Final ID: MDP927
Lentiviral shRNA Library Screen Using Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-derived Cardiomyocytes Identified Mediators of Protection via MAP4K4 Inhibition against Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): BACKGROUND
Doxorubicin (Dox) is a common component in chemotherapy for a wide range of tumors, but the cardiotoxicity has restricted its use. There is an unmet need for novel therapeutics of Dox-induced cardiotoxicity (DIC). We previously identified the protein kinase MAP4K4 as a mediator of DIC. Notably, we showed that blocking MAP4K4 activity via DMX-5804 protected against Dox-induced cell death and dysfunction in human iPSCs derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs). As a powerful tool to study the protective mechanism, pooled library screen performs high-throughput phenotypic examination, but its potential on hiPSC-CMs is poorly explored.
HYPOTHESIS
A pooled lentiviral shRNA library screen in hiPSC-CMs treated with Dox ± DMX-5804 could identify mediators of protection against DIC.
METHODS
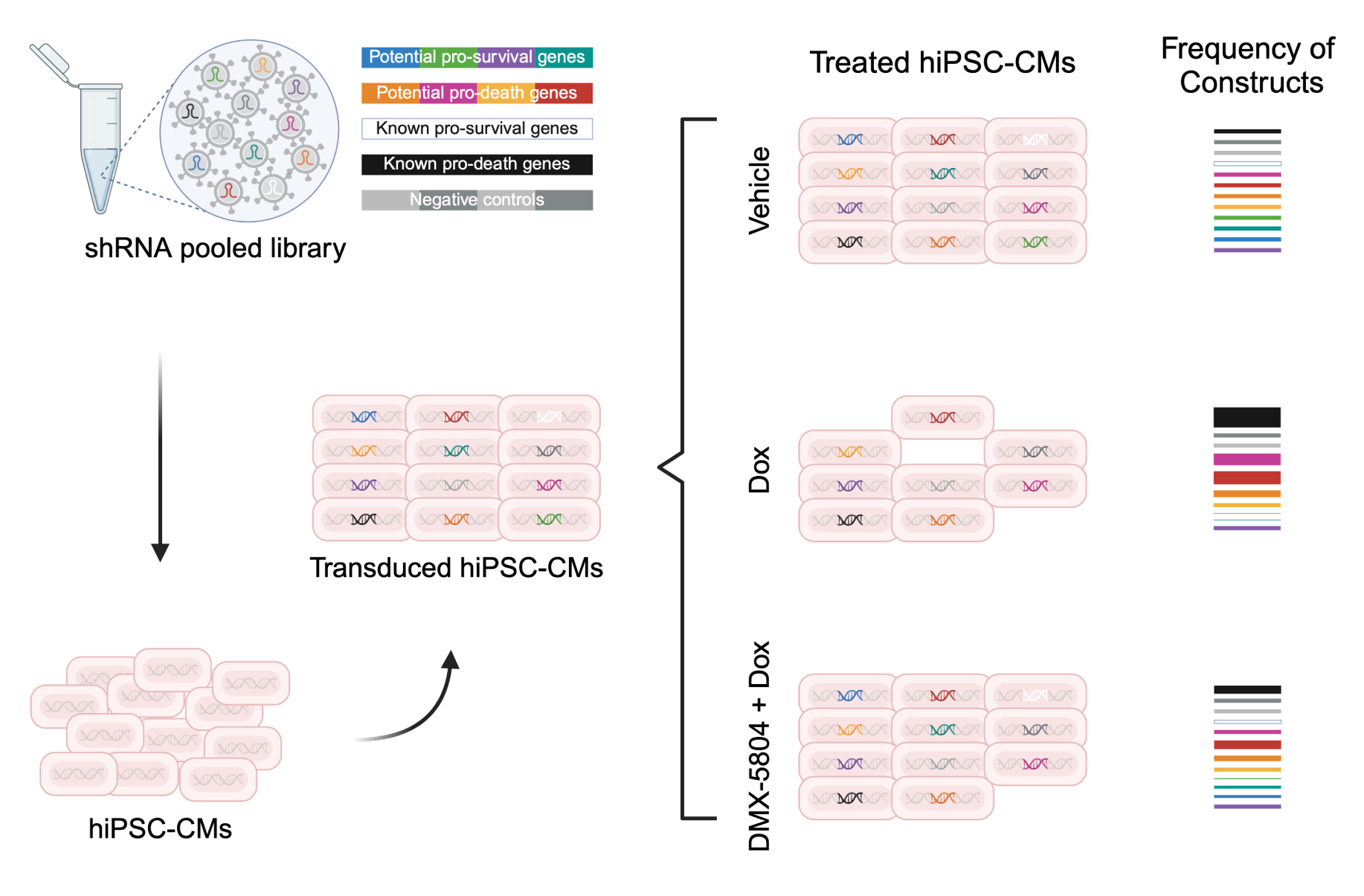
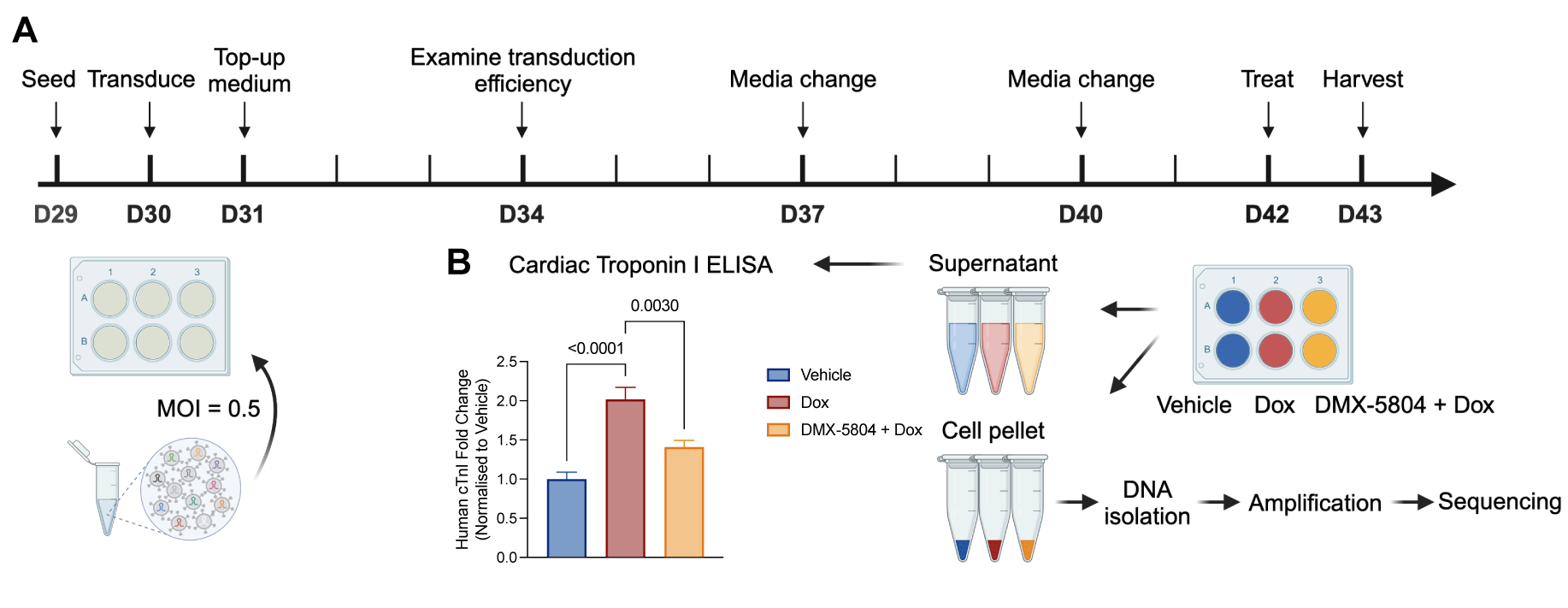
To maximize the chances to uncover key factors mediating DMX-5804 protection, we performed a high-throughput loss-of-function screen. A pooled library of 1731 lentiviral shRNAs was generated. hiPSC-CMs were transduced, then treated with Dox ± DMX-5804. Cardiac troponin I ELISA was used to examine myocyte injury. Genomic DNA was isolated, followed by amplification and sequencing of the integrated shRNAs. Log2 fold change was calculated and transformed into Z score to identify significantly shifted shRNAs.
RESULTS
To build the shRNA library we included 1) genes identified via transcriptomic analysis of hiPSC-CMs treated with Dox ± DMX-5804; 2) genes in the MAP4K4 signaling cascade; 3) previously defined pro-death or pro-survival genes in DIC. To ensure single gene silenced per cell, we used a low MOI of 0.5. After transduction, cells were treated with Dox ± DMX-5804. Confirming the cardiotoxicity and protection, Dox induced a 2-fold increase of cardiac troponin I release and DMX-5804 significantly reversed it.
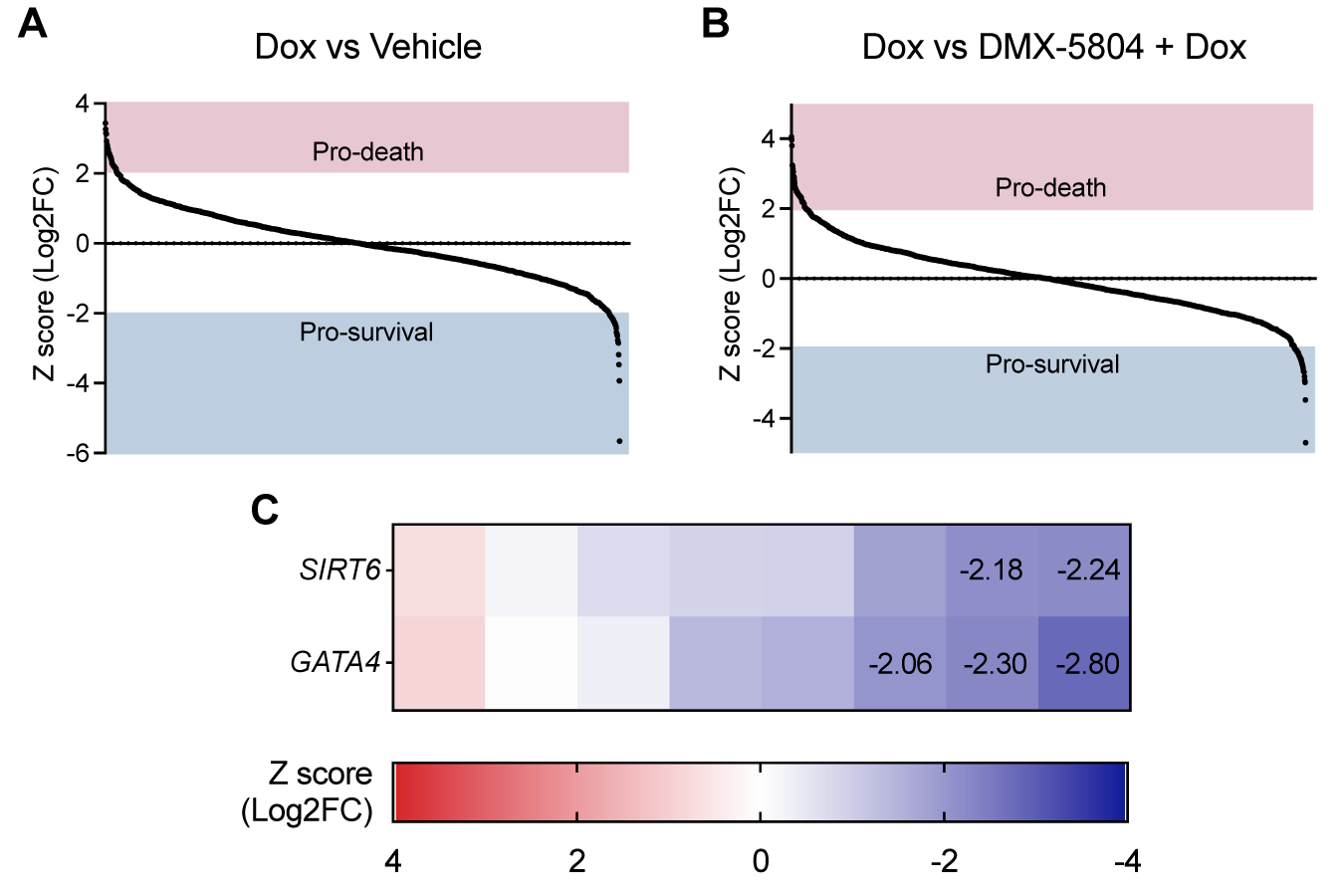
Next, we recovered and sequenced the integrated shRNAs, and quantified the frequency of each. We identified 146 significantly enriched or depleted shRNAs (|Z score| > 2). When comparing Dox treated group to vehicle or DMX-5804 protected group, shRNA enrichment indicates pro-death function of the targeted gene. Conversely, pro-survival genes can be inferred from shRNA depletion. Amongst the 5 most consistently targeted genes, we identified SIRT6 and GATA4 which are known pro-survival in DIC, suggesting the screen is potent to define key genes.
CONCLUSION
We performed a proof-of-concept pooled library screen in human cardiomyocytes and identified mediators of protection against DIC.
Doxorubicin (Dox) is a common component in chemotherapy for a wide range of tumors, but the cardiotoxicity has restricted its use. There is an unmet need for novel therapeutics of Dox-induced cardiotoxicity (DIC). We previously identified the protein kinase MAP4K4 as a mediator of DIC. Notably, we showed that blocking MAP4K4 activity via DMX-5804 protected against Dox-induced cell death and dysfunction in human iPSCs derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs). As a powerful tool to study the protective mechanism, pooled library screen performs high-throughput phenotypic examination, but its potential on hiPSC-CMs is poorly explored.
HYPOTHESIS
A pooled lentiviral shRNA library screen in hiPSC-CMs treated with Dox ± DMX-5804 could identify mediators of protection against DIC.
METHODS
To maximize the chances to uncover key factors mediating DMX-5804 protection, we performed a high-throughput loss-of-function screen. A pooled library of 1731 lentiviral shRNAs was generated. hiPSC-CMs were transduced, then treated with Dox ± DMX-5804. Cardiac troponin I ELISA was used to examine myocyte injury. Genomic DNA was isolated, followed by amplification and sequencing of the integrated shRNAs. Log2 fold change was calculated and transformed into Z score to identify significantly shifted shRNAs.
RESULTS
To build the shRNA library we included 1) genes identified via transcriptomic analysis of hiPSC-CMs treated with Dox ± DMX-5804; 2) genes in the MAP4K4 signaling cascade; 3) previously defined pro-death or pro-survival genes in DIC. To ensure single gene silenced per cell, we used a low MOI of 0.5. After transduction, cells were treated with Dox ± DMX-5804. Confirming the cardiotoxicity and protection, Dox induced a 2-fold increase of cardiac troponin I release and DMX-5804 significantly reversed it.
Next, we recovered and sequenced the integrated shRNAs, and quantified the frequency of each. We identified 146 significantly enriched or depleted shRNAs (|Z score| > 2). When comparing Dox treated group to vehicle or DMX-5804 protected group, shRNA enrichment indicates pro-death function of the targeted gene. Conversely, pro-survival genes can be inferred from shRNA depletion. Amongst the 5 most consistently targeted genes, we identified SIRT6 and GATA4 which are known pro-survival in DIC, suggesting the screen is potent to define key genes.
CONCLUSION
We performed a proof-of-concept pooled library screen in human cardiomyocytes and identified mediators of protection against DIC.
More abstracts on this topic:
Beyond Repair: Resurrecting Neurons through Stem Cell Therapy
Hamdan Tesnim, Witt Iryna, Ascandar Nameer, Basaran Ali, Brewer Yukiko A., Chyshkevych Iryna
Advancing Personalized Medicine through Enhanced Heart-on-Chip Models Incorporating iPSC-Derived Immune CellsMozneb Maedeh, Arzt Madelyn, Moses Jemima, Escopete Sean, Sharma Arun