Final ID: Su2084
Electrophysiologic Characteristics, Outcomes and Potential Predictors of Acute Success After Ventricular Tachycardia Ablation in Patients with Cardiac Sarcoidosis: Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiac sarcoidosis (CS) is a rare condition marked by conduction disturbances, and ventricular tachycardia (VT) resulting from reentrant pathways. VT ablation is typically considered for patients with refractory VT. This systematic review aims to synthesize reported outcomes and identify potential predictors for the success of VT ablation in CS patients.
Methods: A systematic literature review was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines, searching PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and Scopus databases up to May 2024. A random-effects model was used to evaluate electrophysiologic and procedural variables and compare outcomes to identify potential predictors of success.
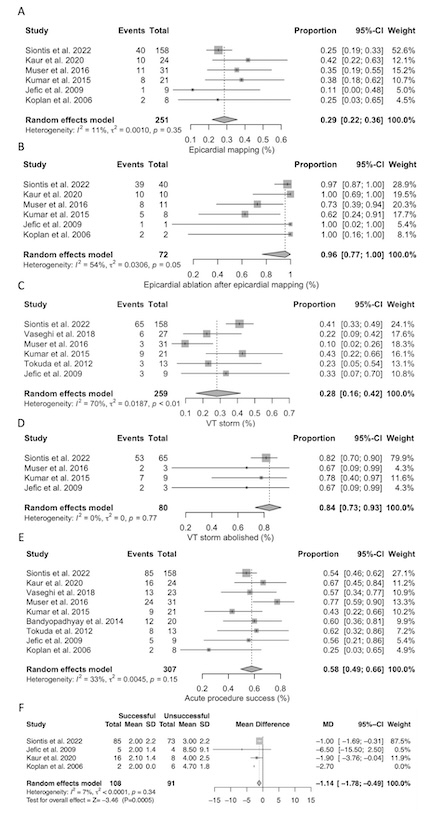
Results: After excluding duplicates, 473 titles and abstracts were screened. Twenty-five studies were fully reviewed, and 9 studies comprising data from 311 CS patients who underwent VT ablation were included. The mean age of patients was 50.5 years, with 30% being female. Epicardial mapping was performed in 29% (CI 22-36%; 72/251) of cases, and 96% (CI 77-100%; 65/72) of those underwent epicardial ablation. The prevalence of VT storm before the procedure was 28% (CI 16-42%; 89/259), with a suppression success rate of 84% (CI 73-93%; 64/76). The acute complete success rate defined as lack of inducibility was 58% (CI 49-66%; 174/307). During follow-up, which ranged from 19 to 58 months, 34% (CI 21-48%; 113/271) of patients survived free from the composite outcome of death, transplantation, or VT recurrence. Patients with acute success had fewer inducible VTs (MD –1.1; CI: -1.8 to -0.5; p < 0.001). No other variables were significantly associated with acute success. However, patients with acute success tended to be older than those with partial or unsuccessful outcomes (MD 7.5; CI: -0.2 to 15.1; p = 0.055).
Conclusion: VT ablation in patients with CS shows acceptable acute success rates. Patients presenting with VT storm have a high rate of arrhythmia acute suppression. A lower number of inducible VTs is associated with higher acute success rates. Despite these results, the prognosis remains poor, with a significant proportion of patients experiencing disease recurrence, death, or requiring heart transplantation.
Methods: A systematic literature review was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines, searching PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and Scopus databases up to May 2024. A random-effects model was used to evaluate electrophysiologic and procedural variables and compare outcomes to identify potential predictors of success.
Results: After excluding duplicates, 473 titles and abstracts were screened. Twenty-five studies were fully reviewed, and 9 studies comprising data from 311 CS patients who underwent VT ablation were included. The mean age of patients was 50.5 years, with 30% being female. Epicardial mapping was performed in 29% (CI 22-36%; 72/251) of cases, and 96% (CI 77-100%; 65/72) of those underwent epicardial ablation. The prevalence of VT storm before the procedure was 28% (CI 16-42%; 89/259), with a suppression success rate of 84% (CI 73-93%; 64/76). The acute complete success rate defined as lack of inducibility was 58% (CI 49-66%; 174/307). During follow-up, which ranged from 19 to 58 months, 34% (CI 21-48%; 113/271) of patients survived free from the composite outcome of death, transplantation, or VT recurrence. Patients with acute success had fewer inducible VTs (MD –1.1; CI: -1.8 to -0.5; p < 0.001). No other variables were significantly associated with acute success. However, patients with acute success tended to be older than those with partial or unsuccessful outcomes (MD 7.5; CI: -0.2 to 15.1; p = 0.055).
Conclusion: VT ablation in patients with CS shows acceptable acute success rates. Patients presenting with VT storm have a high rate of arrhythmia acute suppression. A lower number of inducible VTs is associated with higher acute success rates. Despite these results, the prognosis remains poor, with a significant proportion of patients experiencing disease recurrence, death, or requiring heart transplantation.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Comparison of Characteristics and Outcomes in Patients with and without Adult Congenital Heart Disease Undergoing Catheter Ablation for Ventricular Tachycardia
Futela Pragyat, Poddar Aastha, Kowlgi Gurukripa
Ablation versus Anti-arrhythmic Drug Therapy for Ventricular Tachycardia in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled TrialsKhan Ubaid, Chaudhry Kashif, Amin Ahmed Mazen, A. Ibrahim Ahmed, Imran Muhammad, Rakab Mohamed, Iltaf Arej, M. Albarakat Majd, Ranabhat Chet, Brilliant Justin