Final ID: MDP916
Medical Therapy and Outcomes in Patients with Critical Limb Threatening Ischemia Randomized to an Everolimus Eluting Resorbable Scaffold or Angioplasty in the LIFE-BTK Randomized Trial
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Patients with critical limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI) are at high risk of CV and limb outcomes yet established medical therapies are underutilized. The LIFE-BTK trial demonstrated that a drug-eluting resorbable scaffold (DRS) was superior to angioplasty (ANG) for limb outcomes. The background use of optimal medical therapy (OMT) and the effect of DRS vs. ANG based on OMT at baseline has not been described.
Methods: Patients were randomized 2:1 to DRS vs. ANG, respectively. Sites reported baseline medications. OMT was defined as use of at least one antithrombotic and LDL-C lowering agent. The primary outcome was a composite of amputation above the ankle of the target limb, occlusion of the target vessel, clinically driven revascularization of the target lesion, and binary restenosis of the target lesion. A key secondary outcome was major amputation, target vessel re-occlusion, or clinically driven target lesion revascularization. Data are presented as event rates and relative risk (RR).
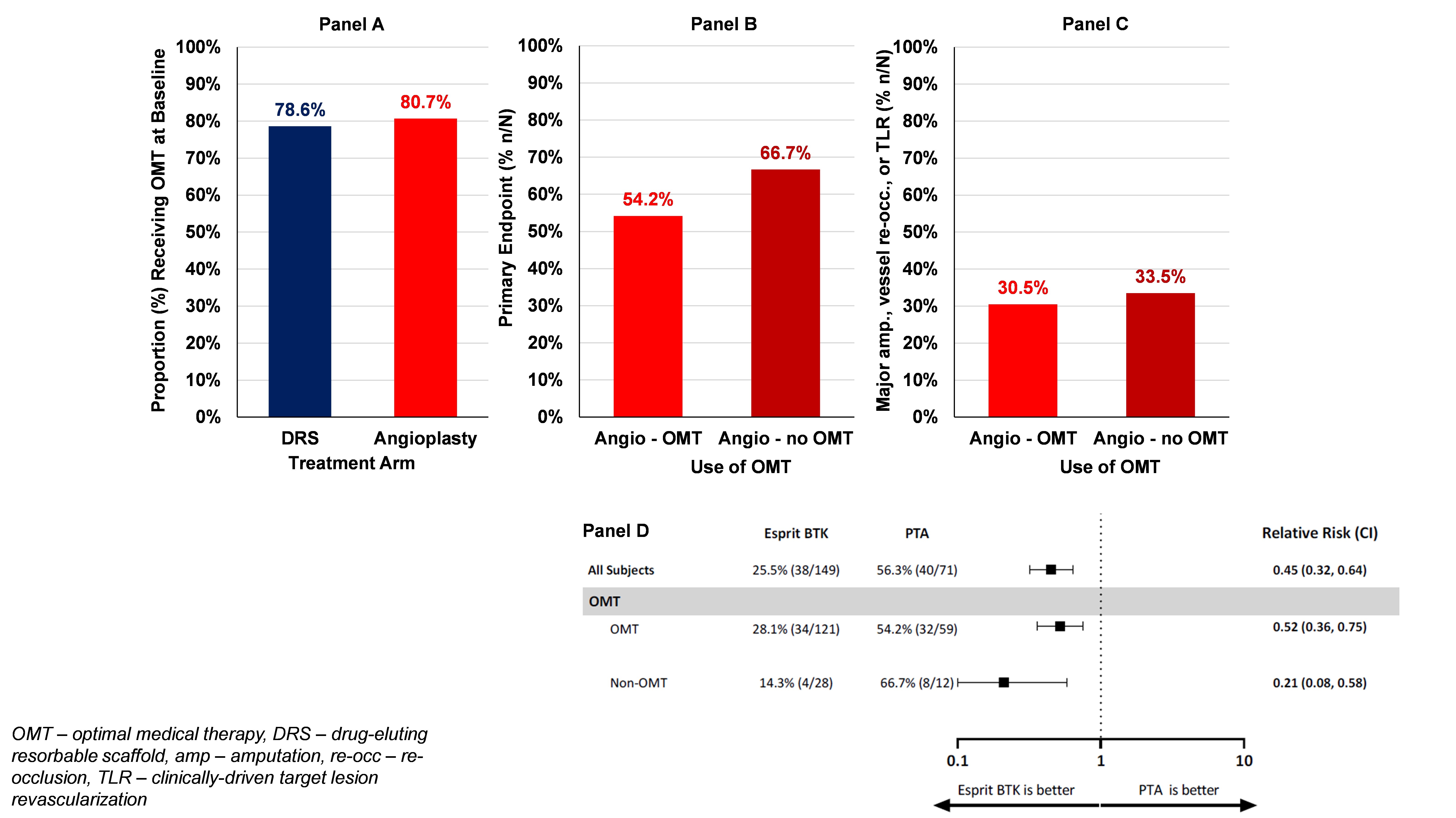
Results: A total of 261 patients were randomized with follow up through 1 year. DRS was superior to ANG for the primary outcome (p<0.001). Approximately 80% of patients received OMT at baseline with use similar between groups (Panel A). Increased adherence was associated with a history of hyperlipidemia and a history of coronary artery disease (CAD). In the ANG arm, use of OMT was associated with lower risk of the primary efficacy outcome (Panel B) and key secondary efficacy outcome (Panel C). Use of DRS was superior to ANG overall with consistent effects in those receiving OMT (RR 0.52, 95% CI 0.36 – 0.75) and those not receiving OMT (RR 0.21, 95% CI 0.08 – 0.58; Panel D).
Conclusions: In a contemporary cohort of patients enrolled in a trial of endovascular therapy for CLTI, the use of OMT was ~80%. Use of OMT was higher in those with risk factors and known CAD. The risk of adverse limb outcomes in the ANG group were lower with OMT than without OMT. The benefit of DRS vs. ANG was consistent regardless of OMT. Efforts to improve use of OMT in PAD are needed and a combined “pharmaco-invasive” approach to CLTI using optimal devices and OMT may improve outcomes.
Methods: Patients were randomized 2:1 to DRS vs. ANG, respectively. Sites reported baseline medications. OMT was defined as use of at least one antithrombotic and LDL-C lowering agent. The primary outcome was a composite of amputation above the ankle of the target limb, occlusion of the target vessel, clinically driven revascularization of the target lesion, and binary restenosis of the target lesion. A key secondary outcome was major amputation, target vessel re-occlusion, or clinically driven target lesion revascularization. Data are presented as event rates and relative risk (RR).
Results: A total of 261 patients were randomized with follow up through 1 year. DRS was superior to ANG for the primary outcome (p<0.001). Approximately 80% of patients received OMT at baseline with use similar between groups (Panel A). Increased adherence was associated with a history of hyperlipidemia and a history of coronary artery disease (CAD). In the ANG arm, use of OMT was associated with lower risk of the primary efficacy outcome (Panel B) and key secondary efficacy outcome (Panel C). Use of DRS was superior to ANG overall with consistent effects in those receiving OMT (RR 0.52, 95% CI 0.36 – 0.75) and those not receiving OMT (RR 0.21, 95% CI 0.08 – 0.58; Panel D).
Conclusions: In a contemporary cohort of patients enrolled in a trial of endovascular therapy for CLTI, the use of OMT was ~80%. Use of OMT was higher in those with risk factors and known CAD. The risk of adverse limb outcomes in the ANG group were lower with OMT than without OMT. The benefit of DRS vs. ANG was consistent regardless of OMT. Efforts to improve use of OMT in PAD are needed and a combined “pharmaco-invasive” approach to CLTI using optimal devices and OMT may improve outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acute loss of PGC1α in adult cardiomyocytes reduces ischemia-reperfusion injury
He Lihao, Young Martin E, Rowe Glenn, Prabhu Sumanth, Sethu Palaniappan, Xie Min, Chen Yunxi, Chu Yuxin, Hua Yutao, Cai Junyan, He Jin, Benavides Gloria, Darley-usmar Victor, Ballinger Scott
Anomalous Origins: Hereditary Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis Mimicking Ischemia in a Patient with Congenital Coronary AnomaliesLabin Jonathan, Carmona Rubio Andres, Liu Joseph, Hanna Mazen, Menon Venu, Higgins Andrew