Final ID: 4141396
Activation of the Wnt Signaling Pathway Links Atrial Myopathy to Atrial Fibrillation in Lamin A/C Heart Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Objective: Pathogenic variants in LMNA are associated with early-onset atrial fibrillation (EOAF) but the pathophysiological mechanisms by which atrial myopathy leads to AF are poorly understood. Here, we investigated electrophysiologic (EP) and epigenetic mechanisms by which a heterozygous pathogenic LMNA-S143P mutation causes EOAF utilizing mature human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived atrial cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-aCMs) generated from a large Caucasian kindred with a strong cardiac phenotype.
Hypothesis: Atrial myopathy due to the LMNA-S143P mutation, creates an arrhythmogenic substrate for AF by causing ion channel and chromatin remodeling.
Approach: We performed clinical phenotyping and genetic testing of the proband and family members. hiPSC-aCMs generated from family members and CRISPR-corrected isogenic control (CRISPR-GC) were characterized by optical voltage mapping, calcium transient measurements, and whole-cell patch clamp analysis. Transcriptomic and epigenetic analysis was performed by RNA-sequencing (seq) and assay for transposase-accessible chromatin followed by sequencing (ATAC-seq).
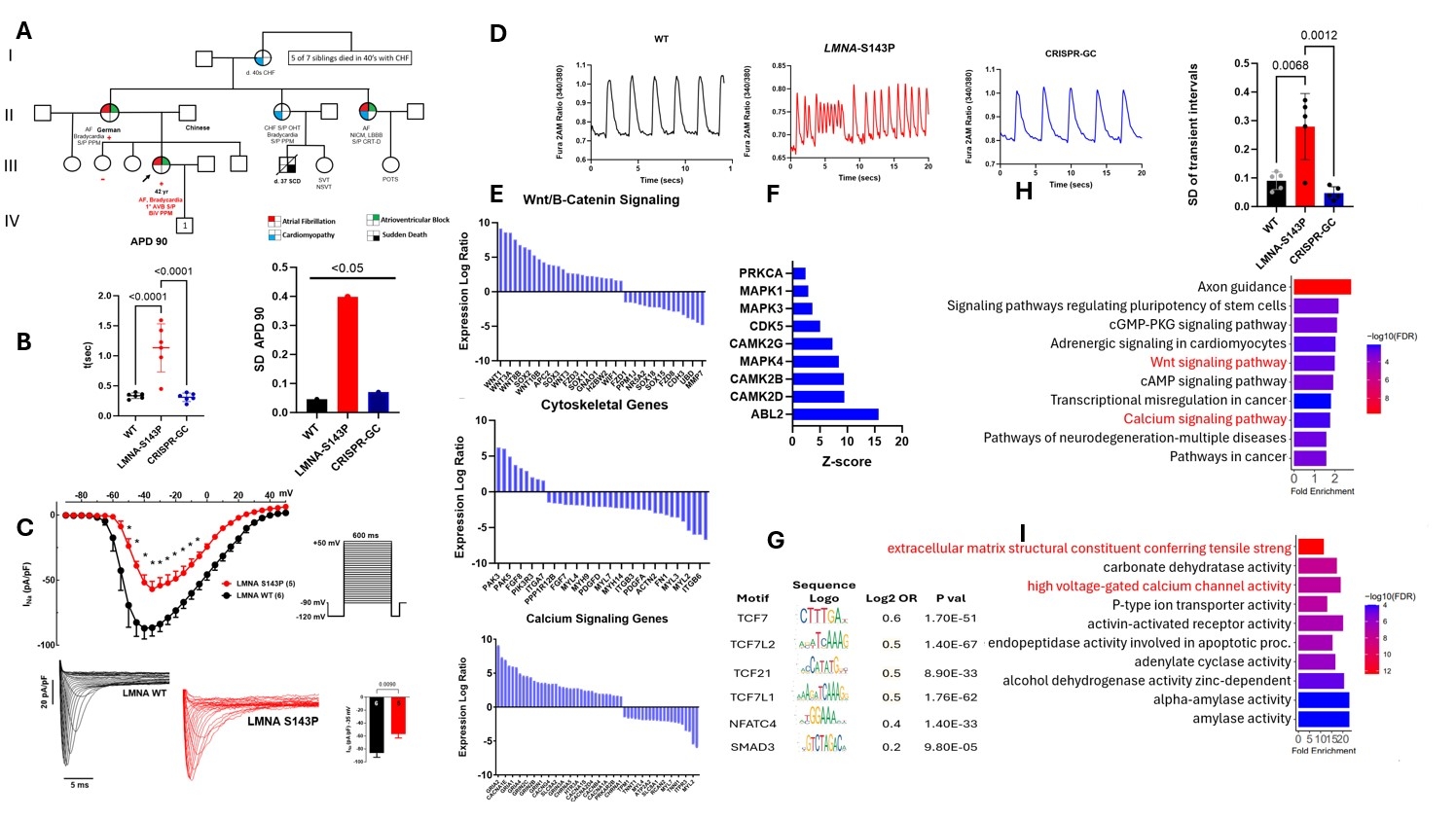
Results: The proband presented with EOAF at 35 years. Cardiac MRI and transthoracic echocardiogram revealed an atrial myopathy and low voltage electrograms but preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (56%). Cascade screening of the LMNA-S143P kindred confirmed co-segregation of the variant with AF, conduction disease, and dilated cardiomyopathy (Fig. A). EP analysis showed that the LMNA-S143P hiPSC-aCMs exhibited heterogeneity of action potential duration (APD)(Fig. B); decreased Na+ current (Fig. C) and delayed after-depolarizations (Fig. D). Integrated analysis of RNA and ATAC-seq revealed significant enrichment of genes associated with Wnt signaling pathway, cytoskeletal remodeling and activation of calcium signaling (Fig. E-I) Congruently, we found high enrichment of CAMK2 kinase as well as TCF and NFAT transcription factors associated with Wnt signaling (Fig. F-G) .
Conclusion: Our results suggest that cytoskeletal remodeling and triggered calcium release mediated by NFAT and CAMK2 respectively create an arrhythmogenic substrate for atrial myopathy and AF highlighting their therapeutic potential.
Hypothesis: Atrial myopathy due to the LMNA-S143P mutation, creates an arrhythmogenic substrate for AF by causing ion channel and chromatin remodeling.
Approach: We performed clinical phenotyping and genetic testing of the proband and family members. hiPSC-aCMs generated from family members and CRISPR-corrected isogenic control (CRISPR-GC) were characterized by optical voltage mapping, calcium transient measurements, and whole-cell patch clamp analysis. Transcriptomic and epigenetic analysis was performed by RNA-sequencing (seq) and assay for transposase-accessible chromatin followed by sequencing (ATAC-seq).
Results: The proband presented with EOAF at 35 years. Cardiac MRI and transthoracic echocardiogram revealed an atrial myopathy and low voltage electrograms but preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (56%). Cascade screening of the LMNA-S143P kindred confirmed co-segregation of the variant with AF, conduction disease, and dilated cardiomyopathy (Fig. A). EP analysis showed that the LMNA-S143P hiPSC-aCMs exhibited heterogeneity of action potential duration (APD)(Fig. B); decreased Na+ current (Fig. C) and delayed after-depolarizations (Fig. D). Integrated analysis of RNA and ATAC-seq revealed significant enrichment of genes associated with Wnt signaling pathway, cytoskeletal remodeling and activation of calcium signaling (Fig. E-I) Congruently, we found high enrichment of CAMK2 kinase as well as TCF and NFAT transcription factors associated with Wnt signaling (Fig. F-G) .
Conclusion: Our results suggest that cytoskeletal remodeling and triggered calcium release mediated by NFAT and CAMK2 respectively create an arrhythmogenic substrate for atrial myopathy and AF highlighting their therapeutic potential.
More abstracts on this topic:
A-band titin-truncating variant promotes the development of arrhythmia-induced cardiomyopathy in a novel genetically-engineered porcine model
Lee Kwonjae, Del Rio Carlos, Mcnally Elizabeth, Pfenniger Anna, Bhatnagar Ashita, Glinton Kristofor, Burrell Amy, Ober Rebecca, Mcluckie Alicia, Bishop Brian, Rogers Christopher, Geist Gail
A Bifunctional Actuator Reverses NaV1.5 Dysfunction Linked To Cardiac ArrhythmiasFossier Lucile, Yehya Marc, Mahling Ryan, Gabelli Sandra, Colecraft Henry, Ben Johny Manu