Final ID: Su2169
Pulmonary dynamic hyperinflation augments pulmonary capillary wedge pressure during exercise in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Adults with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) have an exaggerated rise in pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) with exercise. Pulmonary function in patients with HFpEF is often flow limited, thereby perpetuating dynamic hyperinflation (DH) and breathing at a mechanically unfavorable percentage of total lung volume. We therefore sought to characterize the impact of DH on PCWP in adults with HFpEF during exercise.
Methods
Twenty-seven patients with HFpEF were evaluated (Age: 70 ± 7 years, Female: 70 %, BMI: 38.1±6.3 kg/m2). PCWP and central venous pressure (CVP, right heart catheterization), oxygen uptake (breath by breath), cardiac output (direct Fick), and ventilation were measured upright at rest, 20 W, and peak exercise (73 ± 27 W) on a semi-recumbent cycle ergometer. End-expiratory lung volume was determined by having patients complete inspiratory capacity maneuvers during rest and exercise. DH was defined as an increase in end-expiratory lung volume of >150ml from rest.
Results
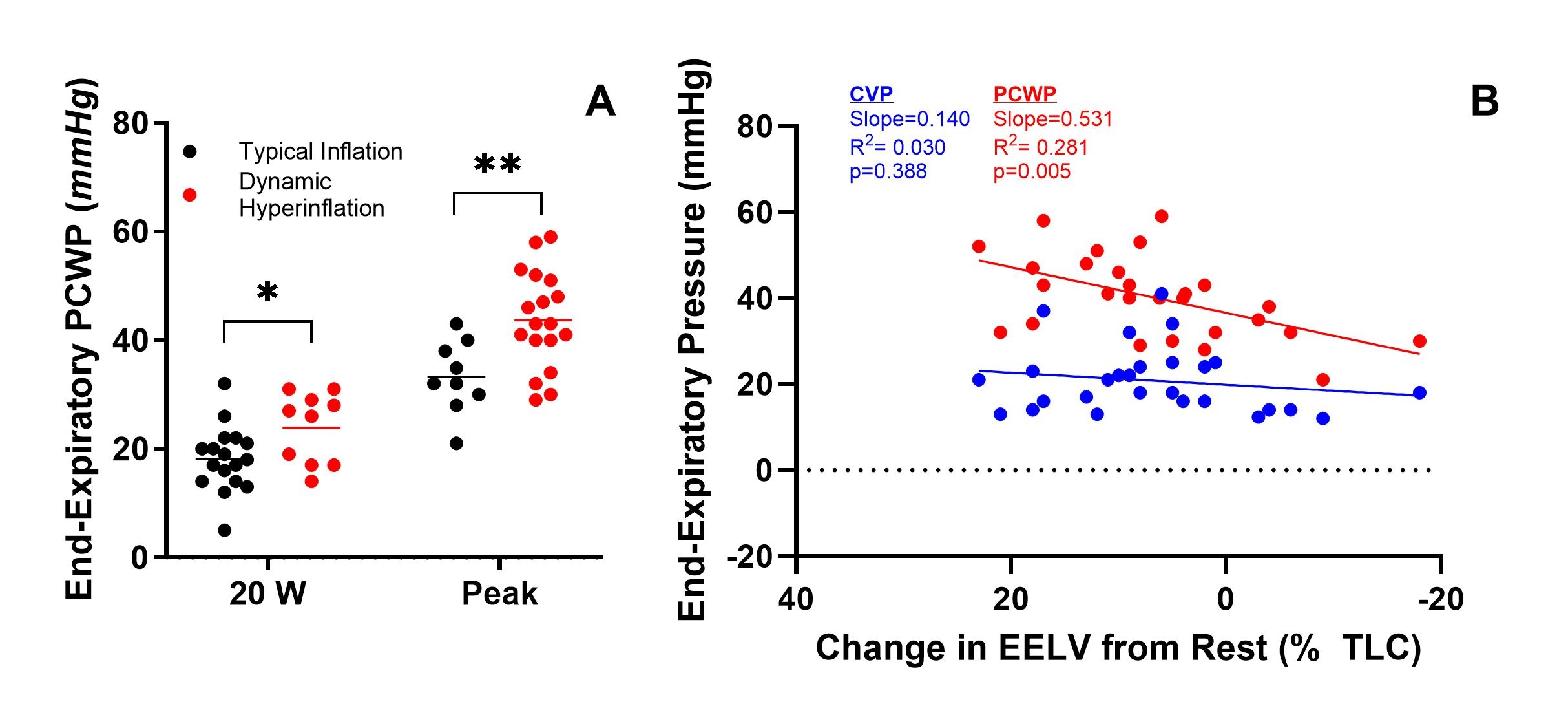
End-expiratory PCWP was greater in patients with DH at 20 W (DH: 24 ± 6 mmHg vs. Normal: 18 ± 6, p=0.033) and peak exercise (DH: 44 ± 9 vs. Normal: 31 ± 6 mmHg, Panel A, p=0.002). The effect of DH occurred despite similar change in stroke volume (DH: 29 ± 15 vs. Normal: 37 ± 11 mL, p=0.164) and cardiac output (DH: 10.4 ± 1.7 vs. Normal: 11.1 ± 2.7 L/min, p=0.420) at peak exercise; however, BMI was greater in patients with DH (40.1 ± 6.0 vs. 34.4 ± 5.4 kg/m2, p=0.020). The degree of dynamic inflation was significantly associated with end-expiratory PCWP during exercise (slope= 0.531, R2= 0.281, p= 0.005, Panel B).
Conclusion
Patients with HFpEF who dynamically hyperinflate during exercise have greater PCWP than those who do not. DH was associated with obesity and the severity of hyperinflation scaled proportionally to higher exercise PCWP. These findings indicate the augmented exercise PCWP in patients with HFpEF may not be entirely attributed to ventricular stiffness, but also a consequence of increased intrathoracic pressure from dysfunctional ventilatory mechanics.
Adults with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) have an exaggerated rise in pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) with exercise. Pulmonary function in patients with HFpEF is often flow limited, thereby perpetuating dynamic hyperinflation (DH) and breathing at a mechanically unfavorable percentage of total lung volume. We therefore sought to characterize the impact of DH on PCWP in adults with HFpEF during exercise.
Methods
Twenty-seven patients with HFpEF were evaluated (Age: 70 ± 7 years, Female: 70 %, BMI: 38.1±6.3 kg/m2). PCWP and central venous pressure (CVP, right heart catheterization), oxygen uptake (breath by breath), cardiac output (direct Fick), and ventilation were measured upright at rest, 20 W, and peak exercise (73 ± 27 W) on a semi-recumbent cycle ergometer. End-expiratory lung volume was determined by having patients complete inspiratory capacity maneuvers during rest and exercise. DH was defined as an increase in end-expiratory lung volume of >150ml from rest.
Results
End-expiratory PCWP was greater in patients with DH at 20 W (DH: 24 ± 6 mmHg vs. Normal: 18 ± 6, p=0.033) and peak exercise (DH: 44 ± 9 vs. Normal: 31 ± 6 mmHg, Panel A, p=0.002). The effect of DH occurred despite similar change in stroke volume (DH: 29 ± 15 vs. Normal: 37 ± 11 mL, p=0.164) and cardiac output (DH: 10.4 ± 1.7 vs. Normal: 11.1 ± 2.7 L/min, p=0.420) at peak exercise; however, BMI was greater in patients with DH (40.1 ± 6.0 vs. 34.4 ± 5.4 kg/m2, p=0.020). The degree of dynamic inflation was significantly associated with end-expiratory PCWP during exercise (slope= 0.531, R2= 0.281, p= 0.005, Panel B).
Conclusion
Patients with HFpEF who dynamically hyperinflate during exercise have greater PCWP than those who do not. DH was associated with obesity and the severity of hyperinflation scaled proportionally to higher exercise PCWP. These findings indicate the augmented exercise PCWP in patients with HFpEF may not be entirely attributed to ventricular stiffness, but also a consequence of increased intrathoracic pressure from dysfunctional ventilatory mechanics.
More abstracts on this topic:
3-Minute Heart Health App: A Feasibility Study
Abdulkarim Iya, Metzger Joseph, Stovitz Steven, Van't Hof Jeremy
The Use of Pod-Type Electronic Cigarettes and Recent Asthma Diagnosis in AdolescentsLee Ju-mi, Kim Ji-hyeon, Nam Hae-sung