Final ID: MDP455
Plant-Based Diet and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality among Patients with Cardiovascular Disease: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The role of plant-based diet in preventing premature death among patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) remained unknown. To explore the relationship of plant-based dietary patterns with all-cause and cause-specific mortality among patients with CVD.
Methods: A sum of 10,841 participants with CVD at baseline were followed up in the UK Biobank. We constructed three types of plant-based diet indexes [an overall plant-based diet index (PDI), a healthy PDI (hPDI), and an unhealthy PDI (uPDI)] by assigning different weights to various food groups from web-based 24-h dietary recall questionnaires. The national death registry documented primary causes of death. The Cox proportional hazards regression models were utilized to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for mortality.
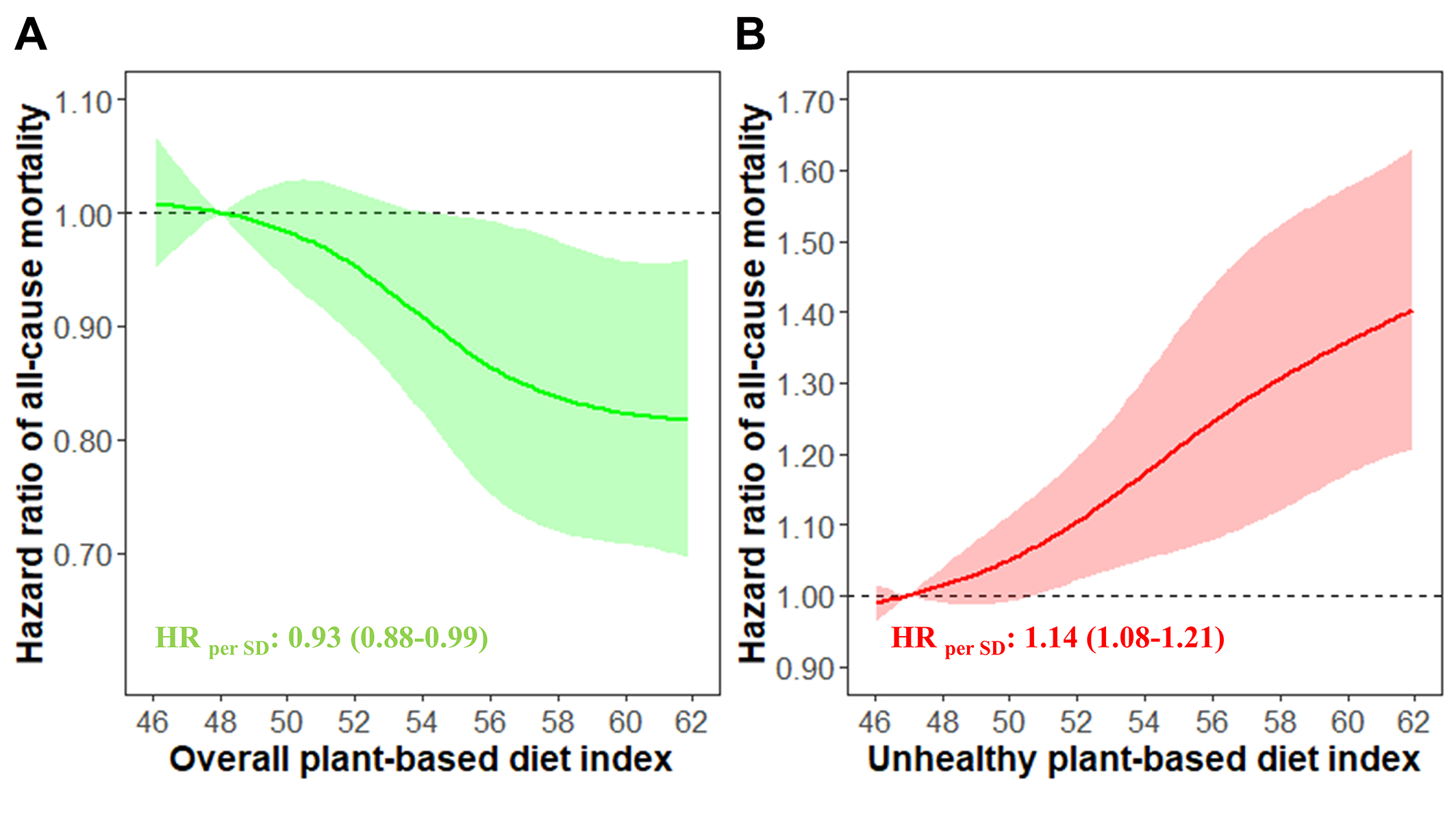
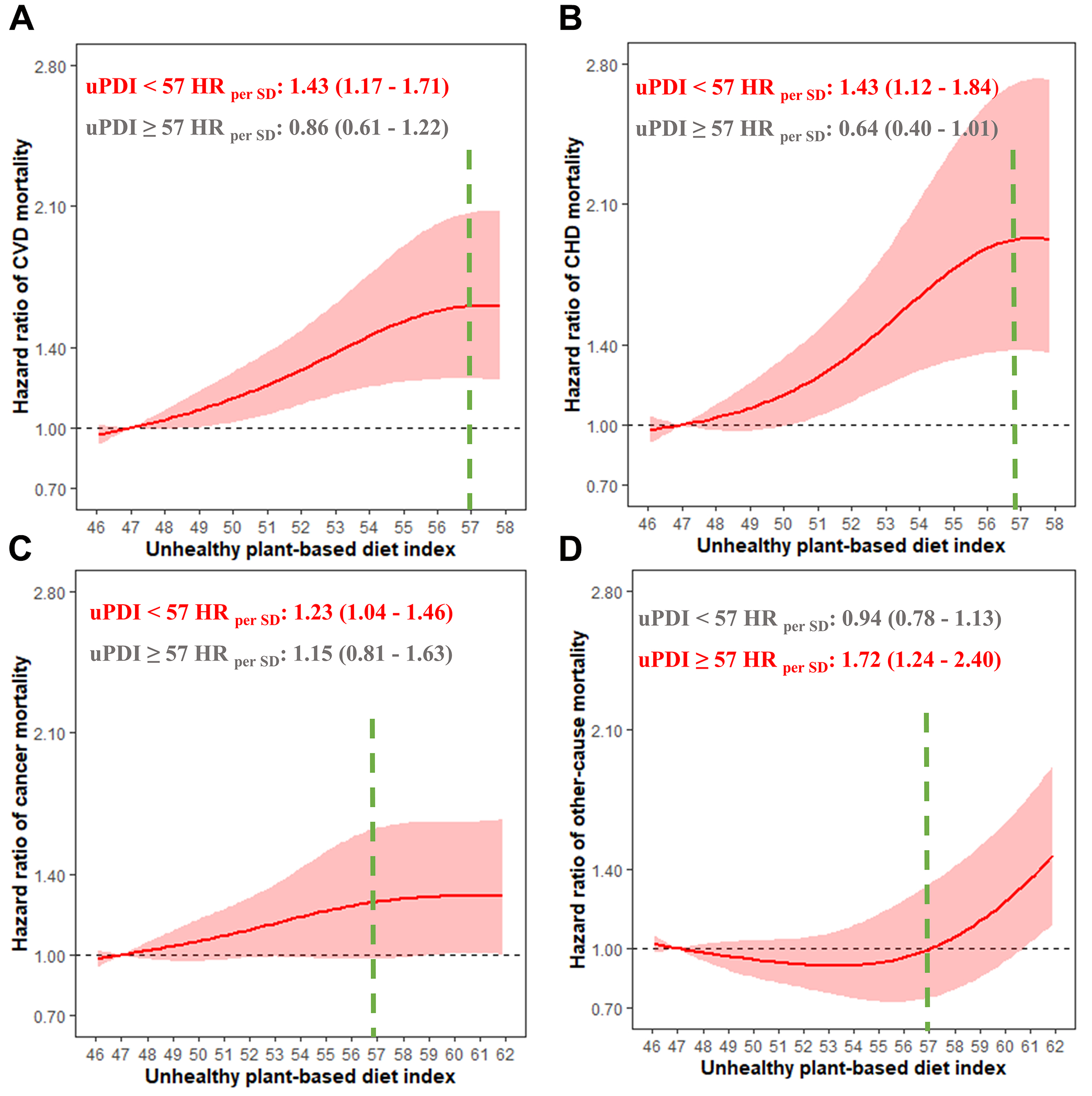
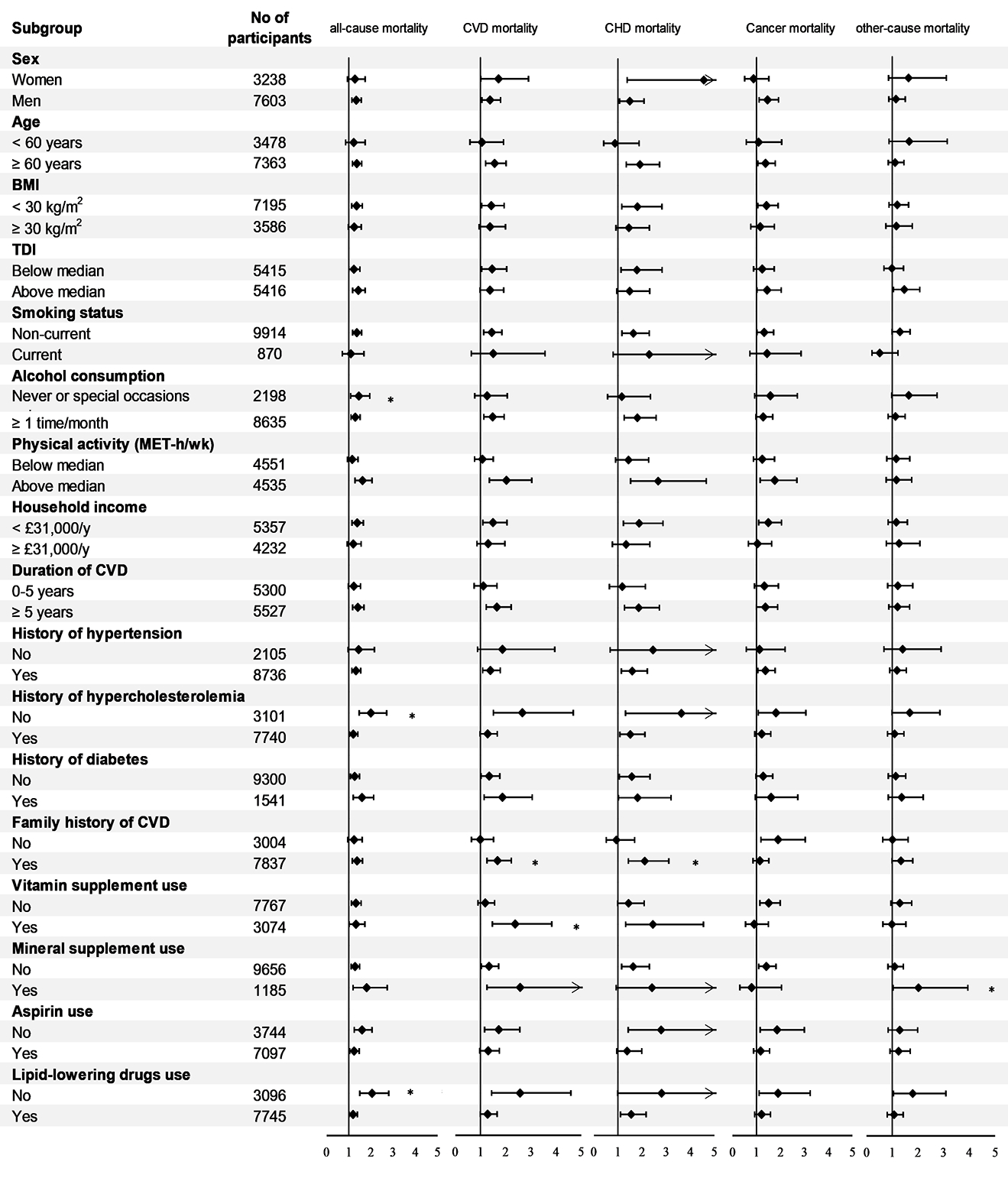
Results: Over a median of 11.3-year follow-up, 1,275 death cases were ascertained. After multivariable adjustment, PDI had a negative correlation with all-cause mortality [HRT3vsT1: 0.81 (0.70-0.94), Ptrend=0.005] and CVD mortality [HRT3vsT1: 0.78 (0.61-0.99), Ptrend=0.040], while uPDI displayed a positive correlation with all-cause mortality [HRT3vsT1: 1.33 (1.16-1.53), Ptrend<0.001] and CVD and cancer mortality. Additionally, in mediation analyses, serum concentration of C-reactive protein (CRP) accounted for 6.2%, 4.0%, and 5.1% of the relationship between uPDI and all-cause, CVD, and cancer mortality, respectively. No significant associations were detected between hPDI and mortality.
Conclusions: Among patients with CVD, stronger adherence to PDI correlated with reduced all-cause and CVD mortality rates. Conversely, adherence to uPDI showed an association with increased mortality, possibly attributable to elevated levels of circulating CRP. Our findings support dietary guidelines that recommend limiting the consumption of unhealthy plant-based foods.
Methods: A sum of 10,841 participants with CVD at baseline were followed up in the UK Biobank. We constructed three types of plant-based diet indexes [an overall plant-based diet index (PDI), a healthy PDI (hPDI), and an unhealthy PDI (uPDI)] by assigning different weights to various food groups from web-based 24-h dietary recall questionnaires. The national death registry documented primary causes of death. The Cox proportional hazards regression models were utilized to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for mortality.
Results: Over a median of 11.3-year follow-up, 1,275 death cases were ascertained. After multivariable adjustment, PDI had a negative correlation with all-cause mortality [HRT3vsT1: 0.81 (0.70-0.94), Ptrend=0.005] and CVD mortality [HRT3vsT1: 0.78 (0.61-0.99), Ptrend=0.040], while uPDI displayed a positive correlation with all-cause mortality [HRT3vsT1: 1.33 (1.16-1.53), Ptrend<0.001] and CVD and cancer mortality. Additionally, in mediation analyses, serum concentration of C-reactive protein (CRP) accounted for 6.2%, 4.0%, and 5.1% of the relationship between uPDI and all-cause, CVD, and cancer mortality, respectively. No significant associations were detected between hPDI and mortality.
Conclusions: Among patients with CVD, stronger adherence to PDI correlated with reduced all-cause and CVD mortality rates. Conversely, adherence to uPDI showed an association with increased mortality, possibly attributable to elevated levels of circulating CRP. Our findings support dietary guidelines that recommend limiting the consumption of unhealthy plant-based foods.
More abstracts on this topic:
Advanced maternal age and association with major adverse cardiovascular events from NHANES from 1999 to 2018
Mehta Adhya, Honigberg Michael, Kennedy Jamie, Spitz Jared, Sharma Garima, Agboola Olayinka, Satti Danish Iltaf, Harrington Colleen, Scott Nandita, Sarma Amy, Saad Antonio, Sullivan Scott, Epps Kelly
Acute Exposure to High PM2.5 Levels Increases the Risk of Late All-Cause Mortality in Patients with STEMIFathieh Sina, Tran Hao, Faour Amir, Pahn Reece, Long Mitchell, Tam Gladys, Figtree Gemma, Negishi Kazuaki, French John