Final ID: MDP278
Development and Content Validation of the Heart Failure Symptom Management Motivation Questionnaire
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Adequate heart failure (HF) self-management is crucial for alleviating distressing symptoms. While disease knowledge is important, it is insufficient for sustained self-care. Patient motivation plays a key role in successful self-management interventions. However, tools assessing motivation for HF symptom self-management are lacking.
Aims: To develop the Heart Failure Symptom Management Motivation (HF-SMM) questionnaire and assess its content validity with nurse experts.
Methods: A cross-sectional study occurred in three phases from November 2022 to April 2024. Initially, we conducted a systematic review to identify motivation assessment instruments for cardiovascular self-care and assess their psychometric properties. We then designed the HF-SMM items based on existing tools, guidelines, and clinical expertise, focusing on four HF symptoms: anxiety, depression, edema, and fatigue. The questionnaire comprised three subscales: autonomous motivation, controlled motivation, and amotivation. Nurse experts with doctoral degrees and HF experience assessed 96 items about questionnaire clarity and relevance via Delphi rounds, using a 4-point Likert scale. Items with a content validity index (I-CVI) between .80 to 1.00 were deemed acceptable. The average I-CVI of all items resulted in the scale content validity index average (S-CVI/Ave) with a cutoff point of .90.
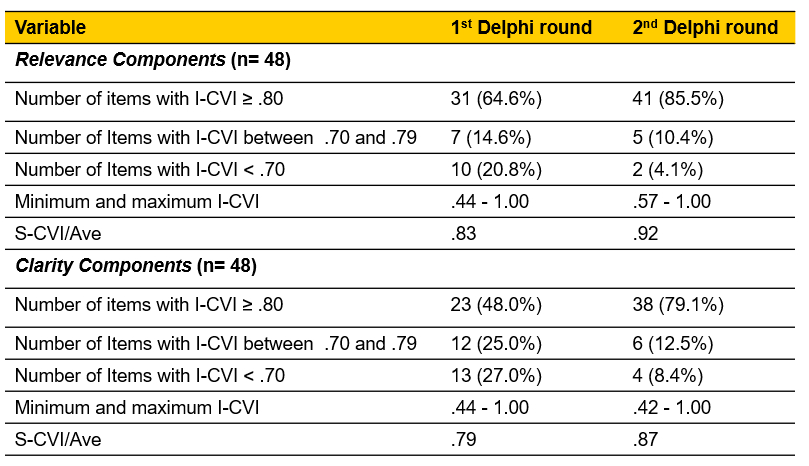
Results: We invited ten experts, with nine participating. They had an average of 17.1 ± 10.7 years of HF clinical experience and 11.6 ± 7.4 years of research experience. In the initial Delphi round, items scored I-CVI ranging from .44 to 1.00 for anxiety, depression, and fatigue, and .66 to 1.00 for edema, resulting in an S-CVI/Ave of .81. After the first round, 54 items with I-CVI >.80 were retained (56.2%), and 42 items were revised (43.8%). A second Delphi round, with 77.7% of the original experts, showed most items with excellent I-CVI scores (> .80; 84; 87.5%), with only ten items needing clarity revisions (10.4%). The overall CVI of the questionnaire was excellent with a S-CVI/ Ave of .90 after two rounds of validation.
Conclusions: The HF-SMM questionnaire demonstrates excellent content validity for assessing motivation in HF self-management. Future studies should incorporate cognitive interviews to understand better patient perceptions about the items.
Aims: To develop the Heart Failure Symptom Management Motivation (HF-SMM) questionnaire and assess its content validity with nurse experts.
Methods: A cross-sectional study occurred in three phases from November 2022 to April 2024. Initially, we conducted a systematic review to identify motivation assessment instruments for cardiovascular self-care and assess their psychometric properties. We then designed the HF-SMM items based on existing tools, guidelines, and clinical expertise, focusing on four HF symptoms: anxiety, depression, edema, and fatigue. The questionnaire comprised three subscales: autonomous motivation, controlled motivation, and amotivation. Nurse experts with doctoral degrees and HF experience assessed 96 items about questionnaire clarity and relevance via Delphi rounds, using a 4-point Likert scale. Items with a content validity index (I-CVI) between .80 to 1.00 were deemed acceptable. The average I-CVI of all items resulted in the scale content validity index average (S-CVI/Ave) with a cutoff point of .90.
Results: We invited ten experts, with nine participating. They had an average of 17.1 ± 10.7 years of HF clinical experience and 11.6 ± 7.4 years of research experience. In the initial Delphi round, items scored I-CVI ranging from .44 to 1.00 for anxiety, depression, and fatigue, and .66 to 1.00 for edema, resulting in an S-CVI/Ave of .81. After the first round, 54 items with I-CVI >.80 were retained (56.2%), and 42 items were revised (43.8%). A second Delphi round, with 77.7% of the original experts, showed most items with excellent I-CVI scores (> .80; 84; 87.5%), with only ten items needing clarity revisions (10.4%). The overall CVI of the questionnaire was excellent with a S-CVI/ Ave of .90 after two rounds of validation.
Conclusions: The HF-SMM questionnaire demonstrates excellent content validity for assessing motivation in HF self-management. Future studies should incorporate cognitive interviews to understand better patient perceptions about the items.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Concomitant Wild-Type Transthyretin and Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis Involving Separate Organs
Chiu Leonard, Afrough Aimaz, Nadeem Urooba, Jebakumar Deborah, Grodin Justin
Cardiovascular Stroke Nursing Best Abstract Award: Digital Health-Based Interventions Improve Healthy Behaviors, Weight Loss, and Psychological Well-Being in Older Adults at Risk for Cardiovascular DiseasCandelaria Dion, Reyes Andrew Thomas, Serafica Reimund, Hildebrand Janett, Cacciata Marysol, Sta. Maria Axel, Lee Jung-ah, Stromberg Anna, Evangelista Lorraine