Final ID: MDP579
Association of HDL-2b and HDL-3 with severe coronary stenosis in acute myocardial infarction patients: effects of age, gender, and comorbidities
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: It is unclear if the novel, functionally unidentified HDL cholesterol subtypes HDL-2b and HDL-3 can be used to predict acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
Methods: This cross-sectional study comprised 1,200 hospitalized patients with AMI identified using ICD-9 coding. The Gensini score was used to assess stenosis severity, defining patients as severe (score ≥50) or mild to moderate (score <50). Differences between groups were determined using one-way analysis of variance or nonparametric testing for continuous variables and chi-square tests for categorical variables. The relationship between HDL-2b, HDL-3, and severe coronary stenosis was investigated using restricted cubic splines (RCS) and logistic regression, with adjustments for age, gender, hypertension, diabetes, stroke, and kidney disease. Each of the covariates listed above was subjected to subgroup analyses. Based on the literature-reported cutoff of 18%, HDL-2b (%) was classified into a new variable, the HDL-2b group (HDL-2b ≥ 18% vs. HDL-2b < 18%).
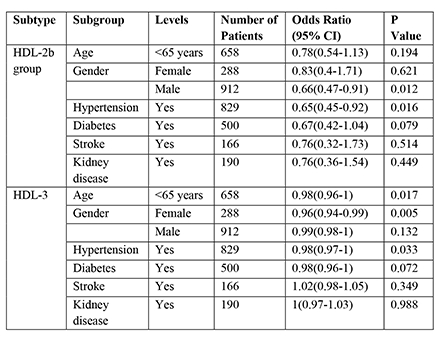
Results: 558 (46.5%) mild to moderate and 642 (53.5%) severe groups differed by HDL-3 (P=0.032) and HDL-2b group (P=0.019), but not by the above covariates or HDL-2b (P=0.324). RCS models revealed strong relationships between severe coronary stenosis and HDL-2b and HDL-3. To predict severe coronary stenosis, the odds ratio (OR) for HDL-3 was 0.98 (95% CI: 0.97-1.00, P=0.010), and for HDL-2b group, the OR was 0.67 (95% CI: 0.50-0.91, P=0.010). HDL-2b, as a continuous variable, had no statistically significant connection with severe coronary stenosis. HDL-3 significantly predicted severe coronary stenosis in subgroups of aged <65 years, females, those with hypertension, without stroke, and without kidney disease (Figure 1). The HDL-2b group was significant in the subgroups aged ≥65 years, males, with hypertension, without stroke, and without kidney disease for the prediction of severe coronary stenosis (Figure 1).
Conclusions: HDL-2b (%) values less than 18 and a drop in HDL-3 in AMI patients are associated with significant severe coronary stenosis, with differences identified among subgroups based on age, gender, and comorbidities.
Methods: This cross-sectional study comprised 1,200 hospitalized patients with AMI identified using ICD-9 coding. The Gensini score was used to assess stenosis severity, defining patients as severe (score ≥50) or mild to moderate (score <50). Differences between groups were determined using one-way analysis of variance or nonparametric testing for continuous variables and chi-square tests for categorical variables. The relationship between HDL-2b, HDL-3, and severe coronary stenosis was investigated using restricted cubic splines (RCS) and logistic regression, with adjustments for age, gender, hypertension, diabetes, stroke, and kidney disease. Each of the covariates listed above was subjected to subgroup analyses. Based on the literature-reported cutoff of 18%, HDL-2b (%) was classified into a new variable, the HDL-2b group (HDL-2b ≥ 18% vs. HDL-2b < 18%).
Results: 558 (46.5%) mild to moderate and 642 (53.5%) severe groups differed by HDL-3 (P=0.032) and HDL-2b group (P=0.019), but not by the above covariates or HDL-2b (P=0.324). RCS models revealed strong relationships between severe coronary stenosis and HDL-2b and HDL-3. To predict severe coronary stenosis, the odds ratio (OR) for HDL-3 was 0.98 (95% CI: 0.97-1.00, P=0.010), and for HDL-2b group, the OR was 0.67 (95% CI: 0.50-0.91, P=0.010). HDL-2b, as a continuous variable, had no statistically significant connection with severe coronary stenosis. HDL-3 significantly predicted severe coronary stenosis in subgroups of aged <65 years, females, those with hypertension, without stroke, and without kidney disease (Figure 1). The HDL-2b group was significant in the subgroups aged ≥65 years, males, with hypertension, without stroke, and without kidney disease for the prediction of severe coronary stenosis (Figure 1).
Conclusions: HDL-2b (%) values less than 18 and a drop in HDL-3 in AMI patients are associated with significant severe coronary stenosis, with differences identified among subgroups based on age, gender, and comorbidities.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Multivariate Scoring System for Diagnosing Post-Myocardial Infarction Pericarditis Following Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Bolaji Olayiwola, Omoru Okiemute, Upreti Prakash, Echari Blanche, Shoar Saeed, Basit Jawad, Alraies M Chadi
A Scoping Review Exploring Cardiovascular Risk and Health Metrics and Cancer PredictionKim Ji-eun, Henriquez Santos Gretell, Kumar Sant, Livinski Alicia, Vo Jacqueline, Joo Jungnam, Shearer Joe, Hashemian Maryam, Roger Veronique