Final ID: Su2126
Relationship between Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices and Tricuspid Regurgitation in the General Population
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Case series suggest that cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) with right ventricular leads may tether the tricuspid valve, leading to clinically relevant tricuspid regurgitation (TR). However, the impact of these devices on tricuspid disease in the general population has not been investigated.
Methods
Using California’s Department of Health Care Access and Information databases, a longitudinal Cox proportional-hazards analysis of adults who received care in an emergency department, hospital, or outpatient surgery facility from 1 January 2005 to 31 December 2020 was performed. Patients with prevalent TR, rheumatic or congenital heart disease, and endocarditis were excluded. Outcomes were (1) the development of TR and (2) tricuspid intervention.
Results
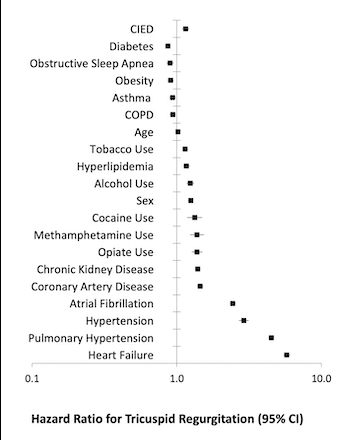
Of 16,893,314 participants contributing 56,095,327 person years, there were 11,234 instances of TR. In the unadjusted analyses, CIED implantation was associated with a 13-fold higher risk of incident TR. After adjusting for age, sex, race and ethnicity, income, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, hypertension, pulmonary hypertension, coronary artery disease, chronic kidney disease, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, obstructive sleep apnea, alcohol use, cocaine use, methamphetamine use, opiate use, and tobacco use, patients with a CIED exhibited a 15% higher risk of TR (Figure 1). Heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, hypertension, and atrial fibrillation each exhibited larger magnitudes of risk for TR than having a CIED.
In the same population, 74 tricuspid valve interventions were identified. While a CIED was associated with a subsequent tricuspid intervention with HR 19.43 (p<0.0001) in the unadjusted model, this lost statistical significance after adjusting for the same covariates listed above (HR 1.3, p=0.34).
Conclusions
Patients with a CIED experienced a higher risk of TR, although the magnitude of the hazard was smaller than other cardiovascular risk factors. While the point estimate favored a higher risk of requiring tricuspid interventions among those with CIEDs, statistical significance was lost after multivariable adjustment, likely due to a small number of outcomes.
Case series suggest that cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) with right ventricular leads may tether the tricuspid valve, leading to clinically relevant tricuspid regurgitation (TR). However, the impact of these devices on tricuspid disease in the general population has not been investigated.
Methods
Using California’s Department of Health Care Access and Information databases, a longitudinal Cox proportional-hazards analysis of adults who received care in an emergency department, hospital, or outpatient surgery facility from 1 January 2005 to 31 December 2020 was performed. Patients with prevalent TR, rheumatic or congenital heart disease, and endocarditis were excluded. Outcomes were (1) the development of TR and (2) tricuspid intervention.
Results
Of 16,893,314 participants contributing 56,095,327 person years, there were 11,234 instances of TR. In the unadjusted analyses, CIED implantation was associated with a 13-fold higher risk of incident TR. After adjusting for age, sex, race and ethnicity, income, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, hypertension, pulmonary hypertension, coronary artery disease, chronic kidney disease, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, obstructive sleep apnea, alcohol use, cocaine use, methamphetamine use, opiate use, and tobacco use, patients with a CIED exhibited a 15% higher risk of TR (Figure 1). Heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, hypertension, and atrial fibrillation each exhibited larger magnitudes of risk for TR than having a CIED.
In the same population, 74 tricuspid valve interventions were identified. While a CIED was associated with a subsequent tricuspid intervention with HR 19.43 (p<0.0001) in the unadjusted model, this lost statistical significance after adjusting for the same covariates listed above (HR 1.3, p=0.34).
Conclusions
Patients with a CIED experienced a higher risk of TR, although the magnitude of the hazard was smaller than other cardiovascular risk factors. While the point estimate favored a higher risk of requiring tricuspid interventions among those with CIEDs, statistical significance was lost after multivariable adjustment, likely due to a small number of outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Brash Syndrome Requiring Permanent Pacemaker: A Case Report
Bhatt Nilay, Mrad Yves Najm, Gupta Shivam, Dickey Curtis
A Case of Spike-on-T Phenomenon and Polymorphic Ventricular TachycardiaTran Brittany, Thimmiah Harun, Rosenthal Lawrence