Final ID: Su2064
Postoperative Risk Stratification For Complex Congenital Heart Disease Based On Age-adjusted NT-proBNP
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) is extensively utilized in the prognosis of cardiovascular disease for adults, but its clinical significance for pediatric cardiology is poorly understood.
Objectives
This study aimed to explore the prognostic value of age-adjusted NT-proBNP (zlog-proBNP) in pediatric patients with CCHD.
Methods
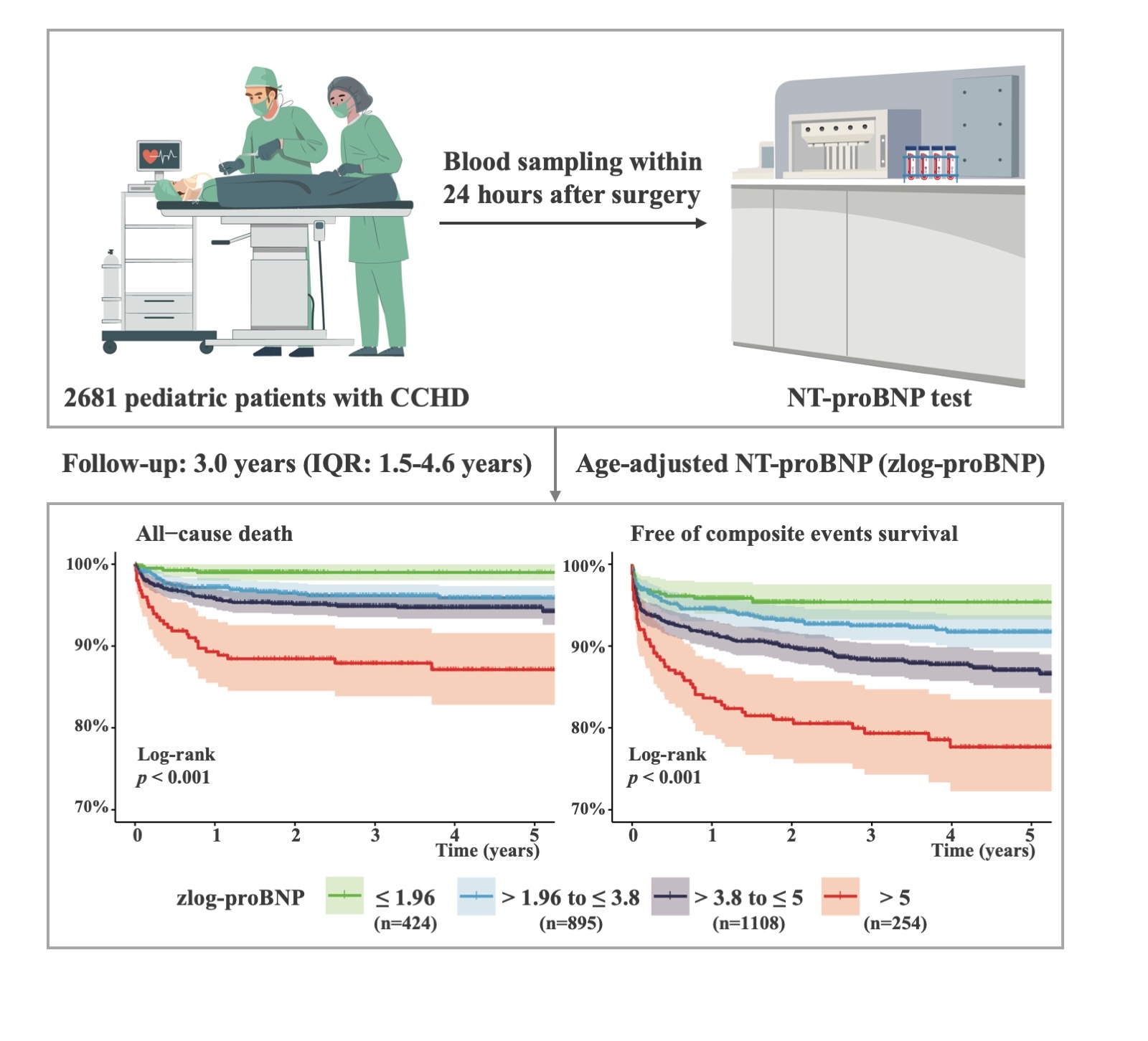
This retrospective study included 2681 patients with CCHD (median age at surgery, 10.6 months; male, 59%), and the median follow-up time was 3.0 years (range, 1 day–6.2 years). The primary endpoint was death, and the composite events were death and unplanned cardiac reintervention. NT-proBNP level was measured within 24 h after surgery and transformed into zlog-proBNP.
Results
NT-proBNP level increased to a median absolute value of 3970 (interquartile range [IQR], 1352–9095), and a median zlog-proBNP value of 3.83 (IQR, 2.93–4.44) on postoperative day 1, reaching its peak at approximately 12h. Compared with patients with low zlog-proBNP value (≤1.96), those with very high zlog-proBNP value (>5; hazard ratio [HR] for death, 9.78 [3.17-30.22, p<0.001]; HR for composite events, 3.64 [1.95-6.79, p<0.001]) had higher risk of death and composite events, followed by patients with high (>3.8 to ≤5; HR for death, 5.27 [1.79-15.53, p=0.003]; HR for composite events, 2.28 [1.29-4.03, p=0.004]) and moderate (>1.96 to ≤3.8; HR for death, 3.83 [1.31-11.17, p=0.014]; HR for composite events, 1.53 [0.87-2.69, p=0.139]) zlog-proBNP values.
Conclusions
Zlog-proBNP demonstrates substantial prognostic significance in patients with CCHD, warranting particular clinical attention in those with a zlog-proBNP value >5.
N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) is extensively utilized in the prognosis of cardiovascular disease for adults, but its clinical significance for pediatric cardiology is poorly understood.
Objectives
This study aimed to explore the prognostic value of age-adjusted NT-proBNP (zlog-proBNP) in pediatric patients with CCHD.
Methods
This retrospective study included 2681 patients with CCHD (median age at surgery, 10.6 months; male, 59%), and the median follow-up time was 3.0 years (range, 1 day–6.2 years). The primary endpoint was death, and the composite events were death and unplanned cardiac reintervention. NT-proBNP level was measured within 24 h after surgery and transformed into zlog-proBNP.
Results
NT-proBNP level increased to a median absolute value of 3970 (interquartile range [IQR], 1352–9095), and a median zlog-proBNP value of 3.83 (IQR, 2.93–4.44) on postoperative day 1, reaching its peak at approximately 12h. Compared with patients with low zlog-proBNP value (≤1.96), those with very high zlog-proBNP value (>5; hazard ratio [HR] for death, 9.78 [3.17-30.22, p<0.001]; HR for composite events, 3.64 [1.95-6.79, p<0.001]) had higher risk of death and composite events, followed by patients with high (>3.8 to ≤5; HR for death, 5.27 [1.79-15.53, p=0.003]; HR for composite events, 2.28 [1.29-4.03, p=0.004]) and moderate (>1.96 to ≤3.8; HR for death, 3.83 [1.31-11.17, p=0.014]; HR for composite events, 1.53 [0.87-2.69, p=0.139]) zlog-proBNP values.
Conclusions
Zlog-proBNP demonstrates substantial prognostic significance in patients with CCHD, warranting particular clinical attention in those with a zlog-proBNP value >5.
More abstracts on this topic:
Anticoagulant therapy for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: A propensity score matching study
Liu Kai, Wei Zhao, Meng Zhang, Qin Dai, Song Bo, Xu Yuming
Cardiac Myosin inhibitors in patients with Symptomatic Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: An updated Systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized trials.Prata Alonzo, Dantas Brígido Alexandra Regia, Katsuyama Eric, Coan Ana Carolina, Fernandes Julia, Scardini Pedro Gabriel, Fukunaga Christian, Falco Neto Wilson, Petri Santos Pinheiro Rafael, Andrade Naieli