Final ID: MDP1563
Increasing handgrip strength in patients with cardiovascular diseases is associated with improving ejection fraction in the longitudinal study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Weakness of muscle strength is one of the indicators of frailty. Moreover, frailty is associated with the prognosis of cardiovascular disease (CVD). However, no reports examine the association between improving ejection fraction (EF) and handgrip strength (HGS) in the longitudinal study.
Purpose: To investigate the factors related to handgrip muscle strength in patients with CVD
Methods: We recruited 133 patients with CVD who all performed HGS and echocardiography twice on the first and second visit. Furthermore, we measured blood samples such as brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and haemoglobin (Hb) twice on the first and second visit as well.
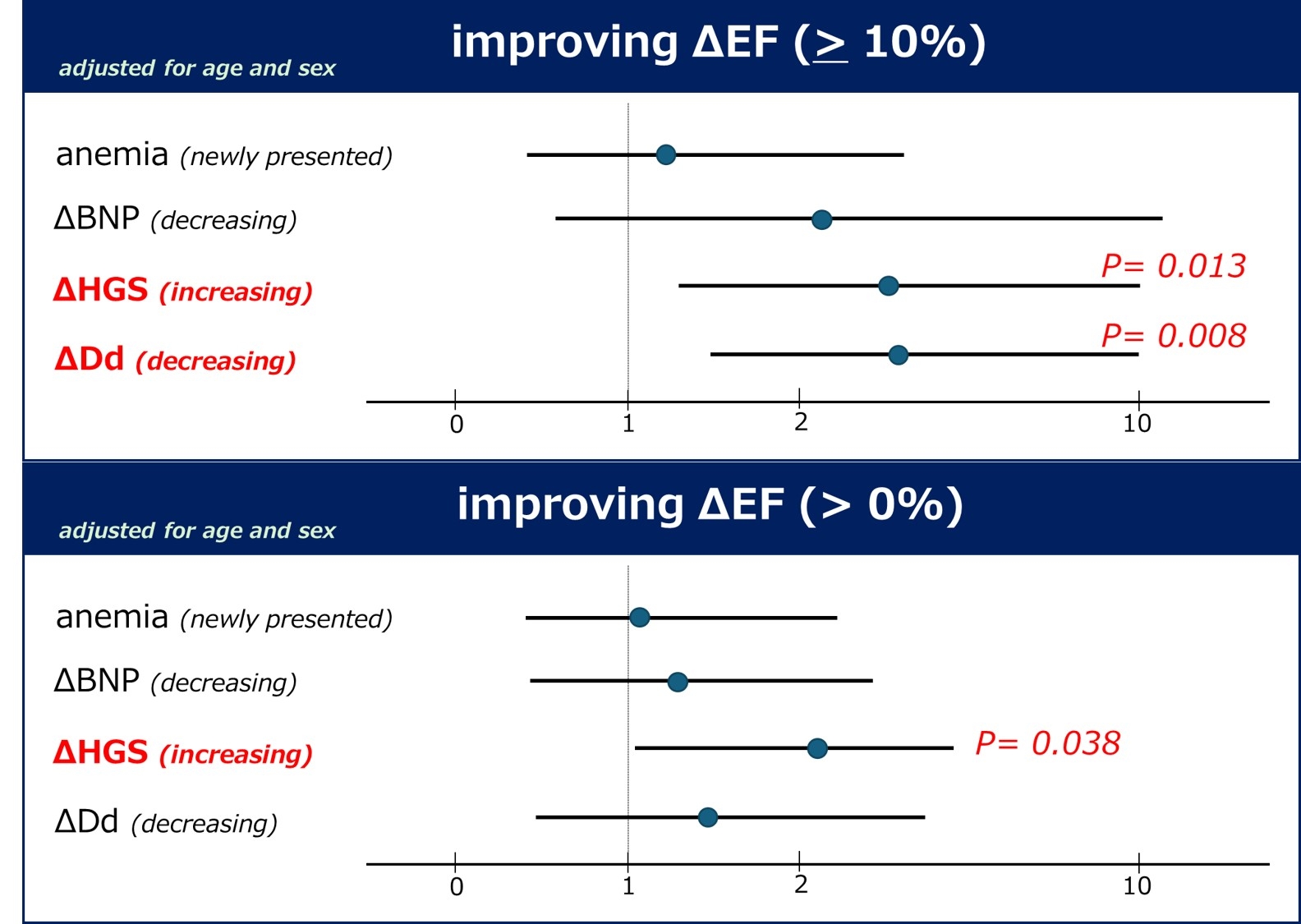
We applied to investigate factors such as the newly presented anaemia, ΔBNP(second visit-first visit), ΔHGS (second visit-first visit), Δleft ventricular end-diastolic diameter (Dd) (second visit-first visit). Two types of assessment were used for EF improvement. One is improving ΔEF, defined as an increase from the baseline. The other is improving ΔEF>10%, defined as a 10% increase from the baseline.
Results: The average follow-up period was 1.5±1.1 years. EF, BNP, and HGS baseline data were 50±19 %, 128±178 pg/mL, and 28.6±10.2 kg, respectively. In multivariate logistic regression analysis adjusted for age and sex, increasing HGS and decreasing Dd were independent risk factors for improving ΔEF>10% (increasing HGS: OR 3.69 CI 1.32-10.3, p=0.013; decreasing Dd: OR 3.76 CI 1.41-10.0, p=0.008). Moreover, in multivariate logistic regression analysis adjusted for age and sex, increasing HGS was only an independent factor for improvingΔEF (OR 2.31 CI 1.05-5.07, p=0.038).
Conclusions: In patients with CVD, improving ΔEF>10% was associated with decreased Dd and increasing HGS. Furthermore, improving ΔEF was associated with increasing HGS. Increased handgrip strength was a significant factor in EF improvement.
Purpose: To investigate the factors related to handgrip muscle strength in patients with CVD
Methods: We recruited 133 patients with CVD who all performed HGS and echocardiography twice on the first and second visit. Furthermore, we measured blood samples such as brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and haemoglobin (Hb) twice on the first and second visit as well.
We applied to investigate factors such as the newly presented anaemia, ΔBNP(second visit-first visit), ΔHGS (second visit-first visit), Δleft ventricular end-diastolic diameter (Dd) (second visit-first visit). Two types of assessment were used for EF improvement. One is improving ΔEF, defined as an increase from the baseline. The other is improving ΔEF>10%, defined as a 10% increase from the baseline.
Results: The average follow-up period was 1.5±1.1 years. EF, BNP, and HGS baseline data were 50±19 %, 128±178 pg/mL, and 28.6±10.2 kg, respectively. In multivariate logistic regression analysis adjusted for age and sex, increasing HGS and decreasing Dd were independent risk factors for improving ΔEF>10% (increasing HGS: OR 3.69 CI 1.32-10.3, p=0.013; decreasing Dd: OR 3.76 CI 1.41-10.0, p=0.008). Moreover, in multivariate logistic regression analysis adjusted for age and sex, increasing HGS was only an independent factor for improvingΔEF (OR 2.31 CI 1.05-5.07, p=0.038).
Conclusions: In patients with CVD, improving ΔEF>10% was associated with decreased Dd and increasing HGS. Furthermore, improving ΔEF was associated with increasing HGS. Increased handgrip strength was a significant factor in EF improvement.
More abstracts on this topic:
Deep Learning-Guided CT Image Analysis Quantifies 18-Month Changes in Regional Muscle Atrophy in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease
Musini Kumudha, Rimmerman Eleanor, Chou Ting-heng, Shin Kyle, Go Michael, Stacy Mitchel
A Bridge from Sweet to Sour: A Case of Recurrent Myocardial Stunning in Diabetic KetoacidosisSatish Vikyath, Pargaonkar Sumant, Slipczuk Leandro, Schenone Aldo, Maliha Maisha, Chi Kuan Yu, Sunil Kumar Sriram, Borkowski Pawel, Vyas Rhea, Rodriguez Szaszdi David Jose Javier, Kharawala Amrin, Seo Jiyoung