Final ID: Mo3120
Longitudinal Assessment Using a Mobile Text-Messaging Based Platform Demonstrates High Rates of Transitions in Dual Users of Electronic and Combustible Cigarettes
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background/Aims
The increasing use of electronic cigarettes (e-cigs) has resulted in complex tobacco use patterns that may change with time within individuals. We developed a mobile platform to capture use patterns and transitions over time in young adults.
Methods
Individuals 18-45 years old in the Cardiovascular Injury Due to Tobacco Use (CITU 2.0) study completed a detailed baseline questionnaire followed by enrollment in a text message-based mobile platform (Agile Health, Inc) that collected self-reported tobacco use patterns and transitions over 24 months. Baseline use patterns (sole e-cig use, sole combustible cigarette use, dual use, and non-use) and transitions (changing from one use group to another) monthly until last follow-up are reported. Models were used to predict likelihood of non-use (no tobacco products) or non-combustible use (sole e-cig or non-use) at follow-up.
Results
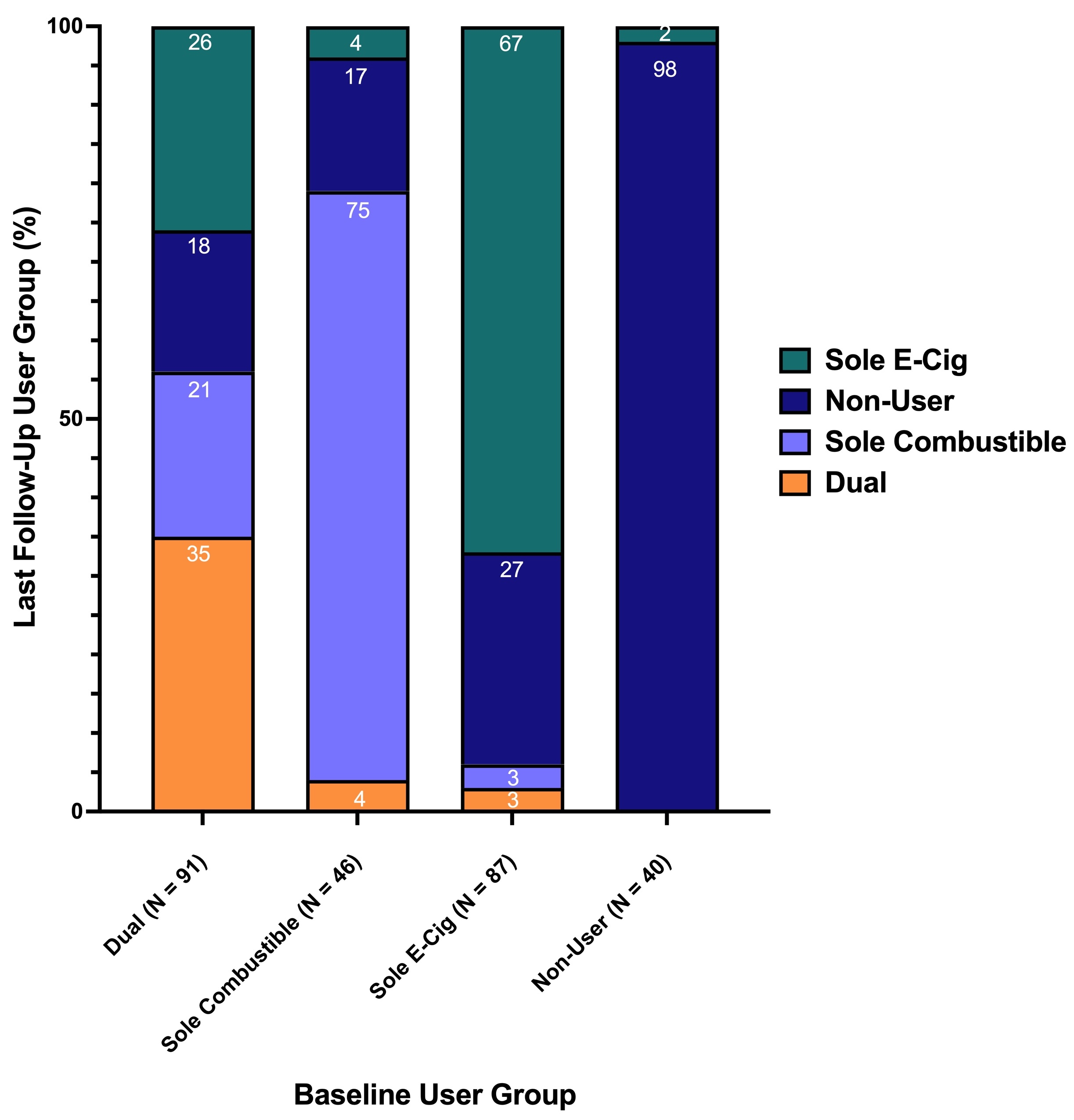
264 individuals were enrolled at baseline: 87 sole e-cig users, 46 sole combustible users, 91 dual users, and 40 non-users. On monthly follow-ups, the dual use pattern was associated with the highest rate of cumulative transitions, 3 by 6 months, compared to 1 for sole e-cig use. By last follow-up, 65% of the dual use pattern transitioned compared to relatively stable use in the sole e-cig and combustible cigarette use groups (Figure). Rate of uptake of combustible cigarette use in sole e-cig users was low (6%).
In logistic regression models, compared to combustible cigarette users, dual users were more likely to make a transition (OR 5.9, p<0.0001), but not sole e-cig users (OR 1.7, p=0.2). Neither group of e-cig users had a higher rate of transition to non-use than combustible cigarette users (dual use OR 1.2, p=0.7, sole e-cig OR 2.1, p=0.1). However, rates of non-combustible use at follow-up were higher in both sole e-cig (OR 55.5, p<0.0001) and dual users (OR 3.2, p=0.006).
Conclusions
Frequent longitudinal assessment of tobacco use patterns revealed important details regarding rates of transitions with highest levels amongst dual users of e-cig and combustible cigarettes. Rates of transition to non-use were low across all tobacco product users, with higher rates of transition to non-combustible use amongst dual users when compared to combustible users. Future studies will be important to understand methods to enhance tobacco product cessation amongst all use groups.
The increasing use of electronic cigarettes (e-cigs) has resulted in complex tobacco use patterns that may change with time within individuals. We developed a mobile platform to capture use patterns and transitions over time in young adults.
Methods
Individuals 18-45 years old in the Cardiovascular Injury Due to Tobacco Use (CITU 2.0) study completed a detailed baseline questionnaire followed by enrollment in a text message-based mobile platform (Agile Health, Inc) that collected self-reported tobacco use patterns and transitions over 24 months. Baseline use patterns (sole e-cig use, sole combustible cigarette use, dual use, and non-use) and transitions (changing from one use group to another) monthly until last follow-up are reported. Models were used to predict likelihood of non-use (no tobacco products) or non-combustible use (sole e-cig or non-use) at follow-up.
Results
264 individuals were enrolled at baseline: 87 sole e-cig users, 46 sole combustible users, 91 dual users, and 40 non-users. On monthly follow-ups, the dual use pattern was associated with the highest rate of cumulative transitions, 3 by 6 months, compared to 1 for sole e-cig use. By last follow-up, 65% of the dual use pattern transitioned compared to relatively stable use in the sole e-cig and combustible cigarette use groups (Figure). Rate of uptake of combustible cigarette use in sole e-cig users was low (6%).
In logistic regression models, compared to combustible cigarette users, dual users were more likely to make a transition (OR 5.9, p<0.0001), but not sole e-cig users (OR 1.7, p=0.2). Neither group of e-cig users had a higher rate of transition to non-use than combustible cigarette users (dual use OR 1.2, p=0.7, sole e-cig OR 2.1, p=0.1). However, rates of non-combustible use at follow-up were higher in both sole e-cig (OR 55.5, p<0.0001) and dual users (OR 3.2, p=0.006).
Conclusions
Frequent longitudinal assessment of tobacco use patterns revealed important details regarding rates of transitions with highest levels amongst dual users of e-cig and combustible cigarettes. Rates of transition to non-use were low across all tobacco product users, with higher rates of transition to non-combustible use amongst dual users when compared to combustible users. Future studies will be important to understand methods to enhance tobacco product cessation amongst all use groups.
More abstracts on this topic:
Mobile Phone Auscultation Using Non-linear Dynamics Analysis to Detect Aortic Stenosis
Kowalski Kailey, Judson Gregory, Martinez Destiny, Zhang Jacob, Diaz Marco, Close Ryan
Circulating Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) Proteins Are Associated with Risk of Late Life Heart Failure: the ARIC StudyDehghan Arshama, Mosley Thomas, Palta Priya, Yu Bing, Shah Amil, Giugni Fernando, Lamberson Victoria, Yang Yimin, Boerwinkle Eric, Fornage Myriam, Giannarelli Chiara, Grams Morgan, Windham B Gwen