Final ID: MDP1717
Impact of SGLT-2 Inhibitor Use on Atrial Fibrillation Incidence Following Heart Failure Hospitalization
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: The development of atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients with heart failure (HF) is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors have demonstrated cardiovascular benefit in patients with both preserved and reduced ejection fractions. Meta analysis of prospective trials suggest reduced incidence and burden of atrial fibrillation in patients taking SGLT-2 inhibitors, though this has not been specifically addressed in prospective trials.
Hypothesis: SGLT-2 inhibitors reduce the incidence of atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure.
Aim: The goal of the study is to assess the impact of SGLT-2 inhibitor on the incidence of atrial fibrillation following heart failure hospitalization.
Methods: The study included consecutive patients who were admitted to an academic tertiary care center over a 3 year time period with a primary diagnosis of heart failure exacerbation and no prior diagnosis of AF. The primary outcome was development of AF within 12 months after hospitalization. Demographic, comorbidity, echocardiographic data, and medications were obtained. Cox-regression analysis was performed to identify the predictors of new-onset AF after HF hospitalization.
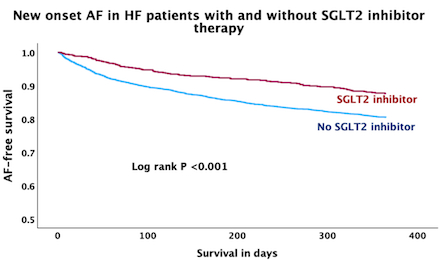
Results: Among the 3,953 patients included in our study, 704 (17.8%) patients were prescribed SGLT-2 inhibitors. Of those taking SGLT-2 inhibitors, 559 (79.4%) patients had diabetes. SGLT-2 inhibitor use is associated with significant reduction of AF at one year (p<0.001; RR 0.65; 95% CI: 0.51-.81). This finding was consistent across patients with reduced ejection fractions (EF<50%) (p=0.001; RR 0.56; 95% CI: 0.40-.80) and preserved ejection fraction (EF>50%)(p=0.001; RR 0.58; 95% CI: 0.42-0.80).
Conclusion: In patients with reduced ejection fraction and preserved ejection fraction heart failure, use of an SGLT-2 inhibitor is associated with a statistically significant lower risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation at one year following HF hospitalization.
Hypothesis: SGLT-2 inhibitors reduce the incidence of atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure.
Aim: The goal of the study is to assess the impact of SGLT-2 inhibitor on the incidence of atrial fibrillation following heart failure hospitalization.
Methods: The study included consecutive patients who were admitted to an academic tertiary care center over a 3 year time period with a primary diagnosis of heart failure exacerbation and no prior diagnosis of AF. The primary outcome was development of AF within 12 months after hospitalization. Demographic, comorbidity, echocardiographic data, and medications were obtained. Cox-regression analysis was performed to identify the predictors of new-onset AF after HF hospitalization.
Results: Among the 3,953 patients included in our study, 704 (17.8%) patients were prescribed SGLT-2 inhibitors. Of those taking SGLT-2 inhibitors, 559 (79.4%) patients had diabetes. SGLT-2 inhibitor use is associated with significant reduction of AF at one year (p<0.001; RR 0.65; 95% CI: 0.51-.81). This finding was consistent across patients with reduced ejection fractions (EF<50%) (p=0.001; RR 0.56; 95% CI: 0.40-.80) and preserved ejection fraction (EF>50%)(p=0.001; RR 0.58; 95% CI: 0.42-0.80).
Conclusion: In patients with reduced ejection fraction and preserved ejection fraction heart failure, use of an SGLT-2 inhibitor is associated with a statistically significant lower risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation at one year following HF hospitalization.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Fat Chance: Paradoxical Embolic Stroke from Lipomatous Hypertrophy of the Interatrial Septum
Kalathoor Abraham
A novel deep learning framework identified associated genes and Interpretable deep learning translation of GWAS findings for drug repurposing in Atrial FibrillationTonegawa-kuji Reina, Xu Jielin, Guntupalli Suman, Barnard John, Chung Mina, Cheng Feixiong