Final ID: Sa3122
The Effect of Weight loss and Weight Maintenance on Branch Chain Amino Acid Levels
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Elevated branch chain amino acid levels (BCAA) have been associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and type-2 diabetes. While weight loss has been shown to improve BCAA levels, few studies have evaluated the impact of weight loss and weight maintenance with the OPTIFAST® weight loss program and supervised exercise training.
Methods: The present study is a secondary analysis of the PREVAIL-P study. During the weight loss phase, overweight and obese adults (N=30) completed a 10-week OPTIFAST® program with supervised aerobic exercise training with the goal of achieving clinically significant weight loss (≥7%). Participants who met the weight loss goal were randomized to levels of aerobic training consistent with physical activity recommendations (PA-REC) (~550 MET minutes per week) or weight maintenance recommendations (WM-REC) (~970 MET minutes per week) for 18 additional weeks. Valine, leucine, isoleucine and total BCAA levels were measured using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) at baseline, after the weight loss phase (10 weeks) and at follow-up (28 Weeks) (LabCorp, Raleigh, NC).
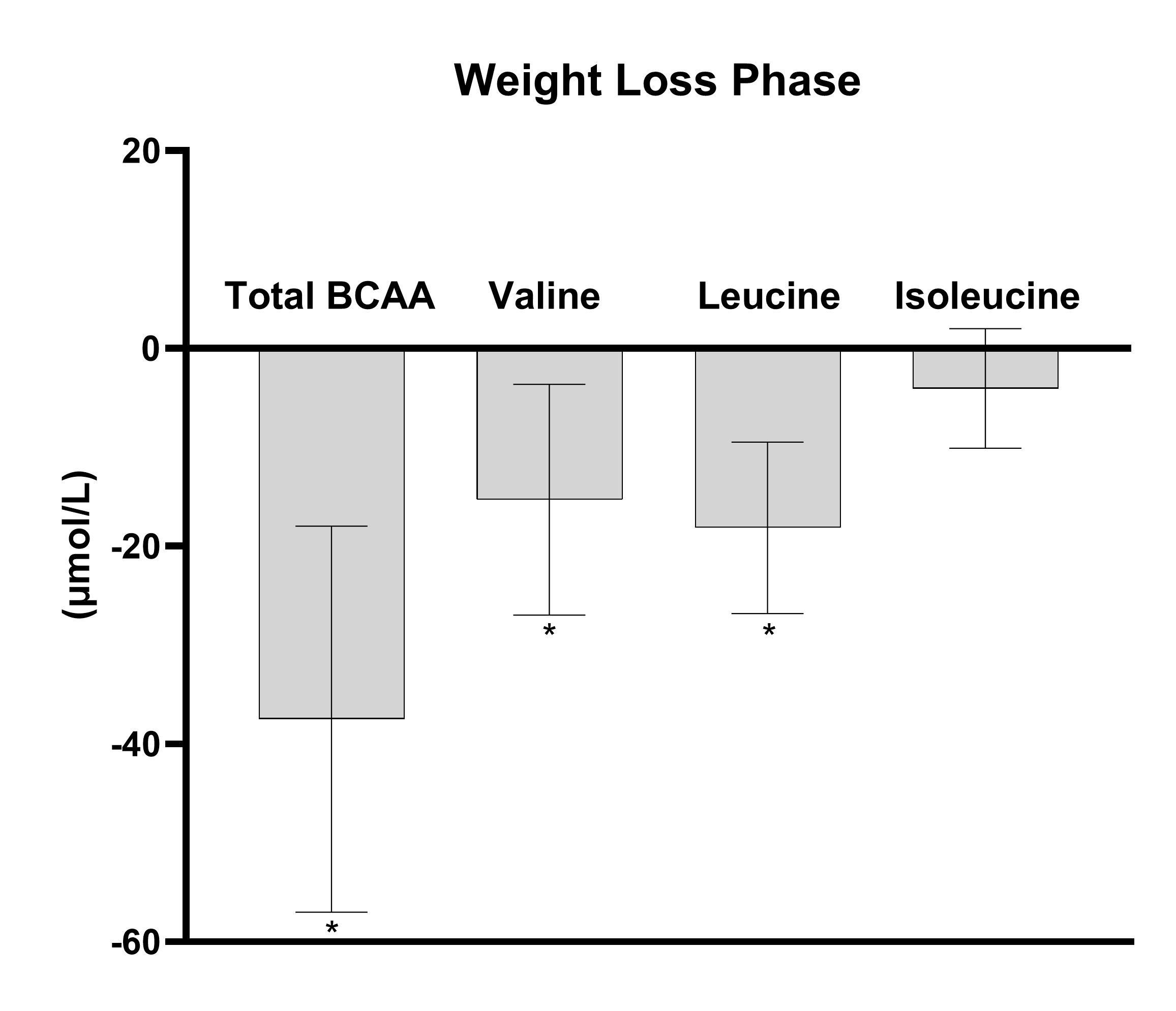
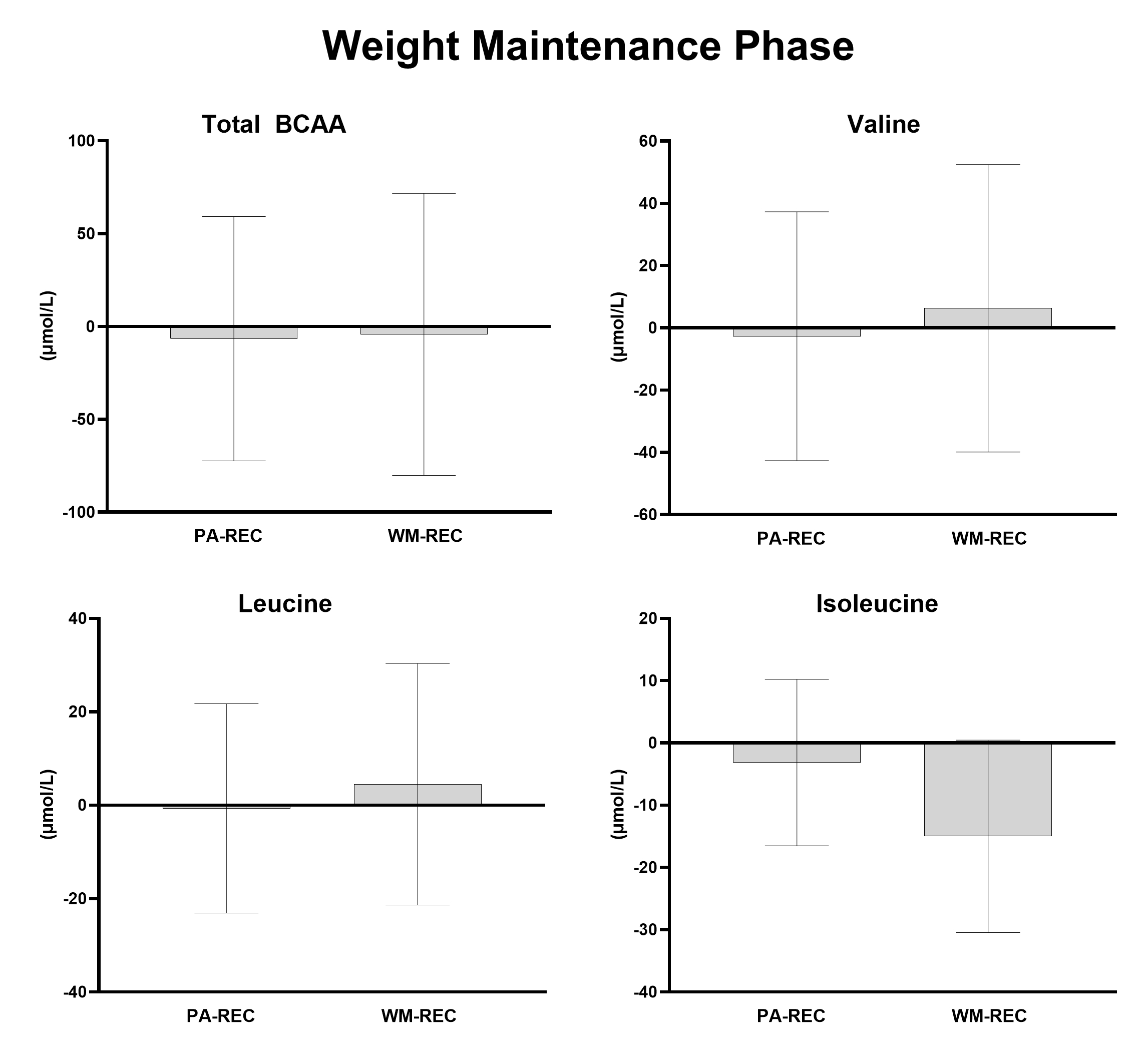
Results: Following the weight loss phase, participants had a significant mean reduction in weight (-8.8 kg, p<0.001), total BCAA (-37.4 μmol/L, p<0.001), valine (-15.2 μmol/L, p=0.012), leucine (-20.0 μmol/L, p<0.001), but not isoleucine (-4.1 μmol/L, p=0.214) levels. Improvements in BCAA levels were associated with changes in HDL levels (r=-0.39, p=0.03) and approached significance for visceral fat (r=0.34, p=0.07). Furthermore, changes in BCAA metabolites were not associated with weight, glucose metabolism or other lipid variables for the weight loss phase (p>0.05). In a subset of participants (N=14) who completed the weight maintenance phase (due to COVID pandemic), there were no group differences in the change in total BCAA, valine, leucine between the PA-REC and the WM-REC groups (all ps >0.05). Changes in total BCAA levels (baseline to 28 weeks) were associated with higher mean aerobic exercise training intensity during the intervention (r=-0.64, p=0.013).
Conclusion: Weight loss using the OPTIFAST® weight loss program diet combined with aerobic exercise improved BCAA levels, which is associated with decreased CVD risk. Lower BCAA levels during weight maintenance may be influenced by higher exercise intensity exercise. Future studies should evaluate the impact of lifestyle interventions on BCAA levels during long-term weight maintenance.
Methods: The present study is a secondary analysis of the PREVAIL-P study. During the weight loss phase, overweight and obese adults (N=30) completed a 10-week OPTIFAST® program with supervised aerobic exercise training with the goal of achieving clinically significant weight loss (≥7%). Participants who met the weight loss goal were randomized to levels of aerobic training consistent with physical activity recommendations (PA-REC) (~550 MET minutes per week) or weight maintenance recommendations (WM-REC) (~970 MET minutes per week) for 18 additional weeks. Valine, leucine, isoleucine and total BCAA levels were measured using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) at baseline, after the weight loss phase (10 weeks) and at follow-up (28 Weeks) (LabCorp, Raleigh, NC).
Results: Following the weight loss phase, participants had a significant mean reduction in weight (-8.8 kg, p<0.001), total BCAA (-37.4 μmol/L, p<0.001), valine (-15.2 μmol/L, p=0.012), leucine (-20.0 μmol/L, p<0.001), but not isoleucine (-4.1 μmol/L, p=0.214) levels. Improvements in BCAA levels were associated with changes in HDL levels (r=-0.39, p=0.03) and approached significance for visceral fat (r=0.34, p=0.07). Furthermore, changes in BCAA metabolites were not associated with weight, glucose metabolism or other lipid variables for the weight loss phase (p>0.05). In a subset of participants (N=14) who completed the weight maintenance phase (due to COVID pandemic), there were no group differences in the change in total BCAA, valine, leucine between the PA-REC and the WM-REC groups (all ps >0.05). Changes in total BCAA levels (baseline to 28 weeks) were associated with higher mean aerobic exercise training intensity during the intervention (r=-0.64, p=0.013).
Conclusion: Weight loss using the OPTIFAST® weight loss program diet combined with aerobic exercise improved BCAA levels, which is associated with decreased CVD risk. Lower BCAA levels during weight maintenance may be influenced by higher exercise intensity exercise. Future studies should evaluate the impact of lifestyle interventions on BCAA levels during long-term weight maintenance.
More abstracts on this topic:
A combined approach of cardiac magnetic resonance and CardioMEMS to assess right ventricular dysfunction during exercise in HFpEF-PH
Bekhuis Youri, Bogaert Jan, La Gerche Andre, Claessen Guido, Janssens Stefan, Droogne Walter, Rosseel Thomas, Barrios Leticia, Verwerft Jan, Timmermans Philippe, Trenson Sander, Dresselaers Tom
Effect of Caloric Restriction on Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Health in Young Adults: Insights from the CALERIE TrialChang Ryan, Claggett Brian, Redman Leanne, Ravussin Eric, Apovian Caroline, Ostrominski John