Final ID: 4138278
A Titin Missense Variant Causes Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Rare loss-of-function variants in TTN, the gene encoding the sarcomeric protein titin, have been causally associated with atrial fibrillation (AF). Missense TTN variants (TTNmv) are generally regarded as benign in relation to dilated cardiomyopathy, but their role in AF is unknown.
Hypothesis: TTNmv are associated with clinical outcomes and AF pathogenesis.
Aims: We aimed to determine if TTNmv are associated with AF/heart failure (HF) hospitalizations and investigate if a rare missense variant (TTN-T32756I) caused AF using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived atrial cardiomyocytes (iPSC-aCMs).
Methods: Whole exome sequencing was performed in 131 adults at an urban academic healthcare system who identified as non-Hispanic Black (NHB) or Hispanic/Latinx (HL). Multivariable Cox proportional hazard models were used to assess cumulative risk of AF/HF hospitalization. Isogenic TTN-T32756I iPSC-aCM mutants were generated using the CRISPR-Cas9 technique. We used confocal microscopy to assess sarcomeric integrity, MuscleMotion to assess contractility, and optical voltage mapping and patch-clamping to assess the electrophysiological (EP) properties.
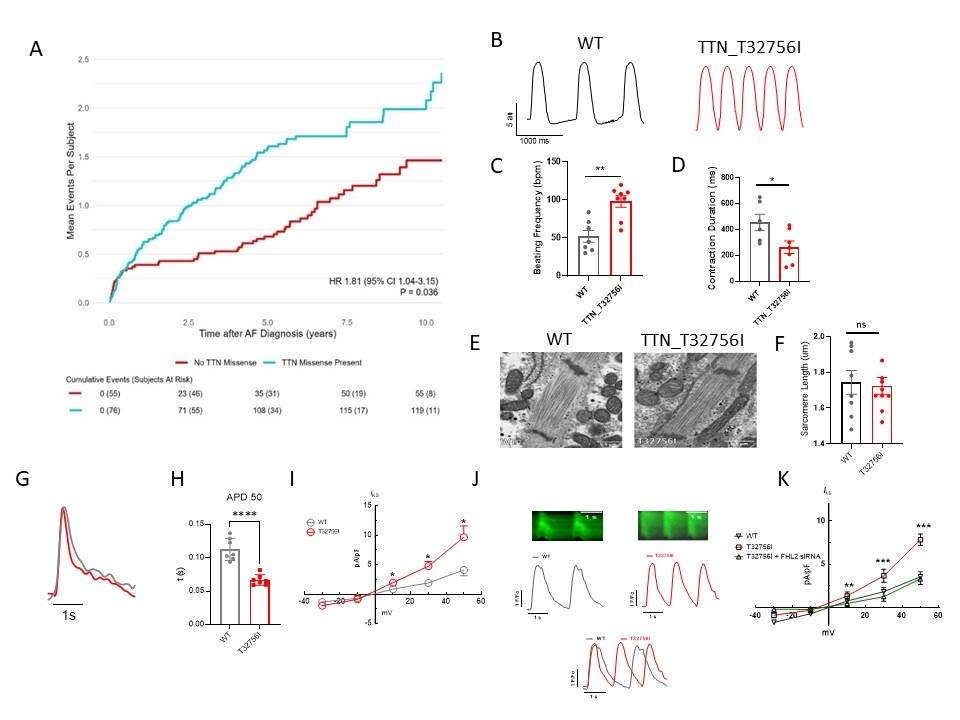
Results: We identified 137 TTNmvs in 76/131 (58.0%) of subjects, which were most commonly in the TTN A-band. 64 AF-related and 110 HF-related hospitalizations occurred after a median follow-up time of 4.16 years. Hospitalization risk was higher in TTNmv carriers (HR 1.81, Fig. 1A). We also identified three patients with early-onset AF who shared a rare missense variant T32756I. TTN-T32756I-iPSC-aCMs displayed aberrant contractility (Fig. 1B-D), shortened action potential duration (Fig. 1G-H), increased activity of cardiac K+ channel (Fig. 1I), and dysregulated Ca2+ homeostasis (Fig. 1J) without compromising sarcomeric integrity (Fig. 1E-F). The titin-binding protein, Four-and-a-Half Lim domains 2 (FHL2), also has increased binding with KCNQ1 and its modulatory subunit KNCE1 in TTN-T32756I-iPSC-aCMs, which may enhance the slow delayed rectifier K+ current (Iks). Suppression of FHL2 normalized Iks, supporting FHL2 as a mediator of the increased Iks (Fig. 1K).
Conclusion: In a single-center multi-ethnic AF cohort, TTNmv were associated with increased AF/HF hospitalization, and the T32756I-TTNmv causes ion channel remodeling and an AF-like EP phenotype. These findings establish a mechanistic link between TTNmv, K+ ion channels, and sarcomeric regulatory proteins that may represent a novel therapeutic target.
Hypothesis: TTNmv are associated with clinical outcomes and AF pathogenesis.
Aims: We aimed to determine if TTNmv are associated with AF/heart failure (HF) hospitalizations and investigate if a rare missense variant (TTN-T32756I) caused AF using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived atrial cardiomyocytes (iPSC-aCMs).
Methods: Whole exome sequencing was performed in 131 adults at an urban academic healthcare system who identified as non-Hispanic Black (NHB) or Hispanic/Latinx (HL). Multivariable Cox proportional hazard models were used to assess cumulative risk of AF/HF hospitalization. Isogenic TTN-T32756I iPSC-aCM mutants were generated using the CRISPR-Cas9 technique. We used confocal microscopy to assess sarcomeric integrity, MuscleMotion to assess contractility, and optical voltage mapping and patch-clamping to assess the electrophysiological (EP) properties.
Results: We identified 137 TTNmvs in 76/131 (58.0%) of subjects, which were most commonly in the TTN A-band. 64 AF-related and 110 HF-related hospitalizations occurred after a median follow-up time of 4.16 years. Hospitalization risk was higher in TTNmv carriers (HR 1.81, Fig. 1A). We also identified three patients with early-onset AF who shared a rare missense variant T32756I. TTN-T32756I-iPSC-aCMs displayed aberrant contractility (Fig. 1B-D), shortened action potential duration (Fig. 1G-H), increased activity of cardiac K+ channel (Fig. 1I), and dysregulated Ca2+ homeostasis (Fig. 1J) without compromising sarcomeric integrity (Fig. 1E-F). The titin-binding protein, Four-and-a-Half Lim domains 2 (FHL2), also has increased binding with KCNQ1 and its modulatory subunit KNCE1 in TTN-T32756I-iPSC-aCMs, which may enhance the slow delayed rectifier K+ current (Iks). Suppression of FHL2 normalized Iks, supporting FHL2 as a mediator of the increased Iks (Fig. 1K).
Conclusion: In a single-center multi-ethnic AF cohort, TTNmv were associated with increased AF/HF hospitalization, and the T32756I-TTNmv causes ion channel remodeling and an AF-like EP phenotype. These findings establish a mechanistic link between TTNmv, K+ ion channels, and sarcomeric regulatory proteins that may represent a novel therapeutic target.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Variant in GNB2 as a Cause of Sick Sinus Syndrome
Bulut Aybike, Karacan Mehmet, Saygili E. Alper, Pirli Dogukan, Aydin Eylul, Ozdemir Ozkan, Balci Nermin, Alanay Yasemin, Bilguvar Kaya, Akgun Dogan Ozlem
4D Cardiac Optogenetics Enable Complex Arrhythmia Modelling and Precise Interventional SimulationWexler Yehuda, Grinstein Harel, Landesberg Michal, Glatstein Shany, Huber Irit, Arbel Gil, Gepstein Lior