Final ID: MDP397
Clinical Characteristics and the Response to IV Antihypertensive Therapy in Severe Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Objective:
Evidence-based recommendations guiding first-line antihypertensive agent selection for treatment of sustained severe hypertension in pregnancy (SSHP) are lacking. Our aim was to identify patient characteristics associated with response to initial IV antihypertensive therapy for SSHP.
Study Design:
We performed a single center retrospective cohort study using EHR data from Jan-Dec 2021. Patients with SSHP, defined as a blood pressure (BP) ≥ 160/110 mmHg for ≥ 15 minutes, were identified from institutional data generated for a state quality improvement project. Patients receiving initial treatment with IV labetalol or hydralazine were included. Patients were excluded if they received nifedipine, did not have a repeat BP measurement within 30 minutes of treatment, had resolution of SSHP without treatment, or did not receive at least two doses of the initial agent prior to changing therapy. Response was defined as a resolution of SSHP with ≤ 2 doses of IV therapy. Variables of interest were identified a priori. Baseline characteristics between groups were compared with standardized mean differences. Multivariable analysis was performed using LASSO regression with 10-fold cross-validation.
Results:
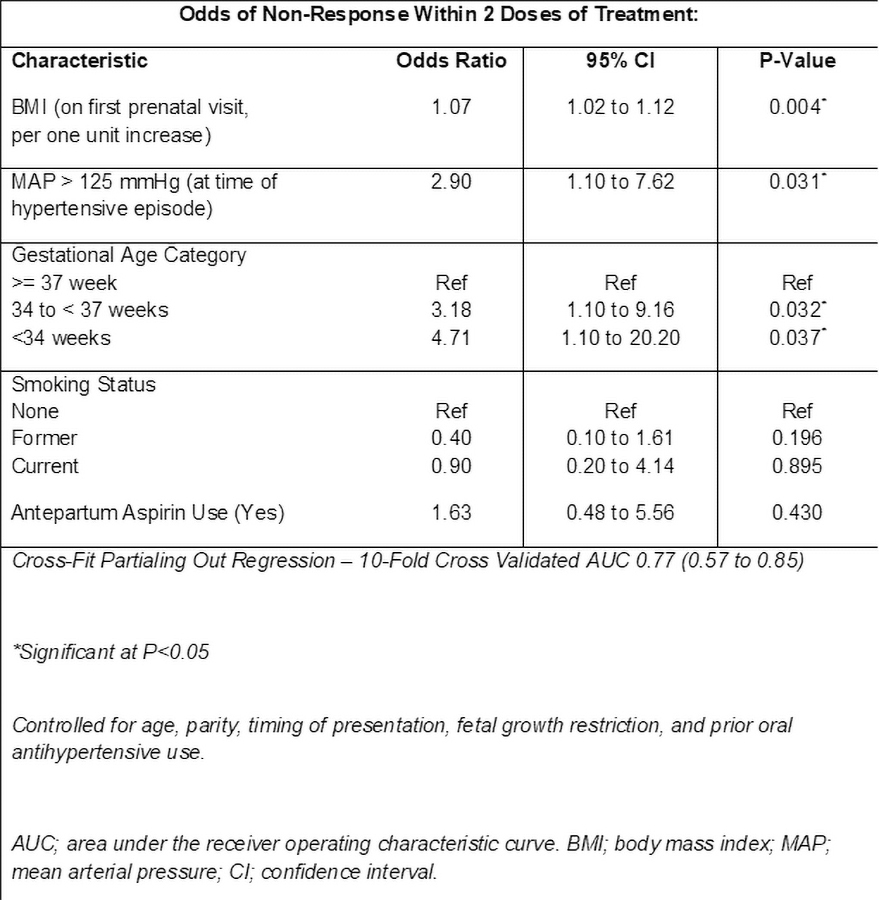
We identified 200 patients with SSHP, of which 114 (57%) received labetalol and 86 (43%) hydralazine. 173 (86.5%) patients were responders: 97 (85.1%) for labetalol vs 76 (88.4%) for hydralazine (p=0.50). Differences between responders and non-responders are listed in the Table. In regression analysis factors significantly associated with non-response included: pre-pregnancy BMI (OR 1.07; 1.02-1.12 per unit increase, kg/m2) pre-treatment MAP > 125 mmHg (2.90; 1.10-7.62), and preterm gestational age (< 34 weeks OR 4.71; 1.10-20.20; 34-37 weeks, OR 3.18; 1.10-9.16) (Table).
Conclusions:
In patients with SSHP, multiple clinical factors are associated with response to initial therapy. Each unit increase in pre-pregnancy BMI) is associated with 7% higher odds of non-response. Clinical characteristics may guide risk stratification and antihypertensive dosing strategies for patients requiring acute treatment for SSHP.
Evidence-based recommendations guiding first-line antihypertensive agent selection for treatment of sustained severe hypertension in pregnancy (SSHP) are lacking. Our aim was to identify patient characteristics associated with response to initial IV antihypertensive therapy for SSHP.
Study Design:
We performed a single center retrospective cohort study using EHR data from Jan-Dec 2021. Patients with SSHP, defined as a blood pressure (BP) ≥ 160/110 mmHg for ≥ 15 minutes, were identified from institutional data generated for a state quality improvement project. Patients receiving initial treatment with IV labetalol or hydralazine were included. Patients were excluded if they received nifedipine, did not have a repeat BP measurement within 30 minutes of treatment, had resolution of SSHP without treatment, or did not receive at least two doses of the initial agent prior to changing therapy. Response was defined as a resolution of SSHP with ≤ 2 doses of IV therapy. Variables of interest were identified a priori. Baseline characteristics between groups were compared with standardized mean differences. Multivariable analysis was performed using LASSO regression with 10-fold cross-validation.
Results:
We identified 200 patients with SSHP, of which 114 (57%) received labetalol and 86 (43%) hydralazine. 173 (86.5%) patients were responders: 97 (85.1%) for labetalol vs 76 (88.4%) for hydralazine (p=0.50). Differences between responders and non-responders are listed in the Table. In regression analysis factors significantly associated with non-response included: pre-pregnancy BMI (OR 1.07; 1.02-1.12 per unit increase, kg/m2) pre-treatment MAP > 125 mmHg (2.90; 1.10-7.62), and preterm gestational age (< 34 weeks OR 4.71; 1.10-20.20; 34-37 weeks, OR 3.18; 1.10-9.16) (Table).
Conclusions:
In patients with SSHP, multiple clinical factors are associated with response to initial therapy. Each unit increase in pre-pregnancy BMI) is associated with 7% higher odds of non-response. Clinical characteristics may guide risk stratification and antihypertensive dosing strategies for patients requiring acute treatment for SSHP.
More abstracts on this topic:
Age-Related Differences in Aortic Valve Calcium Progression and the Risk for Aortic Stenosis: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Marrero Natalie, Thanassoulis George, Rotter Jerome, Blaha Michael, Whelton Seamus, Jha Kunal, Grant Jelani, Razavi Alexander, Budoff Matthew, Shah Sanjiv, Blumenthal Roger, Post Wendy, Shaw Leslee
A major effect of aprocitentan on albuminuria in patients with resistant hypertensionSchlaich Markus, Bakris George, Flack John, Gimona Alberto, Narkiewicz Krzysztof, Sassi-sayadi Mouna, Wang Jiguang, Weber Michael