Final ID: MDP702
AIR-TELTEC-HF Medical Expert System: a new rule-based tool of Intelligent Telemedicine for Chronic Heart Failure
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background. Medical expert systems (MES) proceed on a “knowledge base” of clinical variables linked together by a set of rules written by medical experts. The main goal of our multidisciplinary team of medical experts and knowledge, information engineers was to create an “intelligent telemedicine” able to improve outcomes through early detection of clinical instability in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) and multimorbidity.
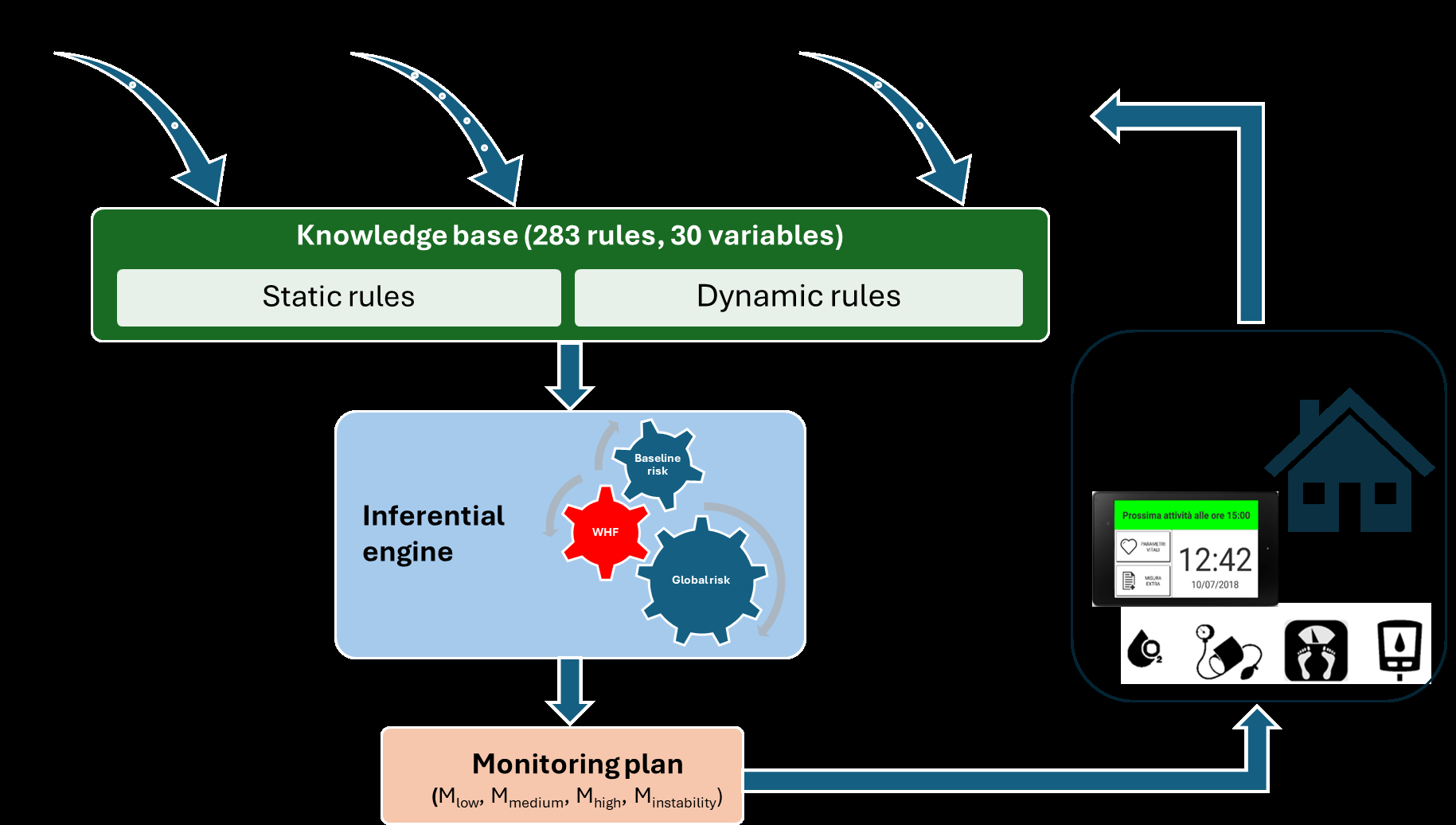
Methods. General Practitioners (GP) and Internal Medicine Specialists designed the "knowledge base" including 30 variables and 283 IF/THEN rules. Variables were: vital signs and symptoms, antropometric, age, sex, pharmacological, clinical and instrumental values of heart and renal failure, indices of cardiovascular comorbidities and other comorbidities determining cardiac and/or renal deterioration. A set of hierarchically organized rules identify: 1) the risk class at the time of enrollment, 2) the global risk, continuously updated from self-measurement data and clinical surveys, 3) the most appropriate monitoring plan (Fig.1).
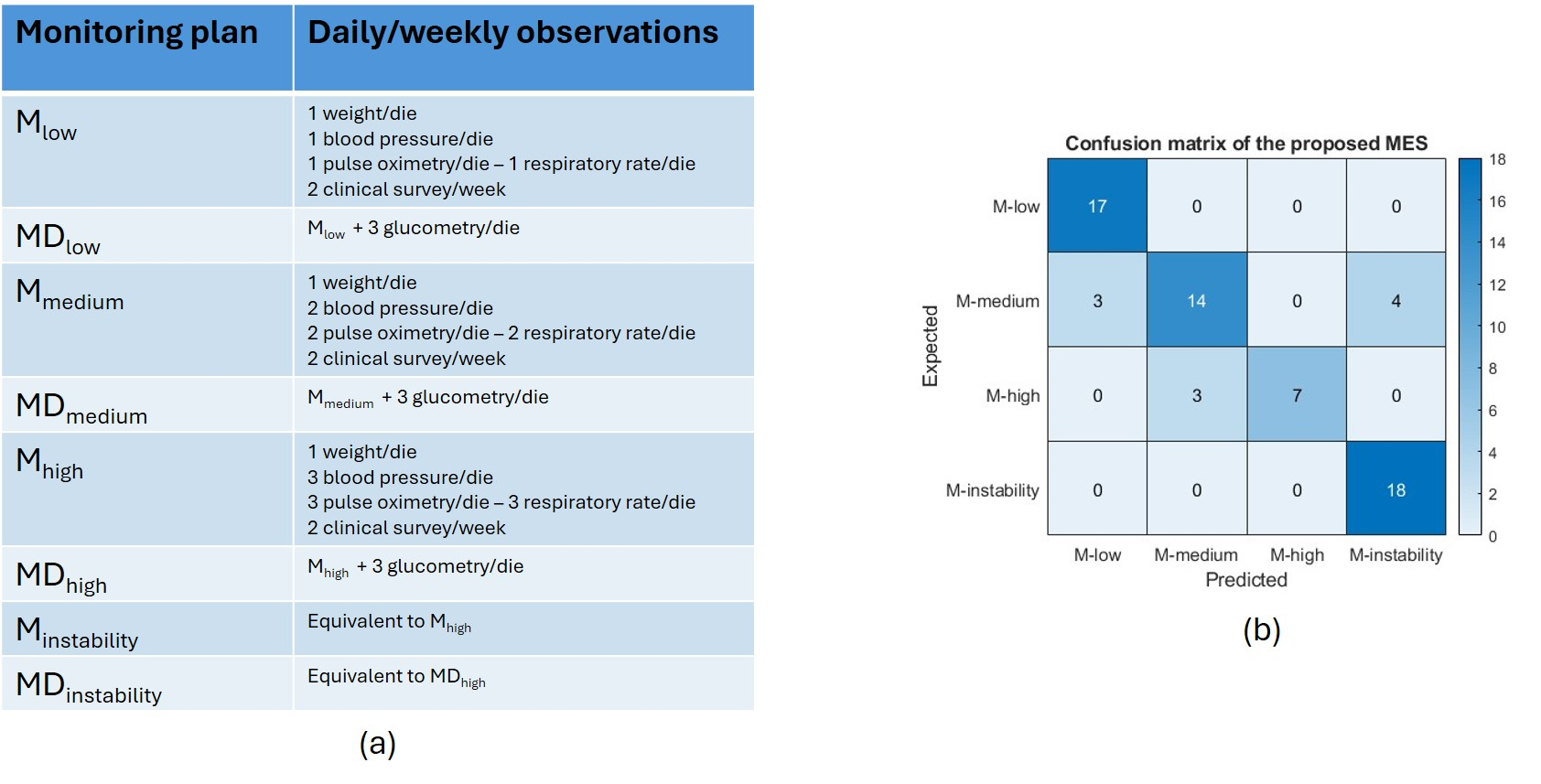
Medical experts provided 8 plans (Fig.2a) for CHF patients, according to their global risk of worsening heart failure (WHF). The higher intensity of monitoring was assigned to all cases the MES was not able to handle.
Results: AIR-TELTEC-HF MES underwent a first validation on 66 clinical cases, comparing its output vs the expected monitoring defined by medical experts. All cases with clinical instability and WHF (n° 18) were correctly assigned by the MES to the highest intensive monitoring plan. Overall, in 56 cases there was agreement between human expert and MES, leading to an F1-Score of 84% (Fig.2b).
Conclusions. Our AIR-TELTEC-HF MES prototype for “intelligent telemedicine” reproduces the work of an expert medical team in telemonitoring settings. This prototype can be further improved involving other leading HF experts to enhance the clinical rules for many other cases of CHF and multimorbidity.
It is easy-of-use and explainable enough to assist GP in clinical practice, and to facilitate multidisciplinary clinical discussion on complex patient with CHF and multimorbidity. Using MES for student training would increase the future accuracy in following CHF patients.
Thanks to an appropriate monitoring of the initial phase of WHF, we would have a sensible decrease in hospitalizations. Moreover AIR-TELTEC-HF MES could be integrated with other MES, clinical records, and information systems to exchange data.
Methods. General Practitioners (GP) and Internal Medicine Specialists designed the "knowledge base" including 30 variables and 283 IF/THEN rules. Variables were: vital signs and symptoms, antropometric, age, sex, pharmacological, clinical and instrumental values of heart and renal failure, indices of cardiovascular comorbidities and other comorbidities determining cardiac and/or renal deterioration. A set of hierarchically organized rules identify: 1) the risk class at the time of enrollment, 2) the global risk, continuously updated from self-measurement data and clinical surveys, 3) the most appropriate monitoring plan (Fig.1).
Medical experts provided 8 plans (Fig.2a) for CHF patients, according to their global risk of worsening heart failure (WHF). The higher intensity of monitoring was assigned to all cases the MES was not able to handle.
Results: AIR-TELTEC-HF MES underwent a first validation on 66 clinical cases, comparing its output vs the expected monitoring defined by medical experts. All cases with clinical instability and WHF (n° 18) were correctly assigned by the MES to the highest intensive monitoring plan. Overall, in 56 cases there was agreement between human expert and MES, leading to an F1-Score of 84% (Fig.2b).
Conclusions. Our AIR-TELTEC-HF MES prototype for “intelligent telemedicine” reproduces the work of an expert medical team in telemonitoring settings. This prototype can be further improved involving other leading HF experts to enhance the clinical rules for many other cases of CHF and multimorbidity.
It is easy-of-use and explainable enough to assist GP in clinical practice, and to facilitate multidisciplinary clinical discussion on complex patient with CHF and multimorbidity. Using MES for student training would increase the future accuracy in following CHF patients.
Thanks to an appropriate monitoring of the initial phase of WHF, we would have a sensible decrease in hospitalizations. Moreover AIR-TELTEC-HF MES could be integrated with other MES, clinical records, and information systems to exchange data.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Deep Learning Topic Analysis Approach for Enhancing Risk Assessment in Heart Failure Using Unstructured Clinical Notes
Adejumo Philip, Pedroso Aline, Khera Rohan
A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Critical Illness and Signs of Myocardial InjuryMueller Joshua, Stepanova Daria, Chidambaram Vignesh, Nakarmi Ukash, Al'aref Subhi