Final ID: Su3161
Development of a User-Friendly Self-Screening Tool for Assessing Metabolic Syndrome Risk in young adults from economically challenged regions
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease and diabetes. Early identification and management are crucial, particularly in economically challenged regions where access to healthcare may be limited.
Research Questions/Hypothesis: User-friendly self-report data accurately predict metabolic outcomes.
Aims: To develop and validate nomograms for individualized estimation of metabolic syndrome risk.
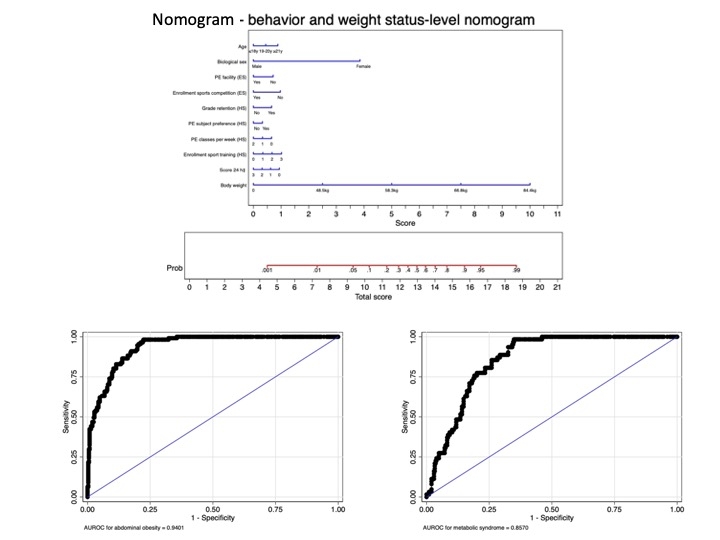
Methods: Data from 521 college students (60.1% aged 17-20 years; 68.7% female; 28.0% white) were collected in 2022/2023 from two Brazilian cities. These cities are located in the country's poorest states, with Gini indices of 0.56 and 0.43. The potential predictors include demographic and economic variables, school-related factors, behaviors, and body weight. Based on predictors for abdominal obesity identified through multilevel logistic regression, we created a nomogram model. We performed the Hosmer-Lemeshow test to assess model calibration and used a bootstrapping approach (B = 150) for internal validation. To evaluate external validity, we assessed metabolic syndrome in a subset of 375 students. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), with a threshold of 0.70, was used to evaluate the model's discrimination accuracy.
Results: We identified 114 (23.0%) college students who were abdominally obese. We found ten variables associated with the primary outcome: age, biological sex, physical education facilities, enrollment in sports competition (during elementary school); grade retention, preferred subject, physical education classes per week; enrollment in sports training (during secondary school); adherence of 24-hour movement behaviors and body weight. The proposed nomogram showed acceptable performance in the AUROC (0.94 [95% CI: 0.92-0.96). The calibration assessment indicated reasonable consistency of our model (p > 0.05). In the internal validation, we observed a decreased predictive capability (AUROC = 0.86).
Conclusion: The 24h-MESYN risk score offers an effective self-screening tool for college students from diverse racial and ethnic backgrounds in economically challenged regions to assess their risk of developing metabolic syndrome.
Research Questions/Hypothesis: User-friendly self-report data accurately predict metabolic outcomes.
Aims: To develop and validate nomograms for individualized estimation of metabolic syndrome risk.
Methods: Data from 521 college students (60.1% aged 17-20 years; 68.7% female; 28.0% white) were collected in 2022/2023 from two Brazilian cities. These cities are located in the country's poorest states, with Gini indices of 0.56 and 0.43. The potential predictors include demographic and economic variables, school-related factors, behaviors, and body weight. Based on predictors for abdominal obesity identified through multilevel logistic regression, we created a nomogram model. We performed the Hosmer-Lemeshow test to assess model calibration and used a bootstrapping approach (B = 150) for internal validation. To evaluate external validity, we assessed metabolic syndrome in a subset of 375 students. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), with a threshold of 0.70, was used to evaluate the model's discrimination accuracy.
Results: We identified 114 (23.0%) college students who were abdominally obese. We found ten variables associated with the primary outcome: age, biological sex, physical education facilities, enrollment in sports competition (during elementary school); grade retention, preferred subject, physical education classes per week; enrollment in sports training (during secondary school); adherence of 24-hour movement behaviors and body weight. The proposed nomogram showed acceptable performance in the AUROC (0.94 [95% CI: 0.92-0.96). The calibration assessment indicated reasonable consistency of our model (p > 0.05). In the internal validation, we observed a decreased predictive capability (AUROC = 0.86).
Conclusion: The 24h-MESYN risk score offers an effective self-screening tool for college students from diverse racial and ethnic backgrounds in economically challenged regions to assess their risk of developing metabolic syndrome.
More abstracts on this topic:
APOE Epsilon 4 Carriers Derive Greater Benefit from Genetically Reduced Factor XI Levels
Clocchiatti-tuozzo Santiago, Rivier Cyprien, Huo Shufan, Hawkes Maximiliano, Schwamm Lee, Ohno-machado Lucila, Sheth Kevin, Gill Thomas, Falcone Guido
Blood Pressure Measures are Not Associated with Early Metabolic Imbalance: The U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination SurveyMendiola Luis, Dwivedi Alok, Cistola David