Final ID: MDP485
Impact of Pre-Existing Cardiovascular Diseases on Severe Maternal Morbidity and Mortality During Delivery in Pregnant Women with Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
While the incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) among pregnant women is increasing, the impact of pre-existing cardiovascular disease (CVD) on pregnant women with AF is not well-described in a large national database.
Objective
This study aimed to compare pregnancy outcomes between those with AF alone and those with AF and pre-existing CVD categorized by the modified World Health Organization classification (mWHO).
Methods
We used the Nationwide Readmissions Database and included all pregnant women with AF (2017-2020). We categorized the cohort into two groups depending on the presence of pre-existing CVD. We assessed the risk of severe maternal morbidity and mortality (SMM) outcomes, as defined by the CDC, between pregnant women with AF alone and those with AF and pre-existing CVD.
Results
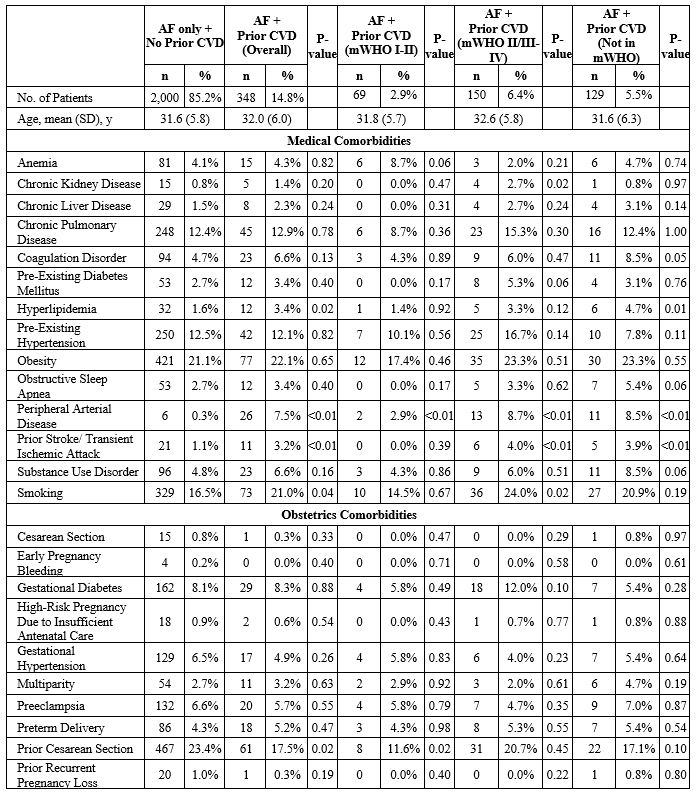
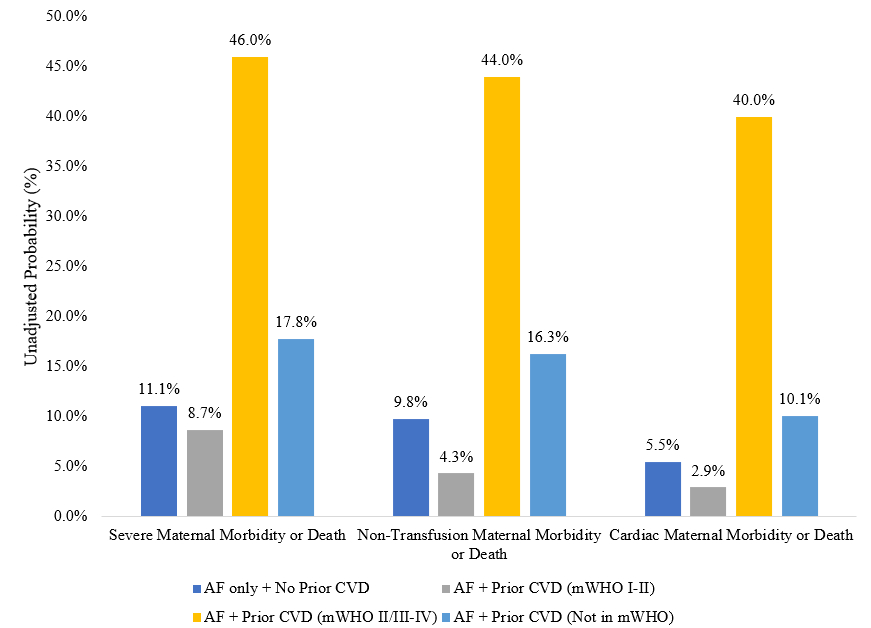
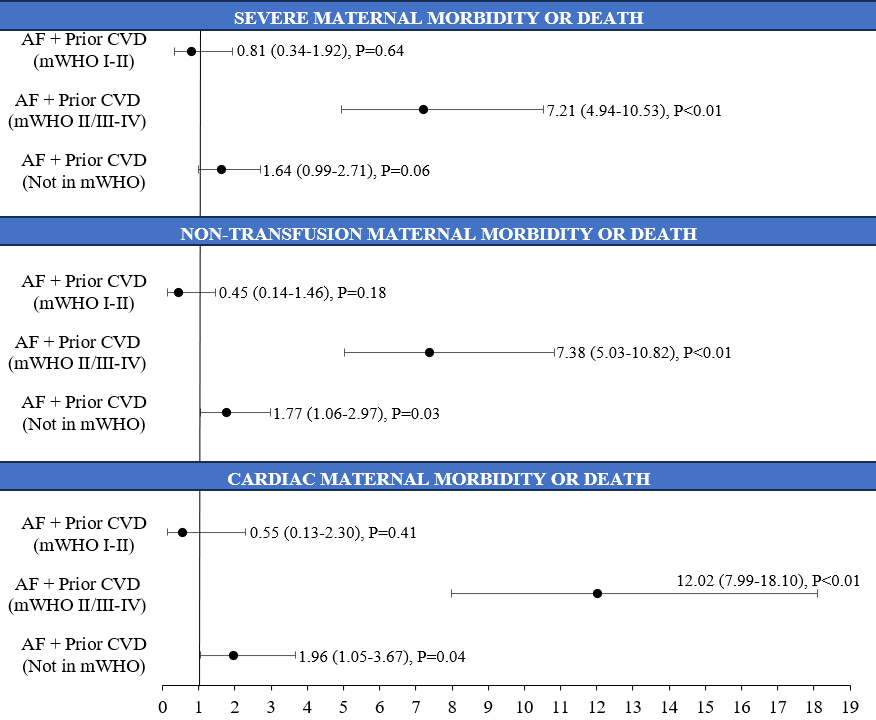
Out of the total 2,348 pregnant women with AF, 348 (14.8%) had pre-existing CVD. 69 (19.8%) had mWHO I- II CVD, 150 (43.1%) had mWHO II/III- IV CVD, and 129 (37.1%) had CVD not classified in mWHO. Overall, those with pre-existing CVD had higher rates of SMM/death (28.2% vs. 11.1%, P<0.01), non-transfusion SMM/death (25.9% vs. 9.8%, P<0.01), and cardiac SMM/death (21.6% vs. 5.5%, P<0.01) than those with AF alone. After adjustment, those with pre-existing mWHO I- II CVD and AF were not associated with higher odds of SMM/death (aOR: 0.81, 95% CI: 0.34-1.92, P=0.64), non-transfusion SMM/death (aOR: 0.45, 95% CI: 0.14-1.46, P=0.18), and cardiac SMM/death (aOR: 0.55, 95% CI: 0.13-2.30, P=0.41) than those with AF alone. Patients with pre-existing mWHO II/III- IV CVD and AF had higher odds of SMM/death (aOR: 7.21, 95% CI: 4.94-10.53, P<0.01), non-transfusion SMM/death (aOR: 7.38, 95% CI: 5.03-10.82, P<0.01), and cardiac SMM/death (aOR: 12.02, 95% CI: 7.99-18.10, P<0.01) than those with AF alone. Patients with pre-existing CVD not classified in mWHO and AF did not have higher odds of SMM/death (aOR: 1.64, 95% CI: 0.99-2.71, P=0.06) but had higher odds of non-transfusion SMM/death (aOR: 1.77, 95% CI: 1.06-2.97, P=0.03) and cardiac SMM/death (aOR: 1.96, 95% CI: 1.05-3.67, P=0.04).
Conclusion
Compared to pregnant women with AF alone, those with pre-existing mWHO II/III- IV CVD and AF were associated with worse SMM/death, non-transfusion SMM/death, and cardiac SMM/death. However, similar findings were not noted in those with pre-existing mWHO I- II CVD and AF pregnant women.
While the incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) among pregnant women is increasing, the impact of pre-existing cardiovascular disease (CVD) on pregnant women with AF is not well-described in a large national database.
Objective
This study aimed to compare pregnancy outcomes between those with AF alone and those with AF and pre-existing CVD categorized by the modified World Health Organization classification (mWHO).
Methods
We used the Nationwide Readmissions Database and included all pregnant women with AF (2017-2020). We categorized the cohort into two groups depending on the presence of pre-existing CVD. We assessed the risk of severe maternal morbidity and mortality (SMM) outcomes, as defined by the CDC, between pregnant women with AF alone and those with AF and pre-existing CVD.
Results
Out of the total 2,348 pregnant women with AF, 348 (14.8%) had pre-existing CVD. 69 (19.8%) had mWHO I- II CVD, 150 (43.1%) had mWHO II/III- IV CVD, and 129 (37.1%) had CVD not classified in mWHO. Overall, those with pre-existing CVD had higher rates of SMM/death (28.2% vs. 11.1%, P<0.01), non-transfusion SMM/death (25.9% vs. 9.8%, P<0.01), and cardiac SMM/death (21.6% vs. 5.5%, P<0.01) than those with AF alone. After adjustment, those with pre-existing mWHO I- II CVD and AF were not associated with higher odds of SMM/death (aOR: 0.81, 95% CI: 0.34-1.92, P=0.64), non-transfusion SMM/death (aOR: 0.45, 95% CI: 0.14-1.46, P=0.18), and cardiac SMM/death (aOR: 0.55, 95% CI: 0.13-2.30, P=0.41) than those with AF alone. Patients with pre-existing mWHO II/III- IV CVD and AF had higher odds of SMM/death (aOR: 7.21, 95% CI: 4.94-10.53, P<0.01), non-transfusion SMM/death (aOR: 7.38, 95% CI: 5.03-10.82, P<0.01), and cardiac SMM/death (aOR: 12.02, 95% CI: 7.99-18.10, P<0.01) than those with AF alone. Patients with pre-existing CVD not classified in mWHO and AF did not have higher odds of SMM/death (aOR: 1.64, 95% CI: 0.99-2.71, P=0.06) but had higher odds of non-transfusion SMM/death (aOR: 1.77, 95% CI: 1.06-2.97, P=0.03) and cardiac SMM/death (aOR: 1.96, 95% CI: 1.05-3.67, P=0.04).
Conclusion
Compared to pregnant women with AF alone, those with pre-existing mWHO II/III- IV CVD and AF were associated with worse SMM/death, non-transfusion SMM/death, and cardiac SMM/death. However, similar findings were not noted in those with pre-existing mWHO I- II CVD and AF pregnant women.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Comparative Analysis of Esophageal Cooling for Preventing Esophageal Injury Post Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Ibrahim Momen Mohamed, Al Hennawi Hussam, Tanas Yousef, Abourady Youmna, Sewedan Nourhan, Hashem Ahmed Magdy, Motawea Karam R.
Advanced maternal age and association with major adverse cardiovascular events from NHANES from 1999 to 2018Mehta Adhya, Honigberg Michael, Kennedy Jamie, Spitz Jared, Sharma Garima, Agboola Olayinka, Satti Danish Iltaf, Harrington Colleen, Scott Nandita, Sarma Amy, Saad Antonio, Sullivan Scott, Epps Kelly