Final ID: MDP377
Title: Mandibular advancement device versus CPAP on cardiovascular health and quality of life in OSA a pre-specified 12 months follow up of outcomes
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) is a significant cause of hypertension. ACC/AHA Guidelines recommended screening and treatment of OSA in patients with hypertension; however, evidence comparing mandibular advancement devices (MAD) to continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) on cardiovascular health is lacking. We present the complete 12 months follow-up data on the comparative effectiveness of MAD versus CPAP in ambulatory BP reduction, QoL, cardiac arrhythmia, and myocardial remodelling.
Method
In a randomized, non-inferiority trial (margin 1.5 mmHg), 321 participants, aged over 40, with hypertension and high cardiovascular risk were recruited. Of these, 220 participants with OSA (apnoea–hypopnea index ≥15 events/h) were randomized to either MAD or CPAP (1:1). Pre-specified secondary outcomes include: ambulatory BP, quality of life (QoL) (sleep-specific: ESS, SAQLI, FOSQ; non-sleep-specific: SF-36, EQ-5D), ambulatory ECG monitoring, and cardiac MRI.
Results
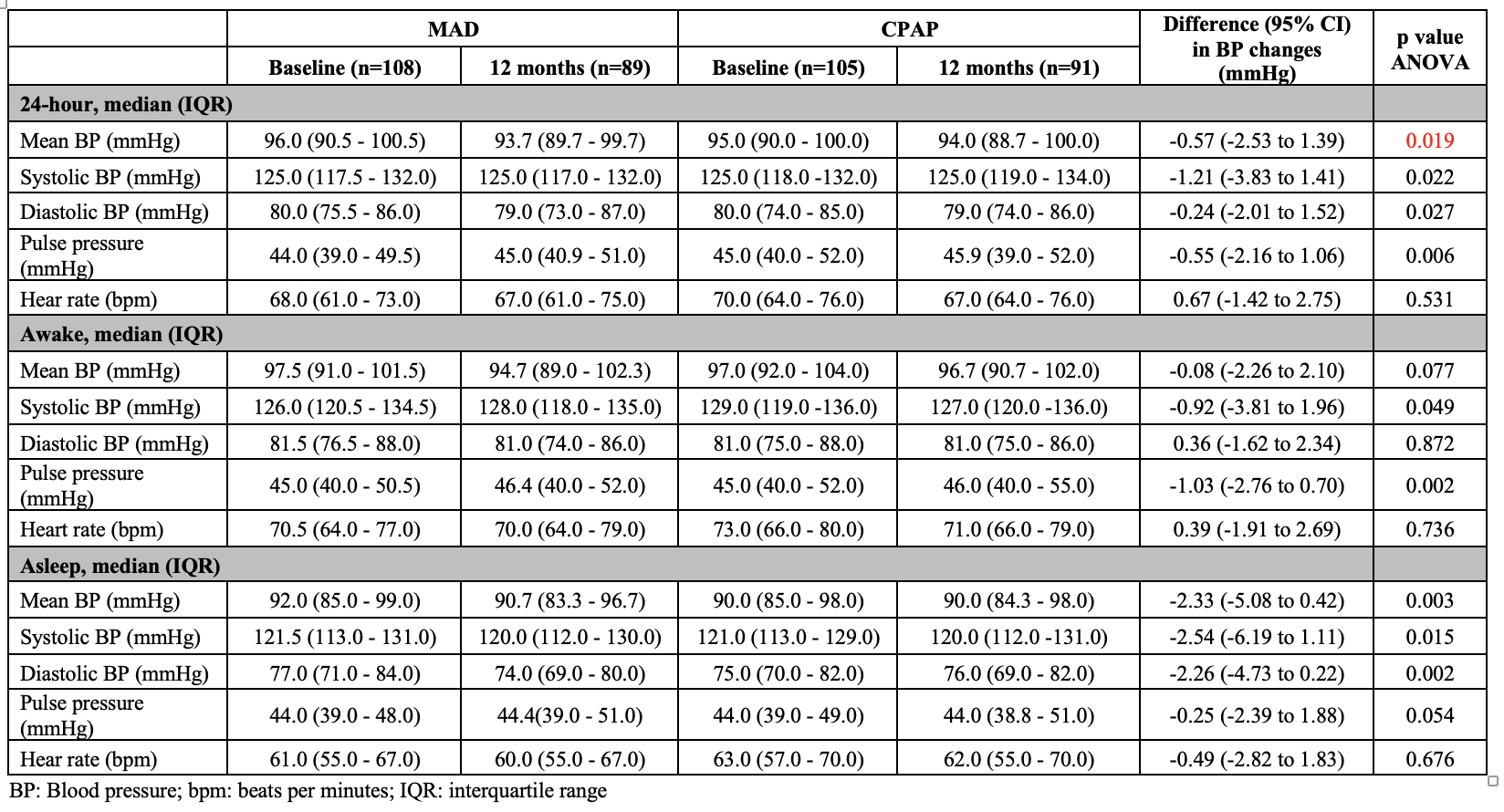
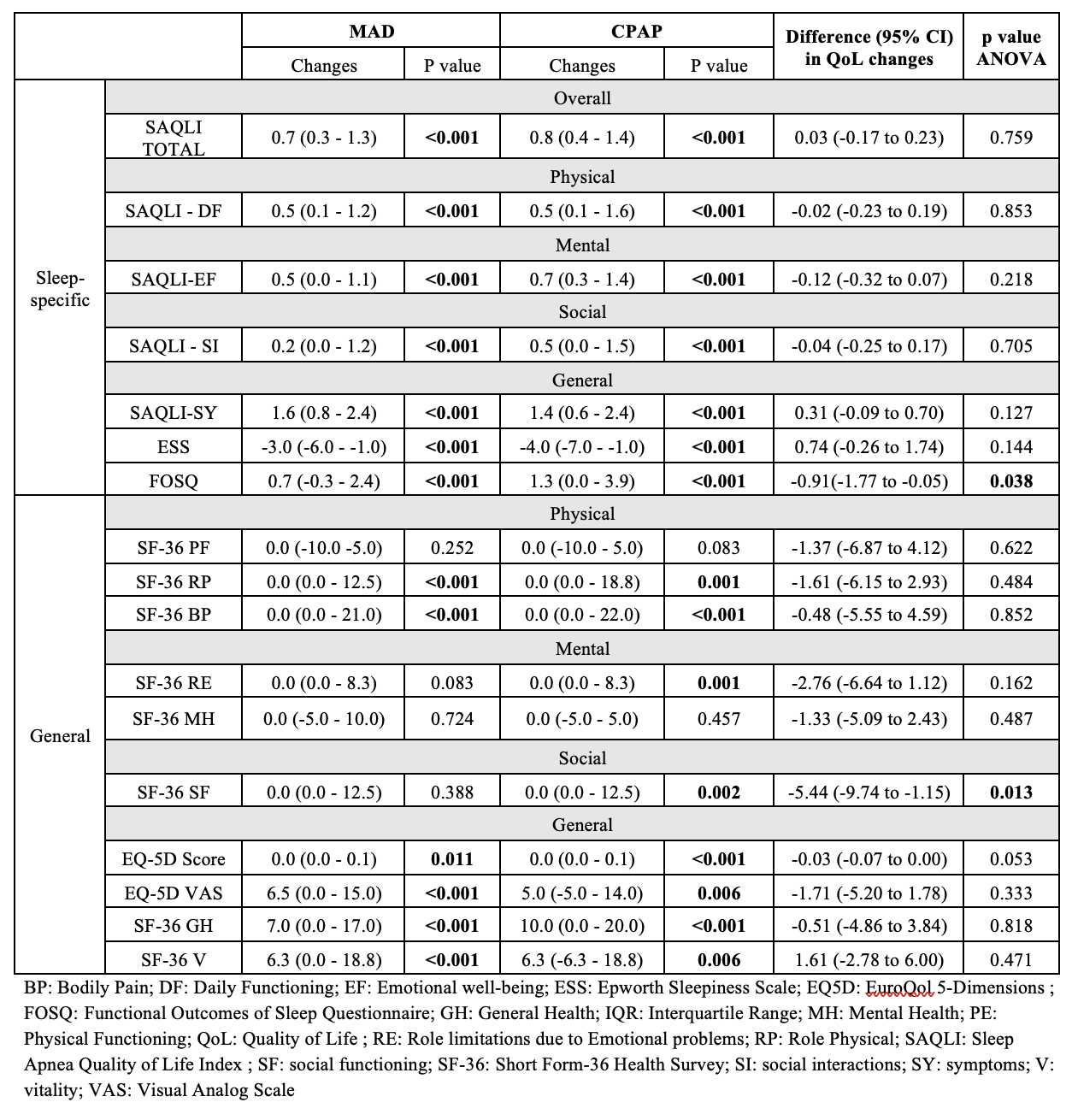
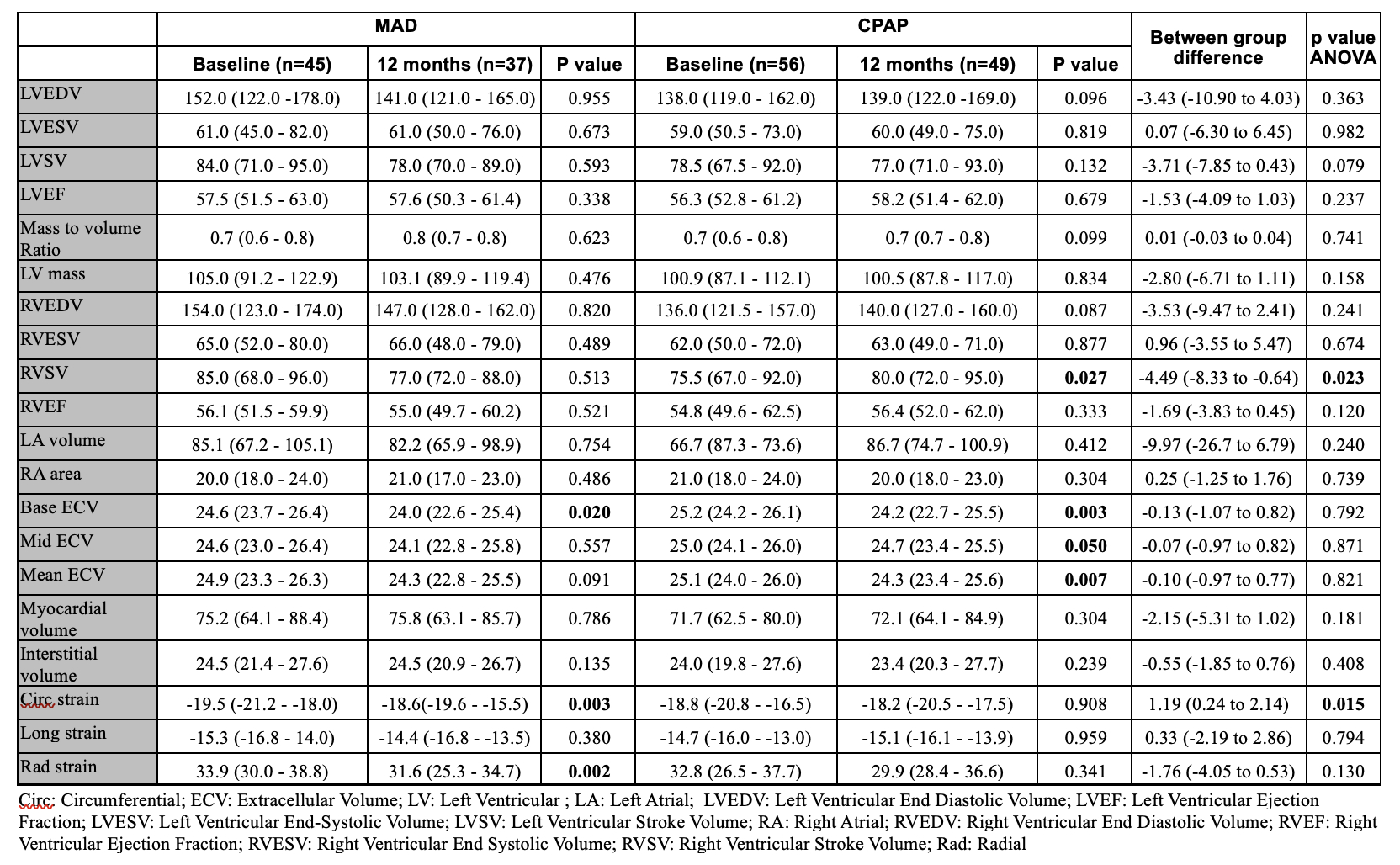
A total of 89 (80.9% of 110) participants from MAD, and 91 (82.7% of 110) participants from CPAP completed 12 months follow-up. The median daily usage was 5.5 hours for MAD and 4.9 hours for CPAP. The between-group difference in 24h mean BP from baseline to 12 months was - 0.57 mmHg (95% confidence interval: (-2.53 to 1.39, non-inferiority P < 0.001). Compared with the CPAP group, MAD group demonstrated a larger reduction in all the 24h with the most pronounced differences observed in the asleep BP parameters (Table 1). Both the MAD and CPAP improved QoL (Table 2). CPAP had greater improvement in FOSQ from sleep-specific questionnaires (P=0.038), and social QoL in SF-36 from non-sleep-specificl questionnaires (P=0.013). The ambulatory ECG monitoring (MAD: 2.8 ± 1.0 days, CPAP: 2.3 ± 1.1 days) showed no between-group differences in % atrial fibrillation(P=0.209), % ventricular ectopic isolated count (P=0.790) and % supraventricular ectopic isolated count (P= 0.333). The cardiac MRI sub-study (101 participants : MAD= 45, CPAP= 56) showed CPAP had greater improvement in right ventricular stroke volume (P=0.023) and MAD had greater improvement in circumferential strain favours the MAD group (P=0.015) (Table 3).
Conclusion
At 12 months , MAD was non-inferior to CPAP for reducing 24h mean arterial BP. MAD showed greater reduction in 24h BPs, especially during asleep. While both the MAD and CPAP are effective in improving QoL, CPAP is more effective in improving FOSQ and social QoL (SF-36).
Obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) is a significant cause of hypertension. ACC/AHA Guidelines recommended screening and treatment of OSA in patients with hypertension; however, evidence comparing mandibular advancement devices (MAD) to continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) on cardiovascular health is lacking. We present the complete 12 months follow-up data on the comparative effectiveness of MAD versus CPAP in ambulatory BP reduction, QoL, cardiac arrhythmia, and myocardial remodelling.
Method
In a randomized, non-inferiority trial (margin 1.5 mmHg), 321 participants, aged over 40, with hypertension and high cardiovascular risk were recruited. Of these, 220 participants with OSA (apnoea–hypopnea index ≥15 events/h) were randomized to either MAD or CPAP (1:1). Pre-specified secondary outcomes include: ambulatory BP, quality of life (QoL) (sleep-specific: ESS, SAQLI, FOSQ; non-sleep-specific: SF-36, EQ-5D), ambulatory ECG monitoring, and cardiac MRI.
Results
A total of 89 (80.9% of 110) participants from MAD, and 91 (82.7% of 110) participants from CPAP completed 12 months follow-up. The median daily usage was 5.5 hours for MAD and 4.9 hours for CPAP. The between-group difference in 24h mean BP from baseline to 12 months was - 0.57 mmHg (95% confidence interval: (-2.53 to 1.39, non-inferiority P < 0.001). Compared with the CPAP group, MAD group demonstrated a larger reduction in all the 24h with the most pronounced differences observed in the asleep BP parameters (Table 1). Both the MAD and CPAP improved QoL (Table 2). CPAP had greater improvement in FOSQ from sleep-specific questionnaires (P=0.038), and social QoL in SF-36 from non-sleep-specificl questionnaires (P=0.013). The ambulatory ECG monitoring (MAD: 2.8 ± 1.0 days, CPAP: 2.3 ± 1.1 days) showed no between-group differences in % atrial fibrillation(P=0.209), % ventricular ectopic isolated count (P=0.790) and % supraventricular ectopic isolated count (P= 0.333). The cardiac MRI sub-study (101 participants : MAD= 45, CPAP= 56) showed CPAP had greater improvement in right ventricular stroke volume (P=0.023) and MAD had greater improvement in circumferential strain favours the MAD group (P=0.015) (Table 3).
Conclusion
At 12 months , MAD was non-inferior to CPAP for reducing 24h mean arterial BP. MAD showed greater reduction in 24h BPs, especially during asleep. While both the MAD and CPAP are effective in improving QoL, CPAP is more effective in improving FOSQ and social QoL (SF-36).
More abstracts on this topic:
3CPR Best Abstract Award: The pathogenic role of ADAMTS13 deficiency in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension
Wu Zhijian, Zheng X. Long, Zheng Liang
A Key Role of Proximal Tubule Renin-Angiotensin System in The Kidney in The Development of Kidney Ischemia and Reperfusion InjuryLi Xiao, Hassan Rumana, Katsurada Akemi, Sato Ryosuke, Zhuo Jia