Final ID: Mo4062
Prevalence, Complications, and Outcomes of Cardiogenic Shock in Breast Cancer Patients; A Population Based Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiovascular disease and cancer are the leading causes of mortality in developed countries. Recent evidence suggests that these conditions share common underlying factors, such as inflammation and oxidative stress. However, there is a lack of data on the association between cardiogenic shock and cancer.
Purpose: Our study aimed to investigate the prevalence and outcomes of cardiogenic shock in patients with a history of breast cancer.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of data from the National Inpatient Sample Database (2018-2020) to identify patients with a primary diagnosis of breast cancer. We employed the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) diagnostic criteria. Our analysis focused on the impact of cardiogenic shock on mortality, morbidity, and resource utilization. We used chi-square tests for categorical variables and t-tests for continuous variables.
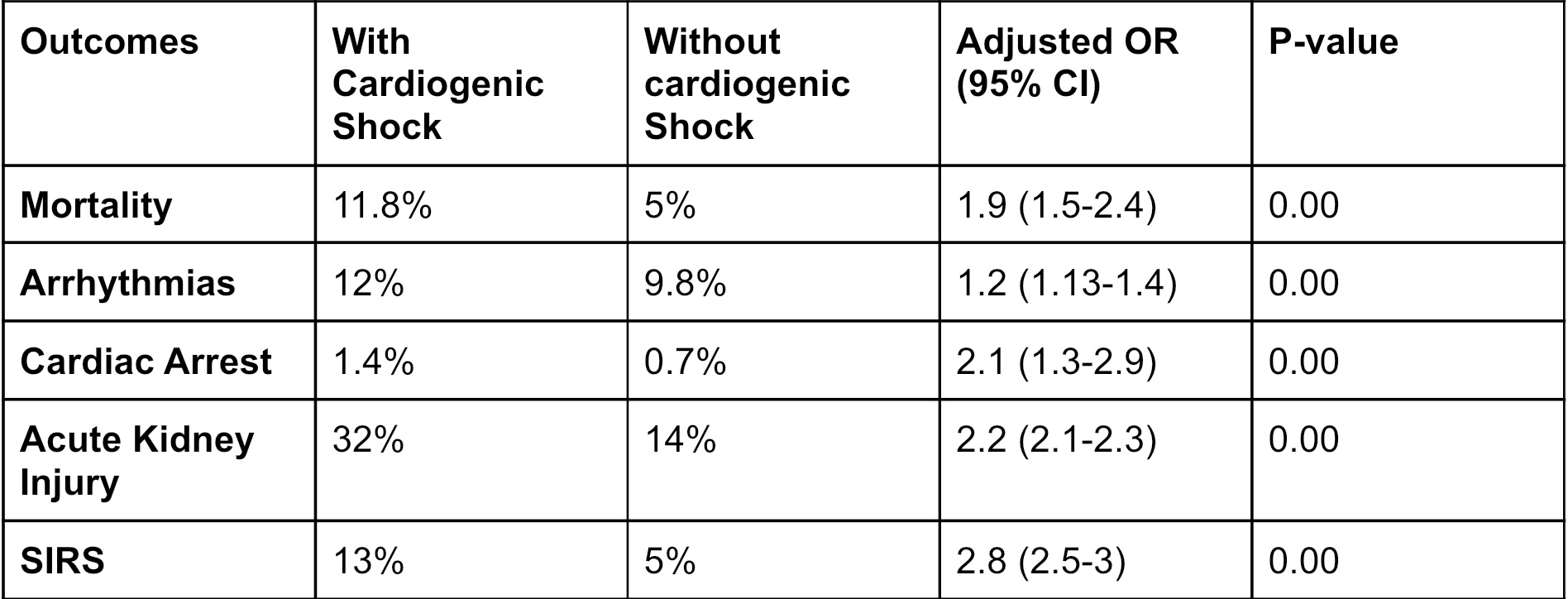
Results: Our analysis identified 516,125 breast cancer patients admitted between 2018 and 2020, with 11.3% experiencing cardiogenic shock. The mean age of these patients was 64 years, with 1.2% males and 98.8% females. The mortality rate among patients with cardiogenic shock was 11.8%, which was significantly higher than the 4.1% mortality rate in those without cardiogenic shock (OR 1.9, CI 1.5-2.4, p-value <0.05). Patients with cardiogenic shock were more likely to experience arrhythmias (OR 1.2, CI 1.13-1.4, p-value <0.05) cardiac arrest (OR 2.1, CI 1.3-2.9, p-value <0.05), acute kidney injury (OR 2.2, CI 2.1-2.3, p-value <0.05), and systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) (OR 2.8, CI 2.5-3, p-value < 0.05). These complications were associated with increased hospitalization costs, with patients with cardiogenic shock incurring $77,185 in costs compared to $64,300 for those without cardiogenic shock (p-value 0.00).
Conclusion: Our study highlights the significant prevalence of cardiogenic shock in patients with breast cancer (11.3%) and its association with increased mortality rates. These findings highlights the importance of immediate management of cardiogenic shock to prevent adverse outcomes and emphasize the need for close monitoring and early intervention to minimize the risk of related complications. Multidisciplinary cooperation between cardiologists, intensivists, and oncologists is crucial during these critical situations.
Purpose: Our study aimed to investigate the prevalence and outcomes of cardiogenic shock in patients with a history of breast cancer.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of data from the National Inpatient Sample Database (2018-2020) to identify patients with a primary diagnosis of breast cancer. We employed the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) diagnostic criteria. Our analysis focused on the impact of cardiogenic shock on mortality, morbidity, and resource utilization. We used chi-square tests for categorical variables and t-tests for continuous variables.
Results: Our analysis identified 516,125 breast cancer patients admitted between 2018 and 2020, with 11.3% experiencing cardiogenic shock. The mean age of these patients was 64 years, with 1.2% males and 98.8% females. The mortality rate among patients with cardiogenic shock was 11.8%, which was significantly higher than the 4.1% mortality rate in those without cardiogenic shock (OR 1.9, CI 1.5-2.4, p-value <0.05). Patients with cardiogenic shock were more likely to experience arrhythmias (OR 1.2, CI 1.13-1.4, p-value <0.05) cardiac arrest (OR 2.1, CI 1.3-2.9, p-value <0.05), acute kidney injury (OR 2.2, CI 2.1-2.3, p-value <0.05), and systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) (OR 2.8, CI 2.5-3, p-value < 0.05). These complications were associated with increased hospitalization costs, with patients with cardiogenic shock incurring $77,185 in costs compared to $64,300 for those without cardiogenic shock (p-value 0.00).
Conclusion: Our study highlights the significant prevalence of cardiogenic shock in patients with breast cancer (11.3%) and its association with increased mortality rates. These findings highlights the importance of immediate management of cardiogenic shock to prevent adverse outcomes and emphasize the need for close monitoring and early intervention to minimize the risk of related complications. Multidisciplinary cooperation between cardiologists, intensivists, and oncologists is crucial during these critical situations.
More abstracts on this topic:
6-Nitrodopamine potentiates the positive chronotopic and inotropic effect induced by noradrenaline in the rat isolated heart
Lima Antonio, Sobanski Joao Fernando, Antunes Edson, De Nucci Gilberto
A Stepwise Approach to Identifying and Assessing the Content Validity of Patient-Reported Outcome (PRO) Measures for Use with Adults with Acute Heart FailureO'connor Meaghan, Loughlin Anita, Waldman Laura, Rucker Sloan, Vaghela Shailja, Kwon Namhee, Sikirica Vanja