Kalan, Chitturi Raja Hamsa, Gondu Sai Vidyanand, Baladaniya Maheshkumar, Annepu Sasidhar
Implantable Epicardial Cell-Based Platform for Localized Immunomodulation of Ischemic MyocardiumGuinn Michael Tyler, Fell Cody, Cabler Jacob, Malik Saad, Mendez Sosa Miguel, Miles Travis, Veiseh Omid, Ghanta Ravi