Final ID: Su1142
Risk Factors of Cumulative Limb Amputation in Patients with Thromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger's Disease): Insights from Nationwide Inpatient Sample
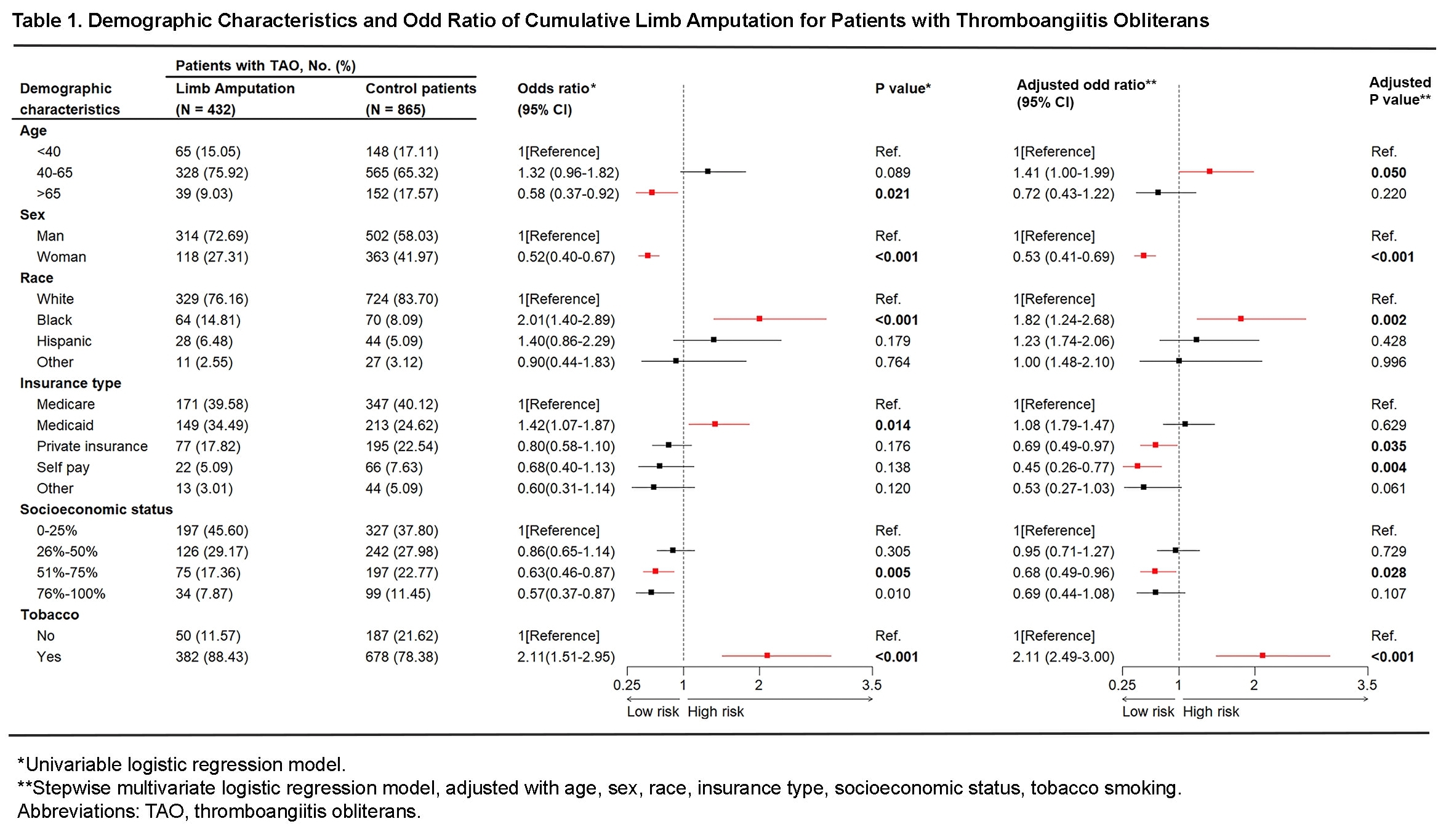
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Thromboangiitis obliterans (TAO) is a rare, nonatherosclerotic, inflammatory disease that typically onsets in male patients at young age with heavy smoking. TAO commonly affects small and medium-sized arteries in extremities, and up to 1/3 of patients with TAO will experience limb amputation. However, the role of social determinants of health (SDoH) are not well studied in TAO patients with limb amputation in a real-world dataset. Methods: A cross-sectional study was performed in Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) of United States, from calendar year 2016-2021. The diagnosis of diseases was identified by ICD-10-CM codes. Univariable logistic regression analysis was performed to identify characteristics associated with cumulative limb amputation (CLA). Stepwise multivariate logistic regression model was further employed to analyze association between significant characteristics and CLA. Results: In this study, 33.3% (N=432) patients with TAO (N=1297) had CLA. Variables showed significant association with CLA identified by univariable analysis were further included in stepwise multivariate logistic regression model. In the multivariate model, middle-age patients had higher risk of CLA than young patients (OR=1.41, 95% CI=1.00-1.99, p=0.050). Female showed lower CLA risk than male patients (OR=0.53, 95% CI=0.41-0.69, p<0.001). Black patients showed higher CLA risk than White (OR=1.82, 95% CI=1.24-2.68, p=0.002). Compared to Medicare insurance, self-pay (OR=0.51, 95% CI=0.30-0.87, p=0.014) and Private insurance (OR=0.69, 95% CI=0.49-0.97, p=0.035) patients had lower CLA risk. Higher socioeconomic status associated with lower CLA risk, and patients in the 3rd percentile had significantly lower CLA risk than those in the 1st percentile (OR=0.68, 95% CI=0.49-0.95, p=0.028). Patients with tobacco smoking showed higher CLA risk (OR=2.11, 95% CI=2.49-3.00, p<0.001). Conclusions: The CLA rate was up to 33.3% among the TAO patients in NIS 2016-2021. SDoH like age, sex, race, insurance type and socioeconomic status showed significant association with CLA risk in TAO patients. Further studies are warranted to explore mechanism, health equity and multidisciplinary care to decrease CLA for patients with TAO.
More abstracts on this topic:
Area-Based Social Risk Measures and In-Hospital Mortality: A Comparative Modeling Study in Coronary Artery Disease Patients
Gao Zihang, Jiang Tian, Hong Haoyun, Thomas Kathie, Hall Jennifer, Zhao Juan
A machine learning approach to examining the associations of minority stressors and physical activity among sexual and gender minority adultsLopez Veneros David, Ensari Ipek, Bhilegaonkar Riya, Sharma Yashika, Caceres Billy