Final ID: MDP1189
Association of Ventricular Arrhythmias with Lamotrigine: An Observational Cohort Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Objective: The chemical reduction of intracellular sodium through inhibition of the voltage-gated sodium channels stabilizes presynaptic neuronal membranes and inhibits presynaptic glutamate and aspartate release making lamotrigine (L) an important strategy for treating patients with Bipolar I disorder (BPI). L also slows cardiac conduction velocity introducing a potential substrate for its proarrhythmic properties. This study’s aim was to examine the association between onset of ventricular tachycardia (VT) and L in patients with BPI.
Methods: A retrospective observational research study was performed using Merative MarketScan® Commercial Claims and Medicare Supplemental Database. Analytic cohort included adult naïve VT or atrial fibrillation patients who filled a prescription for L or control agents (C), including lithium, quetiapine, valproate, or risperidone. Patients were free from arrhythmia, including atrial fibrillation or VT, during the 6-month baseline period before prescription of L or C prescription. The onset of VT was identified by the appearance of newly recorded ICD codes. Cumulative incidence of VT was calculated using Kaplan-Meier estimator, with patients being censored at the last enrollment, treatment switching, discontinuing treatment, or end of one-year follow up. We used a multivariable regression model to calculate hazard ratio for the onset of VT associated with L and C, adjusting for baseline characteristics, with a particular interest in the impact of structured heart disease (SHD).
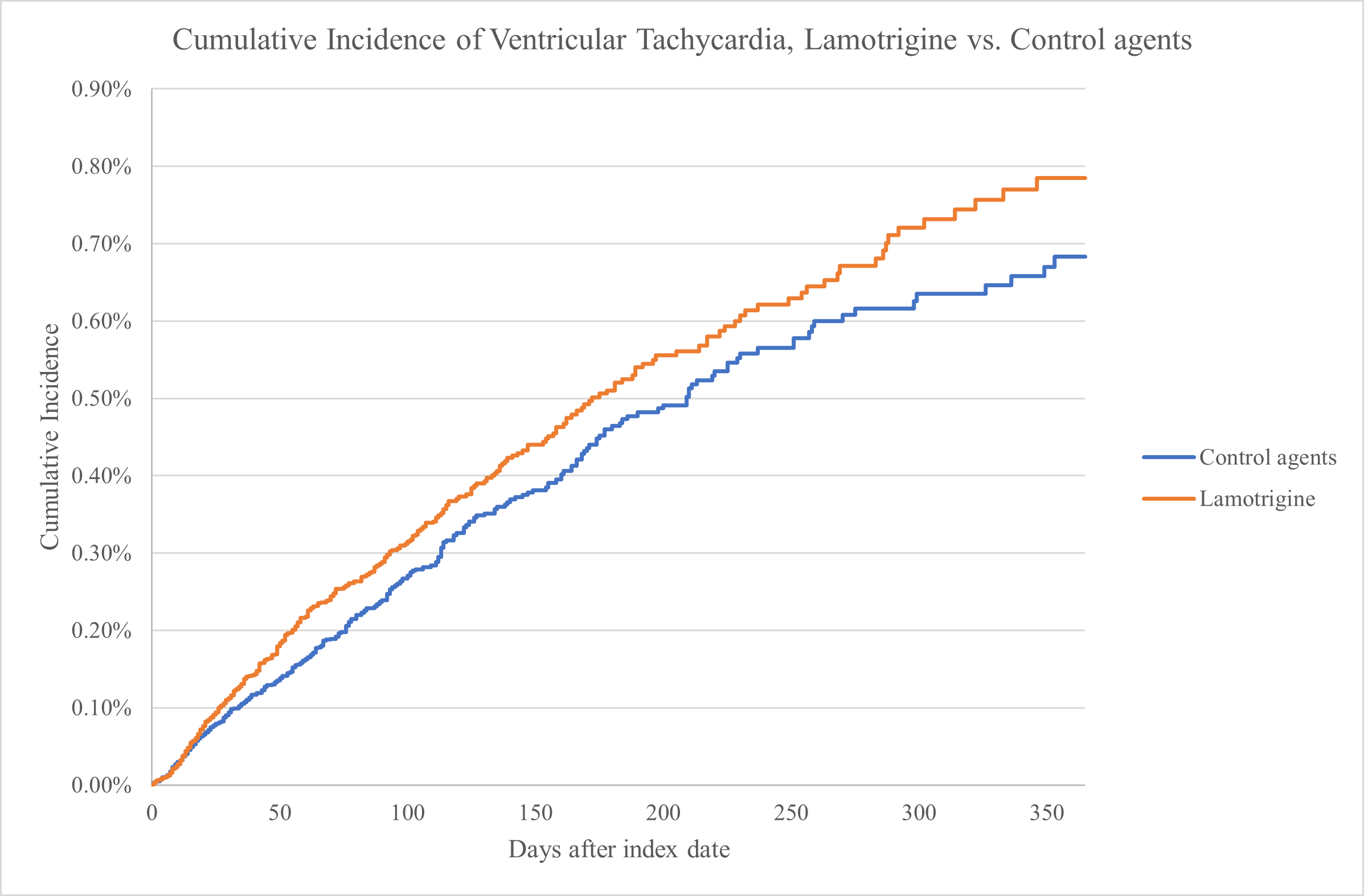
Results: The analytic cohort included 153,852 L and 213,593 C patients with respective mean year age of 37.53 (SD 13.63) and 40.85 (SD 15.74). The 1-year cumulative incidence of VT from L and C was 0.785% and 0.683%, respectively, calculating HR of 1.270 [95% CI: 1.079-1.496], p=0.0041. Figure 1) (After adjusting for the baseline characteristics, HR was 1.326 [1.122-1.568], p-value = 0.0009. From the multivariable analysis, the measure of SHD impact on the onset of VT was HR of 1.538 [1.011-2.341] (p=0.0444).
Conclusions: In adult BPI patients, L has a strong potential to increase the risk of VT compared to C. Notably, baseline SHD has a significant impact on the onset of VT.
Methods: A retrospective observational research study was performed using Merative MarketScan® Commercial Claims and Medicare Supplemental Database. Analytic cohort included adult naïve VT or atrial fibrillation patients who filled a prescription for L or control agents (C), including lithium, quetiapine, valproate, or risperidone. Patients were free from arrhythmia, including atrial fibrillation or VT, during the 6-month baseline period before prescription of L or C prescription. The onset of VT was identified by the appearance of newly recorded ICD codes. Cumulative incidence of VT was calculated using Kaplan-Meier estimator, with patients being censored at the last enrollment, treatment switching, discontinuing treatment, or end of one-year follow up. We used a multivariable regression model to calculate hazard ratio for the onset of VT associated with L and C, adjusting for baseline characteristics, with a particular interest in the impact of structured heart disease (SHD).
Results: The analytic cohort included 153,852 L and 213,593 C patients with respective mean year age of 37.53 (SD 13.63) and 40.85 (SD 15.74). The 1-year cumulative incidence of VT from L and C was 0.785% and 0.683%, respectively, calculating HR of 1.270 [95% CI: 1.079-1.496], p=0.0041. Figure 1) (After adjusting for the baseline characteristics, HR was 1.326 [1.122-1.568], p-value = 0.0009. From the multivariable analysis, the measure of SHD impact on the onset of VT was HR of 1.538 [1.011-2.341] (p=0.0444).
Conclusions: In adult BPI patients, L has a strong potential to increase the risk of VT compared to C. Notably, baseline SHD has a significant impact on the onset of VT.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Atrial Fibrillation with Lamotrigine in Bipolar I Disorder: An Observational Cohort Study
Kim Sodam, Welch Landon, De Los Santos Bertha, Radwanski Przemyslaw, Kim Kibum, Munger Mark
Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) Inhibitor Use Is Associated With Increased Cardiovascular Event Risk in Patients with Migraine: A Nationwide StudyLusk Jay, Mac Grory Brian, Wilson Lauren, Moore Carlene, Yarnell Stephanie, Kalapura Cheryl, Choudhury Aparna, Schrag Matthew, Poli Sven, Li Fan