Final ID: Mo2172
Prospective validation and implementation pilot study of an emergency department heart failure risk stratification tool: STRIDE-HF
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: We previously found the STRIDE-HF emergency department (ED) risk tool accurately predicted risk of a 30-day serious adverse event (SAE), including 30-day mortality, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, intra-aortic balloon pump insertion, intubation, new dialysis, myocardial infarction, or coronary revascularization.
Research question: We sought to prospectively validate STRIDE-HF and describe safety of the deployed model in a clinical pilot. We hypothesized that performance would decrease slightly with prospective evaluation and that real-time risk display would contribute to safe disposition decisions.
Goals: 1) To prospectively validate KPCARES-HF across 21 community EDs among ED patients with acute heart failure (AHF) from January 1, 2023 – December 31st, 2023; and 2) to describe outcomes among patients predicted to be very low risk and discharged home in the clinical pilot.
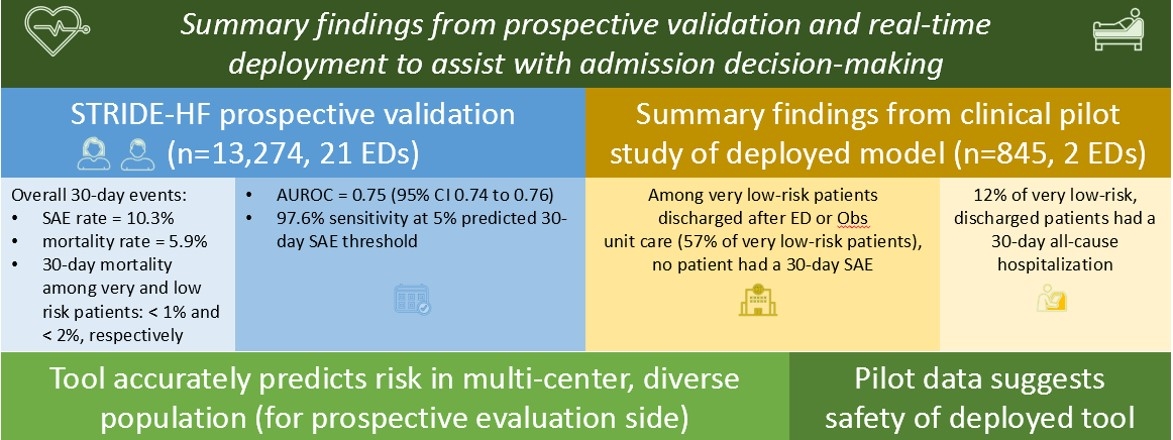
Methods: For prospective validation, we report 30-day mortality rates by risk strata. We assess model performance using area under the receiver operator curve (AUROC) and sensitivity at a key clinical threshold. We describe rates of 30-day SAE among patients predicted to be very low risk and discharged after ED or observation unit care in the clinical pilot.
Results: There were 13,274 ED patients in the prospective validation; median age was 76, 50.8% were female, and 44.5% were non-White. We found 11.4%, 24.8%, 31.9%, and 31.9% of patients were very low, low, moderate, and high risk, respectively, while 21.6%, 15.2% and 63.0% were discharged, observed, and admitted, respectively.
Among discharged patients, 29.2% and 13.3% were moderate or high risk, respectively, and 30-day mortality rates among these patients were 2.2% and 8.4%, respectively. Among 8,363 admitted patients, 27.7% were very low or low risk.
Conclusions: STRIDE-HF maintained high predictive accuracy with prospective validation in this diverse, multi-center cohort. Our findings suggest that use of STRIDE-HF might help better align risk with admission decision and can be safely used to assist providers in identifying patients who may be stable for outpatient care.
Research question: We sought to prospectively validate STRIDE-HF and describe safety of the deployed model in a clinical pilot. We hypothesized that performance would decrease slightly with prospective evaluation and that real-time risk display would contribute to safe disposition decisions.
Goals: 1) To prospectively validate KPCARES-HF across 21 community EDs among ED patients with acute heart failure (AHF) from January 1, 2023 – December 31st, 2023; and 2) to describe outcomes among patients predicted to be very low risk and discharged home in the clinical pilot.
Methods: For prospective validation, we report 30-day mortality rates by risk strata. We assess model performance using area under the receiver operator curve (AUROC) and sensitivity at a key clinical threshold. We describe rates of 30-day SAE among patients predicted to be very low risk and discharged after ED or observation unit care in the clinical pilot.
Results: There were 13,274 ED patients in the prospective validation; median age was 76, 50.8% were female, and 44.5% were non-White. We found 11.4%, 24.8%, 31.9%, and 31.9% of patients were very low, low, moderate, and high risk, respectively, while 21.6%, 15.2% and 63.0% were discharged, observed, and admitted, respectively.
Among discharged patients, 29.2% and 13.3% were moderate or high risk, respectively, and 30-day mortality rates among these patients were 2.2% and 8.4%, respectively. Among 8,363 admitted patients, 27.7% were very low or low risk.
Conclusions: STRIDE-HF maintained high predictive accuracy with prospective validation in this diverse, multi-center cohort. Our findings suggest that use of STRIDE-HF might help better align risk with admission decision and can be safely used to assist providers in identifying patients who may be stable for outpatient care.
More abstracts on this topic:
A RARE CARDIAC COMPLICATION OF LEGIONNAIRES' DISEASE: LEFT VENTRICULAR APICAL THROMBUS WITH SEVERE CARDIOMYOPATHY
Ramalingam Archana, Shabnam Arshiya, Devi Reddy Akhila Reddy, Nookala Vinod
A machine learning model for individualized risk prediction of ischemic heart disease in people with hypertension in ThailandSakboonyarat Boonsub, Poovieng Jaturon, Rangsin Ram