Final ID: Mo2017
The Association of the Muscle Mass with Exercise Capacity and Childhood Opportunity Index in Patients with Fontan Circulation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The Child Opportunity Index (COI) is a validated, comprehensive measure of social context, comprised of 29 indicators of child neighborhood opportunity, split into three domains (education, health and environment, and socioeconomic). Our previous work showed that low COI is associated with a 10% lower percent of predicted peak VO2 post-Fontan. Exercise intolerance is a known prognostic factor for this patient population. Previous studies have shown that health inequities in education, environment, and socioeconomics factor into worse exercise outcomes. Cardiac MRI (CMR) measured muscle mass is a novel practical technique to evaluate muscle mass. We hypothesized that lower muscle mass by CMR is associated with lower exercise capacity and lower COI z-scores.
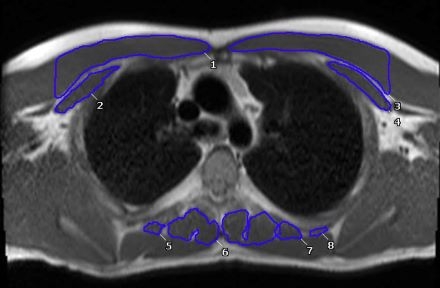
Methods: A retrospective, single-center study was performed, analyzing 75 post-Fontan patients who had CMR completed between 2010 and 2022. The anterior and paraspinal muscles were measured (Figure). COI z-scores were split into low and high levels, and univariate analyses were subsequently performed to determine associations between COI levels, exercise capacity and muscle mass.
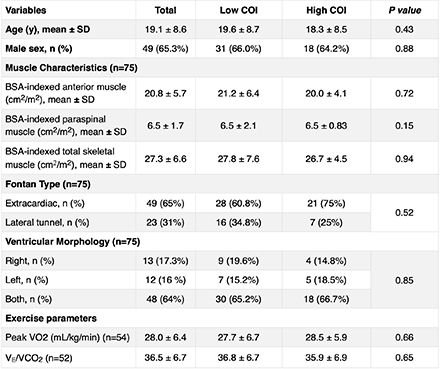
Results: The mean age of the population was 19.09 years ± 8.58 with the majority being male (65.3%). Most patients underwent an extracardiac conduit repair (65.3%) (Table). There was a positive correlation between anterior (r=0.36, p=0.007) and paraspinal (r=0.34, p=0.01) muscle mass to peak VO2. There was no significant difference in paraspinal (p=0.15) or anterior (p=0.72) muscle mass between COI groups. Similarly, there were no significant associations between muscle mass and specific COI domains.
Conclusion: Muscle mass correlated with exercise capacity in our population and is easy to measure by CMR. There was no correlation between COI level and muscle mass in this study, suggesting that the COI impact on exercise capacity is not directly mediated by lower muscle mass and that other factors should continue to be explored.
Methods: A retrospective, single-center study was performed, analyzing 75 post-Fontan patients who had CMR completed between 2010 and 2022. The anterior and paraspinal muscles were measured (Figure). COI z-scores were split into low and high levels, and univariate analyses were subsequently performed to determine associations between COI levels, exercise capacity and muscle mass.
Results: The mean age of the population was 19.09 years ± 8.58 with the majority being male (65.3%). Most patients underwent an extracardiac conduit repair (65.3%) (Table). There was a positive correlation between anterior (r=0.36, p=0.007) and paraspinal (r=0.34, p=0.01) muscle mass to peak VO2. There was no significant difference in paraspinal (p=0.15) or anterior (p=0.72) muscle mass between COI groups. Similarly, there were no significant associations between muscle mass and specific COI domains.
Conclusion: Muscle mass correlated with exercise capacity in our population and is easy to measure by CMR. There was no correlation between COI level and muscle mass in this study, suggesting that the COI impact on exercise capacity is not directly mediated by lower muscle mass and that other factors should continue to be explored.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Bone Mineral Density with Progression and Incidence of Aortic Calcification: the ERA JUMP Study
Carlson Lauren, Kadota Aya, Kadowaki Sayaka, Kondo Keiko, Miura Katsuyuki, Fujiyoshi Akira, Hisamatsu Takashi, Okamura Tomonori, Sekikawa Akira, Li Mengyi, Li Jiatong, Leader Joseph, Bon Jessica, Edmundowicz Daniel, Masaki Kamal, Willcox Bradley, Seto Todd
Analysis of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Vascular Occlusion Test as a Complement to Ankle-Brachial Index and 6-Minute Walk Test in Patients Diagnosed with Peripheral Artery DiseaseRodriguez Cesar, Lanka Santh Prakash, Maraj Joshua, Alsabbagh Yaman, Farres Sam, Ade Carl, Liu Xiuwen, Delp Judy