Final ID: Mo2158
Impact of Ejection Fraction on Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation Following Admission for Heart Failure
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Though the prevalence of atrial fibrillation (AF) is similar amongst heart failure (HF) with reduced, mildly reduced, and preserved ejection fractions, population-level data suggests a modestly increased prevalence in patients with HFpEF compared to those HFrEF. The development of atrial fibrillation is associated with increased risk of stroke, hospitalization, and cardiovascular death in all types of heart failure, though some data suggests morbidity and mortality is worse amongst those with HFpEF. Whether ejection fraction plays a role in development of AF following a HF hospitalization is unclear.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized incidence of AF following heart failure hospitalization is increased in patients with preserved ejection fractions.
Aim: The goal of this study is to assess the impact of ejection fraction on development of new atrial fibrillation following heart failure exacerbation.
Methods: Patients admitted to an academic tertiary care hospital with a primary diagnosis of HF without a previous diagnosis of AF were identified and followed for up to one year for this retrospective study. Demographic, comorbidity, medications, and echocardiography of these patients were obtained from the medical record and analyzed. Consistent with the American Heart Association heart failure guidelines, we defined HFrEF as an EF less than 40%, HFmrEF as an EF between 40-50%, and HFpEF as an EF greater than 50%. This data was analyzed on SPSS using cox-regression and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis.
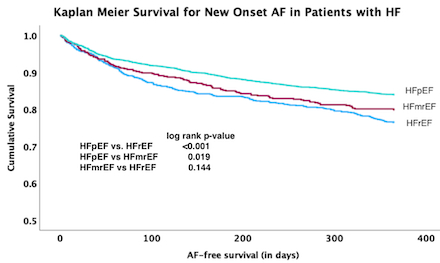
Results: Of the 3,953 patients included in our study, 22.2% had HFrEF, 13.5% had HFmrEF, and 64.3% had HFpEF. At the end of one year 23.5% of those with HFrEF, 20.1% of those with HFmrEF, and 15.9% of those with HFpEF, developed atrial fibrillation. The difference in AF incidence was noted to be statistically significantly lower in HFpEF compared to HFrEF (p<0.001) and HFmrEF (p=0.019). The difference between HFmrEF and HFrEF did not reach statistical significance (p=0.144).
Conclusion: In patients without atrial fibrillation, a reduced ejection fraction is associated with an increased incidence of atrial fibrillation one year following a hospitalization for heart failure compared to a preserved ejection fraction.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized incidence of AF following heart failure hospitalization is increased in patients with preserved ejection fractions.
Aim: The goal of this study is to assess the impact of ejection fraction on development of new atrial fibrillation following heart failure exacerbation.
Methods: Patients admitted to an academic tertiary care hospital with a primary diagnosis of HF without a previous diagnosis of AF were identified and followed for up to one year for this retrospective study. Demographic, comorbidity, medications, and echocardiography of these patients were obtained from the medical record and analyzed. Consistent with the American Heart Association heart failure guidelines, we defined HFrEF as an EF less than 40%, HFmrEF as an EF between 40-50%, and HFpEF as an EF greater than 50%. This data was analyzed on SPSS using cox-regression and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis.
Results: Of the 3,953 patients included in our study, 22.2% had HFrEF, 13.5% had HFmrEF, and 64.3% had HFpEF. At the end of one year 23.5% of those with HFrEF, 20.1% of those with HFmrEF, and 15.9% of those with HFpEF, developed atrial fibrillation. The difference in AF incidence was noted to be statistically significantly lower in HFpEF compared to HFrEF (p<0.001) and HFmrEF (p=0.019). The difference between HFmrEF and HFrEF did not reach statistical significance (p=0.144).
Conclusion: In patients without atrial fibrillation, a reduced ejection fraction is associated with an increased incidence of atrial fibrillation one year following a hospitalization for heart failure compared to a preserved ejection fraction.
More abstracts on this topic:
5-oxoproline/ OPLAH Axis Alleviates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiomyopathy By Inhibiting Ferroptosis
Jiang Meng, Guo Xinning
A machine learning model for individualized risk prediction of ischemic heart disease in people with hypertension in ThailandSakboonyarat Boonsub, Poovieng Jaturon, Rangsin Ram