Final ID: MDP1576
Systematic Examination of the AHA PREVENT Equations
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The novel AHA Predicting Risk of CVD Events (PREVENT) equations newly incorporate predictors (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR]) and outcomes (heart failure [HF]) relevant to the novel construct of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome.
Aims: We sought to characterize the intrinsic properties of the PREVENT equations by simulating different risk profiles across the age and CKM risk spectrum.
Methods: We applied the PREVENT base equations to estimate 10-year predicted risk for total CVD, which includes atherosclerotic CVD and HF. First, we calculated risk estimates for a hypothetical individual varying age from 30-79 years with an average risk factor profile (mean population risk factor levels based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2020 data without diabetes, not on anti-hypertensive or statin medication, and who does not smoke). Second, we examined at which age a hypothetical individual would exceed the previously defined intermediate risk threshold ≥7.5% established by national guidelines. Lastly, we examined the differences in predicted risk with or without diabetes and/or Stage 3 CKD (defined as eGFR 44.5 mL/min/1.73m2).
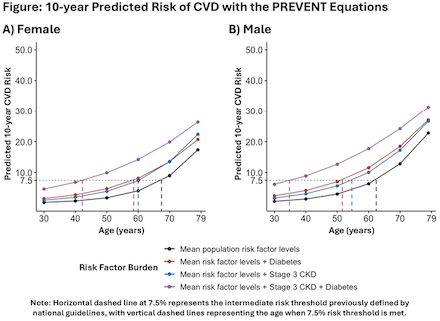
Results: For hypothetical individuals aged 30-79 years with average risk factor levels, predicted 10-year CVD risk is shown in the figure for females (Panel A) and males (Panel B). The predicted risk would exceed the intermediate risk threshold at age 68 years if female and 63 years if male. If the individual had Stage 3 CKD, the predicted risk would exceed the intermediate risk threshold at 60 if female and 55 years if male. If the individual had diabetes, the predicted risk would exceed the intermediate risk threshold at 59 if female and 52 years if male. If both diabetes and Stage 3 CKD were present, the predicted risk would exceed the intermediate risk threshold at age 42 years if female and 35 years if male.
Conclusions: The PREVENT equations enable more granular differentiation of risk among individuals with varying CKM profiles. Understanding risk estimates across the spectrum of age and CKM can support interpretability among clinicians and patients.
Aims: We sought to characterize the intrinsic properties of the PREVENT equations by simulating different risk profiles across the age and CKM risk spectrum.
Methods: We applied the PREVENT base equations to estimate 10-year predicted risk for total CVD, which includes atherosclerotic CVD and HF. First, we calculated risk estimates for a hypothetical individual varying age from 30-79 years with an average risk factor profile (mean population risk factor levels based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2020 data without diabetes, not on anti-hypertensive or statin medication, and who does not smoke). Second, we examined at which age a hypothetical individual would exceed the previously defined intermediate risk threshold ≥7.5% established by national guidelines. Lastly, we examined the differences in predicted risk with or without diabetes and/or Stage 3 CKD (defined as eGFR 44.5 mL/min/1.73m2).
Results: For hypothetical individuals aged 30-79 years with average risk factor levels, predicted 10-year CVD risk is shown in the figure for females (Panel A) and males (Panel B). The predicted risk would exceed the intermediate risk threshold at age 68 years if female and 63 years if male. If the individual had Stage 3 CKD, the predicted risk would exceed the intermediate risk threshold at 60 if female and 55 years if male. If the individual had diabetes, the predicted risk would exceed the intermediate risk threshold at 59 if female and 52 years if male. If both diabetes and Stage 3 CKD were present, the predicted risk would exceed the intermediate risk threshold at age 42 years if female and 35 years if male.
Conclusions: The PREVENT equations enable more granular differentiation of risk among individuals with varying CKM profiles. Understanding risk estimates across the spectrum of age and CKM can support interpretability among clinicians and patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acute and Chronic Phosphorylation of CaMKII on Coronary Microvascular/Endothelial Function
Iddrisu Hanisah, Xing Hang, Shi Guangbin, Liu Yuhong, Feng Jun
Adoptive Transfer of Lupus Patient PBMCs Promotes Salt-Sensitive Hypertension and Kidney Injury in Immunodeficient MiceSaleem Mohammad, Ormseth Michelle, Kirabo Annet, Ahmad Taseer, Haynes Alexandria, Albritton Claude, Arshad Suha, Kulapatana Phicharmon, Posey Olivia, Major Amy, Stein Charles