Final ID: Su3001
Comparison of Dietary Macronutrient Interventions for Weight and Cardiovascular Risk Factor Reduction: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Dietary interventions play a crucial role in weight management and reducing cardiovascular risk factors. Our study aims to compare the effectiveness of four dietary macronutrient interventions on weight loss and cardiovascular (CV) risk factor reduction through a systematic review and network meta-analysis.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive literature search on PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Cochrane Library up till May 2024 to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing four macronutrient dietary interventions including Mediterranean Diet (MD), Keto, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), and Intermittent Fasting (IF) with study period ≥ 6 months or 24 weeks. The primary outcomes of interest were weight loss, systolic blood pressure (SBP), Diastolic blood pressure (DBP), Body Mass Index (BMI), High density lipoprotein (HDL), Low density Lipoprotein (LDL), cholesterol levels and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. Outcomes were reported as standard mean difference (SMD).
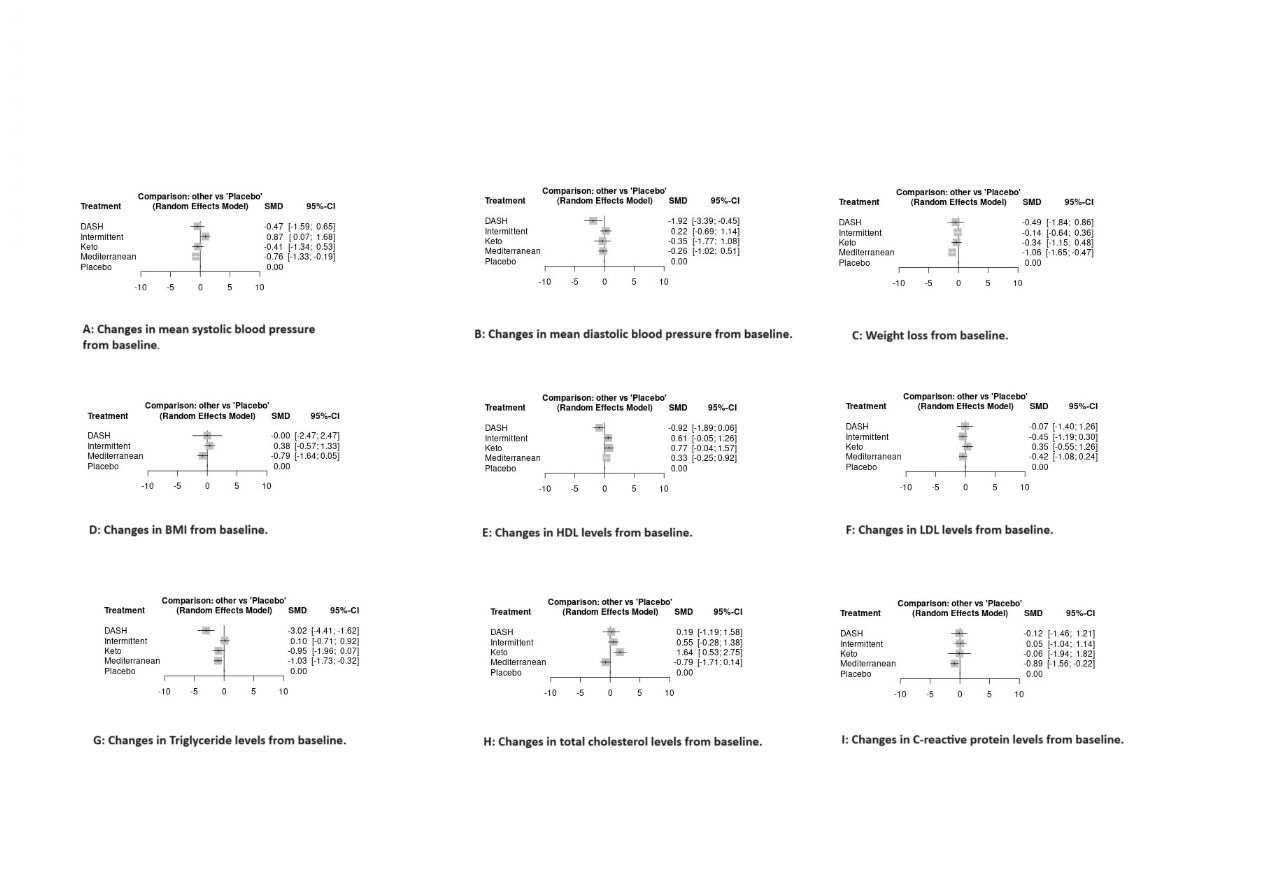
Results: Our analysis identified 50 studies enrolling 5368 patients (MD=3554; DASH=838; Keto=206; IF=770). Regarding BP outcome, MD and DASH had significant reduction in SBP and DBP respectively (MD [SBP]: -0.76 mmHg vs DASH [DBP]: -1.92 mmHg) respectively. In contrast, IF showed a significant rise in SBP (0.87). MD participants also had significant weight loss (-1.06 kg) and a moderate decrease in BMI (-0.79) when compared with other diets. Furthermore, IF, keto, and MD showed moderate increase in HDL levels (0.61, 0.77 and 0.33) respectively. In contrast, DASH resulted in a moderate decline in HDL levels (-0.92). IF and MD resulted in modest decline in LDL levels (-0.45 and -0.42) respectively. In contrast, Keto demonstrated non-significant rise in LDL (0.35). DASH showed a significant decrease in triglycerides (-3.02). Lastly, MD demonstrated a significant reduction in CRP (-0.89).
Conclusions: MD and DASH were superior to other dietary interventions in terms of weight loss and CV risk factors. Further research is required to tailor specific types of dietary interventions and assess their long-term efficacy on weight loss and CV risk reduction.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive literature search on PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Cochrane Library up till May 2024 to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing four macronutrient dietary interventions including Mediterranean Diet (MD), Keto, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), and Intermittent Fasting (IF) with study period ≥ 6 months or 24 weeks. The primary outcomes of interest were weight loss, systolic blood pressure (SBP), Diastolic blood pressure (DBP), Body Mass Index (BMI), High density lipoprotein (HDL), Low density Lipoprotein (LDL), cholesterol levels and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. Outcomes were reported as standard mean difference (SMD).
Results: Our analysis identified 50 studies enrolling 5368 patients (MD=3554; DASH=838; Keto=206; IF=770). Regarding BP outcome, MD and DASH had significant reduction in SBP and DBP respectively (MD [SBP]: -0.76 mmHg vs DASH [DBP]: -1.92 mmHg) respectively. In contrast, IF showed a significant rise in SBP (0.87). MD participants also had significant weight loss (-1.06 kg) and a moderate decrease in BMI (-0.79) when compared with other diets. Furthermore, IF, keto, and MD showed moderate increase in HDL levels (0.61, 0.77 and 0.33) respectively. In contrast, DASH resulted in a moderate decline in HDL levels (-0.92). IF and MD resulted in modest decline in LDL levels (-0.45 and -0.42) respectively. In contrast, Keto demonstrated non-significant rise in LDL (0.35). DASH showed a significant decrease in triglycerides (-3.02). Lastly, MD demonstrated a significant reduction in CRP (-0.89).
Conclusions: MD and DASH were superior to other dietary interventions in terms of weight loss and CV risk factors. Further research is required to tailor specific types of dietary interventions and assess their long-term efficacy on weight loss and CV risk reduction.
More abstracts on this topic:
Estimating Resting Metabolic Rate in Youth with Obesity and Elevated Blood Pressure
Moore Jafar-i, Vizthum Diane, Brady Tammy
Apolipoprotein A1 infusion in patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of randomized trialsPrata Alonzo, Gioli-pereira Luciana, Fukunaga Christian, Katsuyama Eric, Coan Ana Carolina, Scardini Pedro Gabriel, Petri Santos Pinheiro Rafael, Falco Neto Wilson, Fernandes Julia, Andrade Naieli