Final ID: Su3063
Can Machine Learning Help Prioritise Who to Screen for Elevated Lipoprotein(a) (Lp[a]) in the General Population vs a Screen all Approach? An Analysis from UK Biobank
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Elevated lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is an inherited, currently non-modifiable risk marker that increases lifetime ASCVD risk. Guidance vary on Lp(a) levels at which risk increases; hence prevalence of “elevated” Lp(a) depends on putative thresholds e.g. >1.3 billion people globally have Lp(a)≥125 nmol/L. Lp(a) levels are >90% genetically determined and stable throughout life; hence measurement once in adulthood is recommended. Awareness of Lp(a) levels may change patient management with more intensive control of traditional risk factors. However, testing all adults is costly and the test is not universally available.
Research Question
Can Machine Learning (ML) models reduce the number needed to screen (NNS) compared to population universal screening for identifying individuals with elevated Lp(a)?
Aims & Objectives
To derive a model from ML to help prioritise individuals likely to have high levels for Lp(a) testing and compare its yield to universal screening at different Lp(a) cut-points. This approach could enable automatic screening of large databases like EHRs for Lp(a) testing.
Method
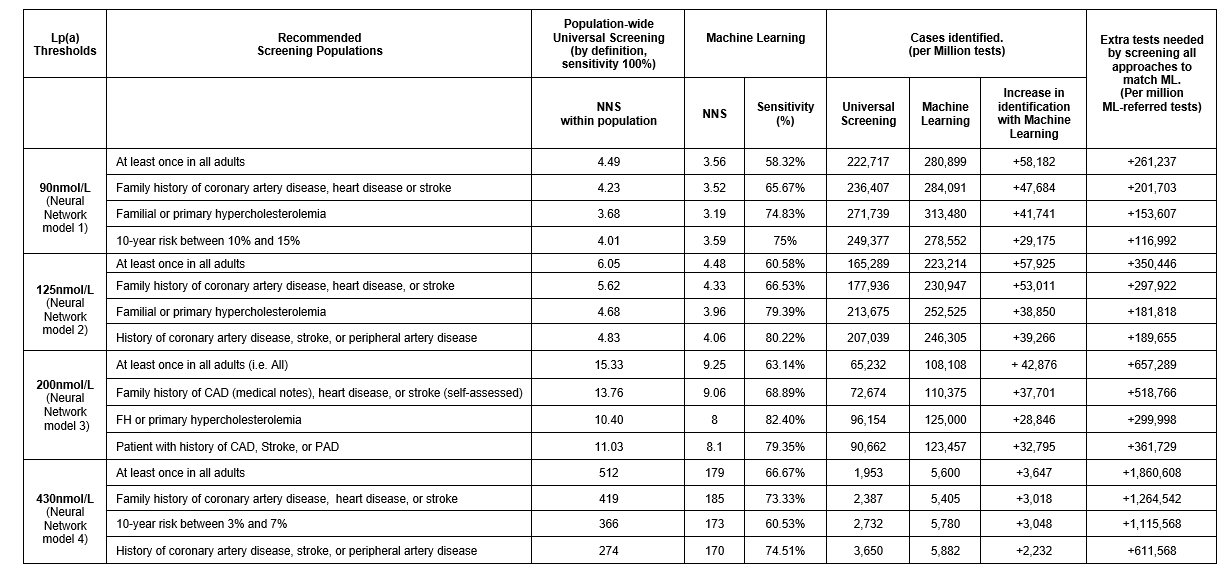
We conducted a cross-sectional predictive analysis using UK Biobank, including individuals ≥40 years old with Lp(a) measurements, split into feature importance, derivation, and validation datasets. Eight ML classification algorithms were used for feature importance analysis and model derivation. Models' performance was evaluated in the validation set using sensitivity and NNS in comparison with the discrimination ability of the following guidelines across different populations: The 2019’s Heart UK and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) and Society of Cardiology guidelines, the 2022 EAS Consensus Statement, and threshold used in clinical trial —respective cut-offs: 90,430,125,200nmol/L.
Results
438,579 patients were included. The best ML models were neural networks with different weights. Regardless of the Lp(a) threshold used, ML models resulted in higher rates of high Lp(a) cases identified per million tests with lower NNS compared to universal screening (Table 1). Using higher Lp(a) thresholds (200-430nmol/L) increased models sensitivity with far fewer tests required to identify those with high Lp(a).
Conclusion
ML models could reduce the number of tests needed to identify individuals with high Lp(a), increasing efficiency and potentially helping to prioritize Lp(a) testing, with a potentially scalable cost-effective option for health systems.
Work supported by Novartis
Elevated lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is an inherited, currently non-modifiable risk marker that increases lifetime ASCVD risk. Guidance vary on Lp(a) levels at which risk increases; hence prevalence of “elevated” Lp(a) depends on putative thresholds e.g. >1.3 billion people globally have Lp(a)≥125 nmol/L. Lp(a) levels are >90% genetically determined and stable throughout life; hence measurement once in adulthood is recommended. Awareness of Lp(a) levels may change patient management with more intensive control of traditional risk factors. However, testing all adults is costly and the test is not universally available.
Research Question
Can Machine Learning (ML) models reduce the number needed to screen (NNS) compared to population universal screening for identifying individuals with elevated Lp(a)?
Aims & Objectives
To derive a model from ML to help prioritise individuals likely to have high levels for Lp(a) testing and compare its yield to universal screening at different Lp(a) cut-points. This approach could enable automatic screening of large databases like EHRs for Lp(a) testing.
Method
We conducted a cross-sectional predictive analysis using UK Biobank, including individuals ≥40 years old with Lp(a) measurements, split into feature importance, derivation, and validation datasets. Eight ML classification algorithms were used for feature importance analysis and model derivation. Models' performance was evaluated in the validation set using sensitivity and NNS in comparison with the discrimination ability of the following guidelines across different populations: The 2019’s Heart UK and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) and Society of Cardiology guidelines, the 2022 EAS Consensus Statement, and threshold used in clinical trial —respective cut-offs: 90,430,125,200nmol/L.
Results
438,579 patients were included. The best ML models were neural networks with different weights. Regardless of the Lp(a) threshold used, ML models resulted in higher rates of high Lp(a) cases identified per million tests with lower NNS compared to universal screening (Table 1). Using higher Lp(a) thresholds (200-430nmol/L) increased models sensitivity with far fewer tests required to identify those with high Lp(a).
Conclusion
ML models could reduce the number of tests needed to identify individuals with high Lp(a), increasing efficiency and potentially helping to prioritize Lp(a) testing, with a potentially scalable cost-effective option for health systems.
Work supported by Novartis
More abstracts on this topic:
Association between Elevated Lipoprotein(a) and Cardiovascular Events and Mortality in a Nationally Representative Sample of US Medicare, Medicaid, and Commercial Enrollees with ASCVD
Hu Xingdi, Lozama Tony, Petrilla Allison, Agatep Barnabie, Mcmorrow Donna, Mohammadi Iman, Reisman Lonny, Wong Nathan
A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Signature of Advanced Cardiac and Vascular Aging Defines Elevated Risk of Cardiovascular DiseasePerera Sudheesha, Biswas Dhruva, Dhingra Lovedeep, Aminorroaya Arya, Coppi Andreas, Khera Rohan