Final ID: Su2137
Modification Effect of Flu-like Illness on the Genetic Association of Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background and Aims: Previous studies have speculated that a viral infection may act as a trigger in the development of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) among people genetically at risk. This study aimed to describe the frequency of DCM patients who experienced a flu-like illness prior to the diagnosis and examine if this experience modifies the association of DCM with carrying DCM-relevant genetic variants.
Methods: We analyzed data from the DCM Precision Medicine Study conducted between June 2016 and April 2021. Medical history including flu-like illness prior to DCM diagnosis was obtained from patient interview and medical record review. Exome sequencing identified DCM-related rare variants [pathogenic (P), likely pathogenic (LP), or uncertain significance (VUS)] and common variants via GWAS. Logistic mixed models with a case-only design were used to examine if flu-like illness modified the association between DCM and genetic risk. After imputation using the TOPMed Imputation Server, Firth logistic regression was used to examine if flu-like illness modified the association of DCM with each of 13,443,192 common autosomal variants (minor allele frequency >=1%).
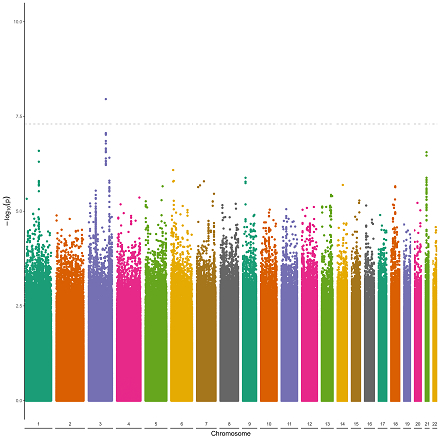
Results: Of 1,164 patients with DCM, 351 (30.2%) reported episodes of flu-like illness proximal to their DCM diagnosis. The percent with a history of flu-like illness was higher among those aged <45 than those aged >45 (35.2% vs. 27.4%, P=0.004) and among ever smokers than non-smokers (32.4% vs. 28.2%, P=0.04), but did not differ by other demographics, clinical comorbidities, or seasons. The percent with a history of flu-like illness by variant classification was 29.9% for LP/P, 29.6% for VUS only, and 30.1% for no LP/P/VUS. The odds ratio for an interaction between a history of flu-like illness and presence of any P, LP or VUS variants was 1.0 (95% CI: 0.7-1.3). A genome-wide significant association between rs2102158 and flu-like illness (p=1.1*10^-8) was identified at chromosome 3q24.
Conclusions: We did not find evidence that a flu-like illness modified the association of DCM with DCM-relevant rare variants; however, our GWAS analysis suggested that flu-like illness may modify the effect of a common variant on the odds of DCM.
Background and Aims: Previous studies have speculated that a viral infection may act as a trigger in the development of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) among people genetically at risk. This study aimed to describe the frequency of DCM patients who experienced a flu-like illness prior to the diagnosis and examine if this experience modifies the association of DCM with carrying DCM-relevant genetic variants.
Methods: We analyzed data from the DCM Precision Medicine Study conducted between June 2016 and April 2021. Medical history including flu-like illness prior to DCM diagnosis was obtained from patient interview and medical record review. Exome sequencing identified DCM-related rare variants [pathogenic (P), likely pathogenic (LP), or uncertain significance (VUS)] and common variants via GWAS. Logistic mixed models with a case-only design were used to examine if flu-like illness modified the association between DCM and genetic risk. After imputation using the TOPMed Imputation Server, Firth logistic regression was used to examine if flu-like illness modified the association of DCM with each of 13,443,192 common autosomal variants (minor allele frequency >=1%).
Results: Of 1,164 patients with DCM, 351 (30.2%) reported episodes of flu-like illness proximal to their DCM diagnosis. The percent with a history of flu-like illness was higher among those aged <45 than those aged >45 (35.2% vs. 27.4%, P=0.004) and among ever smokers than non-smokers (32.4% vs. 28.2%, P=0.04), but did not differ by other demographics, clinical comorbidities, or seasons. The percent with a history of flu-like illness by variant classification was 29.9% for LP/P, 29.6% for VUS only, and 30.1% for no LP/P/VUS. The odds ratio for an interaction between a history of flu-like illness and presence of any P, LP or VUS variants was 1.0 (95% CI: 0.7-1.3). A genome-wide significant association between rs2102158 and flu-like illness (p=1.1*10^-8) was identified at chromosome 3q24.
Conclusions: We did not find evidence that a flu-like illness modified the association of DCM with DCM-relevant rare variants; however, our GWAS analysis suggested that flu-like illness may modify the effect of a common variant on the odds of DCM.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Clozapine-Induced Myocarditis: An Under-described Side Effect
Ibrahim Rand, Clearo Kellie
Effects of Influenza Vaccination Among Patients With Myocardial Ischemia and Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled TrialsSantos Charles Karel, Ramos Miranda Maria Clara, Barbosa Gabriel, Nogueira Thallys, Da Silva Menezes Junior Antonio