Final ID: MDP906
Bioresponsive Liposomal Nanoparticle-based Co-Delivery of tPA and DNase I Lyses tPA-Resistant Neutrophil Extracellular-Rich Clots
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): The nonsurgical standard of care for thrombosis is the administration of tPA. However, 40% of occlusive thrombi resist lysis by tPA. These resistant thrombi include both arterial and venous types, particularly those linked to ischemic stroke and deep vein thrombosis. Clot recalcitrance to tPA therapy is largely due to neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), protein-rich extrusions of DNA that generate in blood clots following neutrophil recruitment and activation. However, the mechanism by which NETs contribute to tPA resistance remains unexplored.
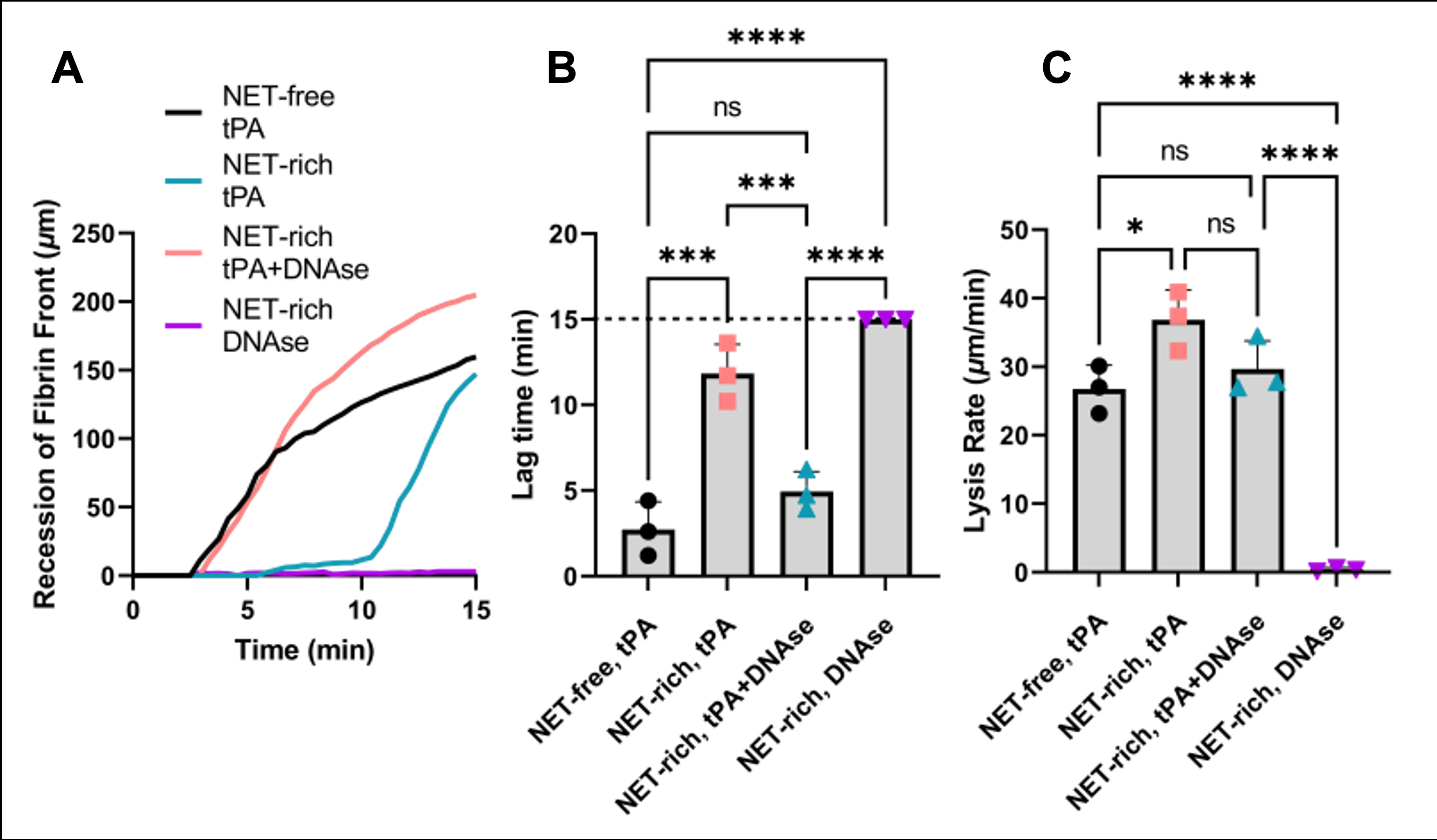
To investigate NET-dependent tPA recalcitrance, we developed several microfluidic models for NET-rich blood clots. In these models, NET-rich blood clots were characterized by a core-shell structure, with NETs most tightly intercalated in the shell, and thicker fibrin colocalized with NETs. Correspondingly, only the shell exhibited significant resistance to tPA therapy in fibrinolysis assays. We observed that neutrophil elastase (NE), the primary enzymatic component of NETs, reduced the efficacy of tPA while DNase I increased its efficacy in the absence of NETs.
Therapeutic concentrations of tPA took 12.3±2.7 min to breach the tPA-resistant shell, which is significantly longer than the in vivo half life of tPA (5 minutes). DNase I, an enzyme that degrades NETs, restored tPA efficacy, allowing breach of the shell within 2.5 ± 1.2 min. Building on these findings, we hypothesized that localized co-delivery of tPA and DNase using nanoparticles could remediate clot recalcitrance while minimizing iatrogenic effects and protecting the drugs from degrading in circulation.
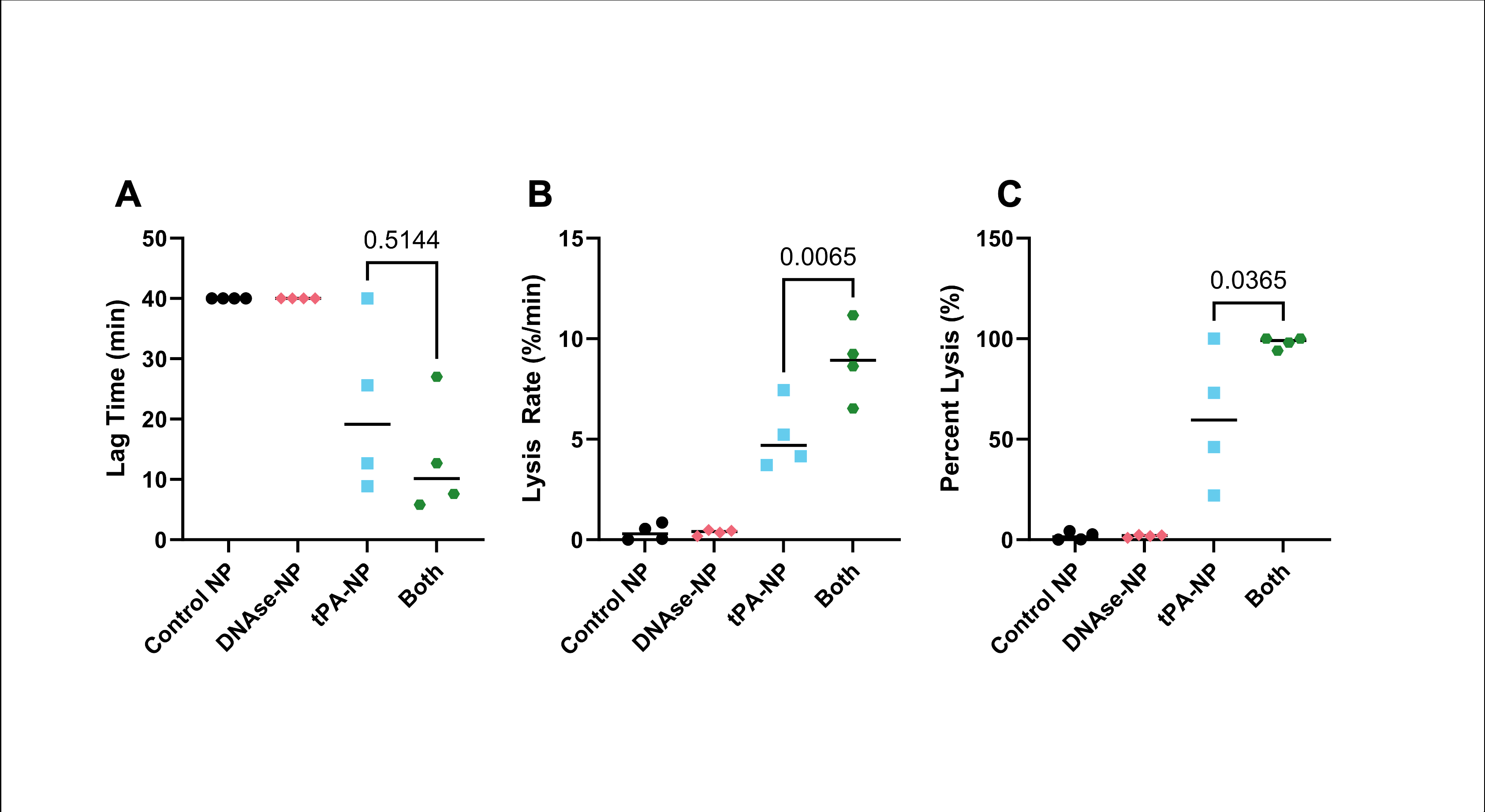
We engineered tPA-loaded nanoparticles (tPA-NPs) decorated with a fibrin-targeting peptide, and DNase-loaded nanoparticles (DNase-NPs) decorated with a NE-targeting peptide. A thrombin-cleavable substrate was incorporated into tPA-NPs such that they degraded upon exposure to thrombin, and an NE-cleavable substrate was incorporated into DNase-NPs such that they degraded upon exposure to NE. Upon triggered release, the nanoparticles achieved a concentration of 2 µg/mL tPA and NET-lytic activity equivalent to 50 IU/mL DNase I respectively.
In functional assays, the combination of DNase-NPs and tPA-NPs triggered complete clot dissolution within 12 min (n=4, p<0.05). In conclusion, the functionalized drug delivery system achieved localized co-delivery of tPA and DNase, resulting in complete lysis of clots that are recalcitrant to traditional therapies.
To investigate NET-dependent tPA recalcitrance, we developed several microfluidic models for NET-rich blood clots. In these models, NET-rich blood clots were characterized by a core-shell structure, with NETs most tightly intercalated in the shell, and thicker fibrin colocalized with NETs. Correspondingly, only the shell exhibited significant resistance to tPA therapy in fibrinolysis assays. We observed that neutrophil elastase (NE), the primary enzymatic component of NETs, reduced the efficacy of tPA while DNase I increased its efficacy in the absence of NETs.
Therapeutic concentrations of tPA took 12.3±2.7 min to breach the tPA-resistant shell, which is significantly longer than the in vivo half life of tPA (5 minutes). DNase I, an enzyme that degrades NETs, restored tPA efficacy, allowing breach of the shell within 2.5 ± 1.2 min. Building on these findings, we hypothesized that localized co-delivery of tPA and DNase using nanoparticles could remediate clot recalcitrance while minimizing iatrogenic effects and protecting the drugs from degrading in circulation.
We engineered tPA-loaded nanoparticles (tPA-NPs) decorated with a fibrin-targeting peptide, and DNase-loaded nanoparticles (DNase-NPs) decorated with a NE-targeting peptide. A thrombin-cleavable substrate was incorporated into tPA-NPs such that they degraded upon exposure to thrombin, and an NE-cleavable substrate was incorporated into DNase-NPs such that they degraded upon exposure to NE. Upon triggered release, the nanoparticles achieved a concentration of 2 µg/mL tPA and NET-lytic activity equivalent to 50 IU/mL DNase I respectively.
In functional assays, the combination of DNase-NPs and tPA-NPs triggered complete clot dissolution within 12 min (n=4, p<0.05). In conclusion, the functionalized drug delivery system achieved localized co-delivery of tPA and DNase, resulting in complete lysis of clots that are recalcitrant to traditional therapies.
More abstracts on this topic:
Amyloidogenic Medin Induces Prothrombotic Activation in Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Morrow Kaleb, Karamanova Nina, Nabaty Natalie, Maerivoet Alana, Madine Jillian, Li Ming, Migrino Raymond
Is It Safe to Discontinue Oral Anticoagulation After Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation? A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisLucena Larissa, Giorgi Juliana, Cavalcante Deivyd, Sousa Julio Cesar, De Oliveira William, De Oliveira Neto Nestor, Costa Borges Rafael, Paiva Irina, Arruda De Oliveira Antonio Lucas, Silva Carvalho Natália, Leite Victória, Medeiros Amanda