Final ID: MDP1087
Association of Eicosanoid Metabolites with Body Mass Index
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: The specific molecular pathways from obesity to inflammation to cardiovascular disease remain unclear. Eicosanoids are a unique class of bioactive lipids that govern the upstream initiation of pro- and anti-inflammatory activity.
Objective: We leveraged a novel lipidomic platform to quantify > 800 eicosanoid metabolites and examined their association with body mass index (BMI).
Methods: We studied Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) participants with available samples for eicosanoid analysis. Eicosanoids and related metabolites were assessed using a directed, non-targeted mass spectrometry-based platform. We examined the cross-sectional association of eicosanoid metabolites with BMI using multivariable linear regression models. Analyses were considered significant at FDR q-value <0.01.
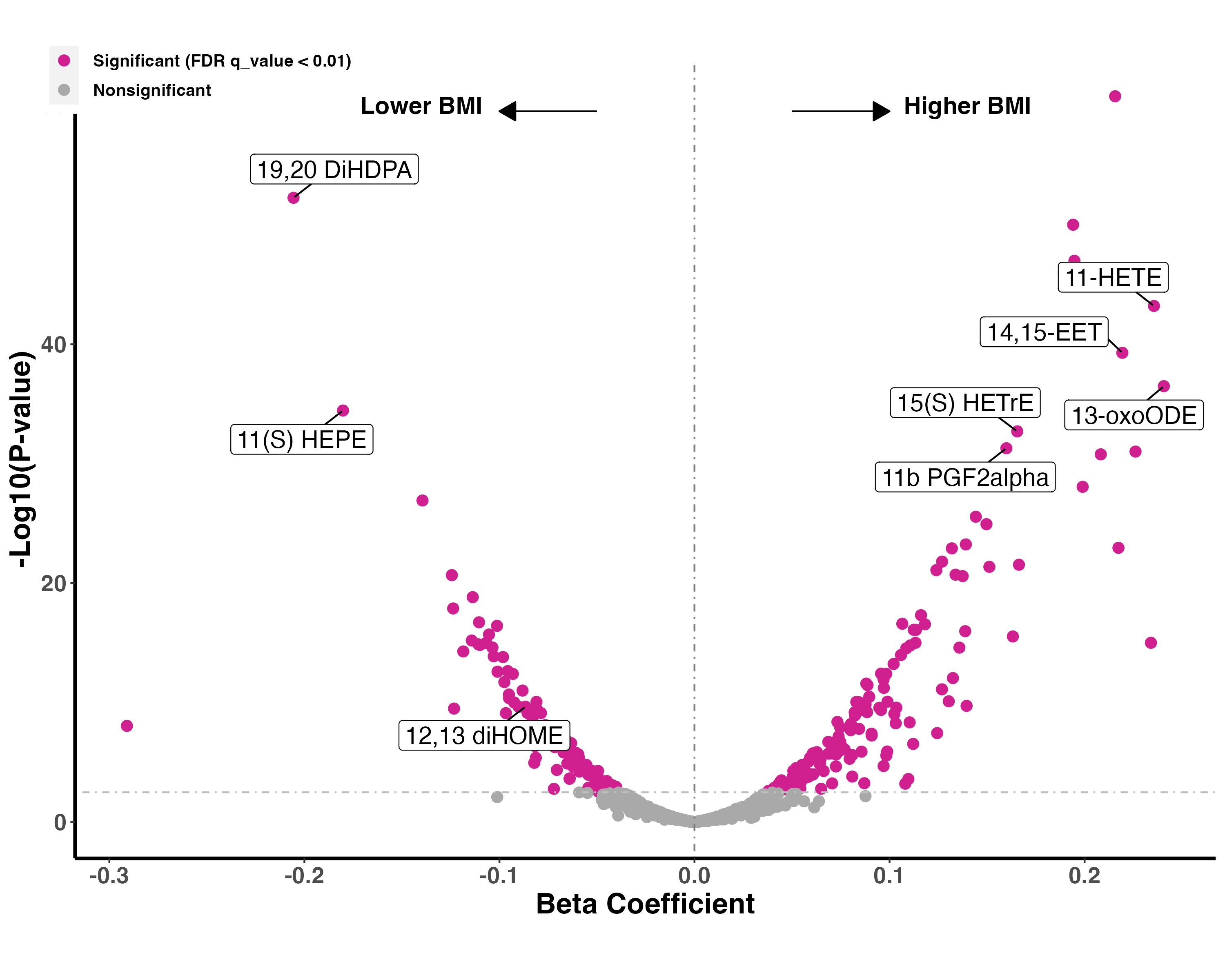
Results: A total of 5101 individuals (age 63 ± 10 years; 53% women, 60% non-Whites) were included. The mean BMI was 28.3 ± 5.1 kg/m2. Of 811 eicosanoids analyzed, 255 showed a significant association with BMI (see Figure for putative metabolite identities; FDR q-value <0.01 for all). Derivatives of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; 19,20 DiHDPA, β = - 0.206, standard error [SE] = 0.013) and eicosatetraenoic acid (11(S) HEPE, β = - 0.180, SE = 0.014) were associated with lower BMI. Linoleic acid derivatives (12,13 diHOME, an exercise-induced lipokine) had a similar association. Conversely, derivatives of linoleic acid (13-oxoODE, β = 0.241, SE = 0.01) and arachidonic acid (11-HETE, β = 0.236, SE = 0.017) were associated with higher BMI. Other derivatives of linoleic acid (15 (S) HETrE) and prostaglandin (11b PGF2α) were also associated with higher BMI.
Conclusions: We found that specific eicosanoid metabolites, including DHA and linoleic acid derivatives with known anti-inflammatory, atheroprotective, and beneficial metabolic effects (e.g., 19,20 DiHDPA; 12,13 diHOME), were associated with lower BMI. By contrast, specific arachidonic acid and prostaglandin derivatives with known pro-inflammatory and adverse CV effects (e.g. oxylipin 11-HETE; PGF2α; 13-oxoODE) were associated with higher BMI. These findings further the understanding of specific inflammatory pathways underlying the development of obesity-related CVD.
Objective: We leveraged a novel lipidomic platform to quantify > 800 eicosanoid metabolites and examined their association with body mass index (BMI).
Methods: We studied Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) participants with available samples for eicosanoid analysis. Eicosanoids and related metabolites were assessed using a directed, non-targeted mass spectrometry-based platform. We examined the cross-sectional association of eicosanoid metabolites with BMI using multivariable linear regression models. Analyses were considered significant at FDR q-value <0.01.
Results: A total of 5101 individuals (age 63 ± 10 years; 53% women, 60% non-Whites) were included. The mean BMI was 28.3 ± 5.1 kg/m2. Of 811 eicosanoids analyzed, 255 showed a significant association with BMI (see Figure for putative metabolite identities; FDR q-value <0.01 for all). Derivatives of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; 19,20 DiHDPA, β = - 0.206, standard error [SE] = 0.013) and eicosatetraenoic acid (11(S) HEPE, β = - 0.180, SE = 0.014) were associated with lower BMI. Linoleic acid derivatives (12,13 diHOME, an exercise-induced lipokine) had a similar association. Conversely, derivatives of linoleic acid (13-oxoODE, β = 0.241, SE = 0.01) and arachidonic acid (11-HETE, β = 0.236, SE = 0.017) were associated with higher BMI. Other derivatives of linoleic acid (15 (S) HETrE) and prostaglandin (11b PGF2α) were also associated with higher BMI.
Conclusions: We found that specific eicosanoid metabolites, including DHA and linoleic acid derivatives with known anti-inflammatory, atheroprotective, and beneficial metabolic effects (e.g., 19,20 DiHDPA; 12,13 diHOME), were associated with lower BMI. By contrast, specific arachidonic acid and prostaglandin derivatives with known pro-inflammatory and adverse CV effects (e.g. oxylipin 11-HETE; PGF2α; 13-oxoODE) were associated with higher BMI. These findings further the understanding of specific inflammatory pathways underlying the development of obesity-related CVD.
More abstracts on this topic:
Bioactive Oxylipins Predict Aortic Vascular Calcification Severity in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Aradhyula Vaishnavi, Manandhar Sareeta, Maddipati Krishna Rao, Brewster Pamela, Smith Robert, Haller Steven, Kennedy David, Khouri Samer, Gupta Rajesh, Fares Anas, Vergis John, Dube Prabhatchandra, Sherafati Alborz, Kloster Alex, Khatib-shahidi Bella, Elzanaty Ahmed, Sajdeya Omar
Additive Value of Lipoprotein(a), Remnant Cholesterol, and Inflammation for Risk Stratification of Myocardial Infarction: Evidence from the UK BiobankKazibwe Richard, Schaich Christopher, Kingsley Jeffrey, Rikhi Rishi, Namutebi Juliana, Chevli Parag, Mirzai Saeid, Shapiro Michael