Final ID: Sa3110
Low Serum Albumin as a Predictor of All-Cause Mortality in HFpEF Patients
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is an increasingly prevalent form of heart failure (HF) in the US today. Our prior work revealed low albumin at first hospitalization for HF exacerbation with underlying HFpEF to be an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in a small cohort of patients. We now sought to confirm our earlier findings across a larger and more diverse patient population.
Methods: Seven thousand, eight hundred and forty patients had a first admission to Mayo Clinic for HF exacerbation with an echo-confirmed left ventricular ejection fraction>50% between 2010 and 2020. Patient baseline demographics, co-morbidities, admission laboratory values, echocardiographic parameters, discharge medications, and outcomes were obtained from chart abstraction. To validate our previous model, patients were grouped based on the number of risk factors as previously defined: age>80 years, serum albumin level<3.2 g/dl, medial E/e'≥20, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) >5,000 pg/mL, and the presence of hypertension (HTN). The association with 1 year mortality was studied using Cox regression. Kaplan Meier curves were generated based on the number of factors present per patient.
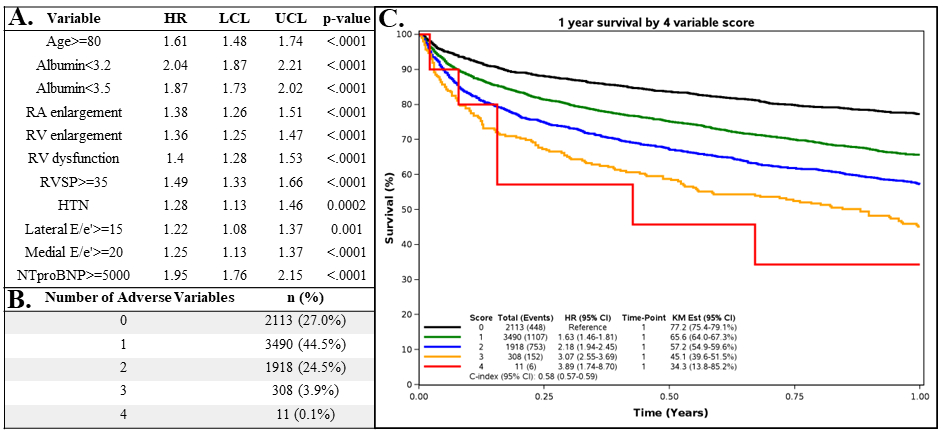
Results: Eleven significant univariate predictors of all-cause mortality were identified from the data (Fig. 1A), with hazard ratios (HR) ranging from 1.22-2.04 (p<0.001 for all). Notably, four previously identified prognosticators (age, albumin, medial E/e’, , HTN) were noted as significant independent predictors of all-cause mortality in HFpEF (HR 1.67, 2.14, 1.18, and 1.15, respectively, p<0.004 for all ; Fig. 1B). Multivariate regression modeling identified low albumin on presentation as being a significant adverse prognosticator (HR=2.14; p-value<0.001).
Conclusion: Our analysis of 7840 HFpEF patients confirms our prior findings, suggesting that this model is a strong predictive tool for assessing the prognosis of HFpEF. Taken together, these five variables are easily available in the in-patient setting and can be incorporated into a model predictive of 1-year all-cause mortality.
Methods: Seven thousand, eight hundred and forty patients had a first admission to Mayo Clinic for HF exacerbation with an echo-confirmed left ventricular ejection fraction>50% between 2010 and 2020. Patient baseline demographics, co-morbidities, admission laboratory values, echocardiographic parameters, discharge medications, and outcomes were obtained from chart abstraction. To validate our previous model, patients were grouped based on the number of risk factors as previously defined: age>80 years, serum albumin level<3.2 g/dl, medial E/e'≥20, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) >5,000 pg/mL, and the presence of hypertension (HTN). The association with 1 year mortality was studied using Cox regression. Kaplan Meier curves were generated based on the number of factors present per patient.
Results: Eleven significant univariate predictors of all-cause mortality were identified from the data (Fig. 1A), with hazard ratios (HR) ranging from 1.22-2.04 (p<0.001 for all). Notably, four previously identified prognosticators (age, albumin, medial E/e’, , HTN) were noted as significant independent predictors of all-cause mortality in HFpEF (HR 1.67, 2.14, 1.18, and 1.15, respectively, p<0.004 for all ; Fig. 1B). Multivariate regression modeling identified low albumin on presentation as being a significant adverse prognosticator (HR=2.14; p-value<0.001).
Conclusion: Our analysis of 7840 HFpEF patients confirms our prior findings, suggesting that this model is a strong predictive tool for assessing the prognosis of HFpEF. Taken together, these five variables are easily available in the in-patient setting and can be incorporated into a model predictive of 1-year all-cause mortality.
More abstracts on this topic:
4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal Alters Alternative Polyadenylation to Regulate mRNA Isoform Diversity in the Transition from Human Cardiac Fibroblasts to Myofibroblasts
Natarajan Kartiga, Neupane Rahul, Yalamanchili Hari Krishna, Palaniyandi Suresh, Wagner Eric, Guha Ashrith, Amirthalingam Thandavarayan Rajarajan
β1-adrenergic autoantibodies (β1-AA) augment macropinocytosis in CD4+ T cells, leading to the expansion of CD4+CD28− T cell subsets in heart failure.Sun Fei, Yao Junyan, Li Bingjie, Zhang Suli, Liu Huirong