Final ID: MDP828
Impact of serum chloride levels for ventricular arrhythmias in patients with heart failure undergoing cardiac resynchronization therapy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: As previous reports of ventricular arrhythmia (VA) as a prognostic marker of mortality in heart failure (HF) patients included those with implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) and cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices, little is known about the risk factors of VA among patients undergoing cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), especially those without previous VA. The prognostic role of electrolyte abnormalities has been highlighted in HF patients. This study evaluated the impact of serum chloride levels for VA and all-cause death in patients with HF who underwent CRT without VA before CRT implantation.
Methods: From the retrospective cohort of 397 HF patients (age 63+/-13, male 74%) who undergoing CRT implantation between 2010 and 2020, this study enrolled 175 patients (82% implanted CRT with a defibrillator) without a previous history of VA (sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) of ventricular fibrillation (VF)). We studied the impact of serum chloride levels before CRT implantation. The primary endpoint was defined as VA, VA with ICD therapy and sudden cardiac death. The secondary endpoint was all-cause mortality.
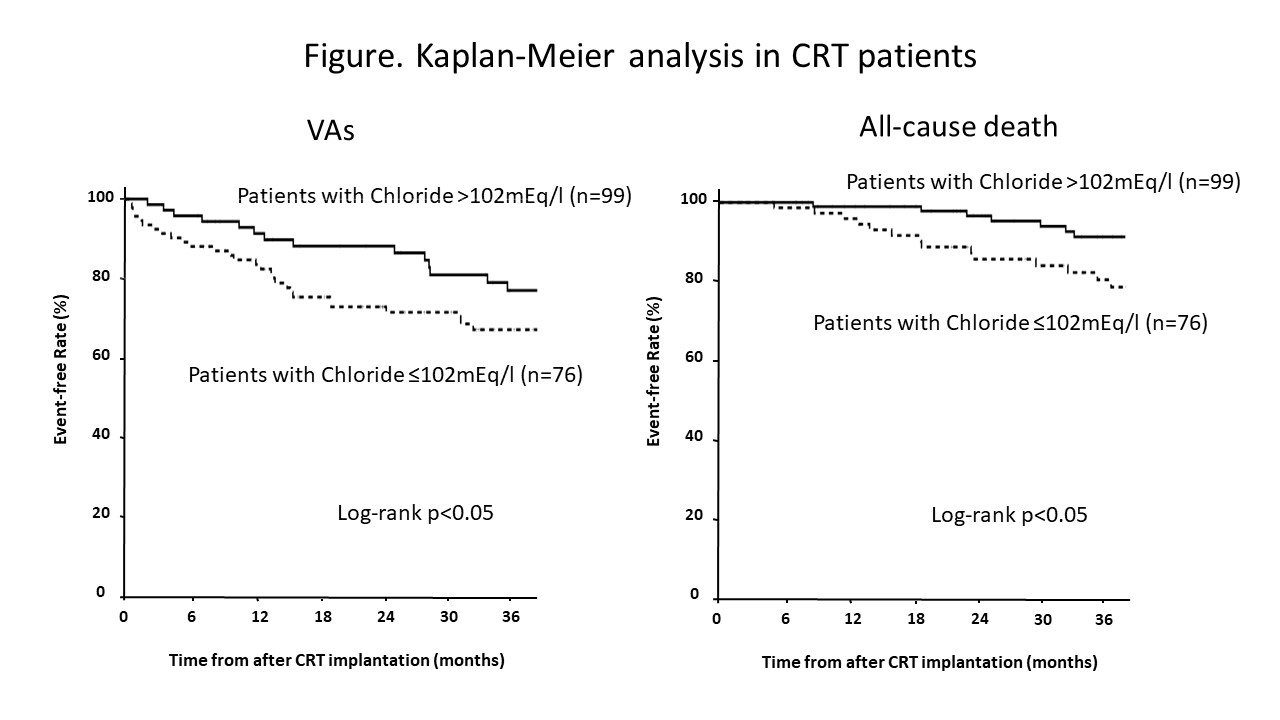
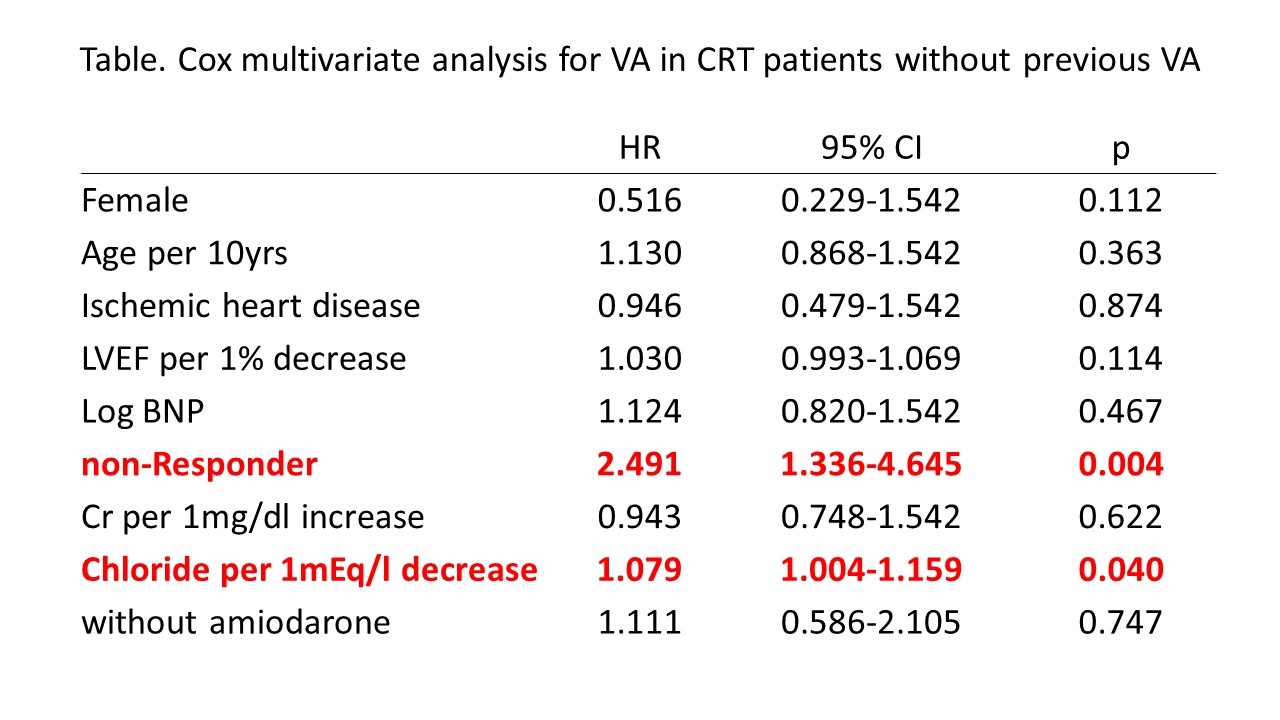
Results: During median follow-up of 35 months, 53 patients (30%) experienced VA. Patients with VA had a tendency toward high LVESV (172ml vs. 150ml, p<0.09) and low left ventricular ejection fraction (26 vs. 29, p<0.09), and significantly reduced rate of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (30% vs. 70%, p<0.05) at the time of CRT implantation. The rate of CRT responders was significantly higher in patients without VA than with VA (59% vs. 40%, p<0.05). The cut-off value of chloride for VA was determined to be 102mEq/l using receiver operating characteristic analysis. The patients with chloride ≤102mEq/l had significantly higher rates of VA (41% vs. 25%, log-rank p<0.05) and mortality (33% vs. 18%, log-rank p<0.05) (Figure). By multivariate cox analysis, the level of chloride had an independent predictive value of VA in patients with CRT (hazard ratio [HR] 1.08 per 1mEq/l decrease, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.00-1.16, p<0.05) (Table).
Conclusions: The chloride level had a predictive value for VA after CRT implantation in HF patients without previous VA. The management of electrolytes, including chloride, might be important for preventing fatal arrhythmia in patients with HF undergoing CRT implantation.
Methods: From the retrospective cohort of 397 HF patients (age 63+/-13, male 74%) who undergoing CRT implantation between 2010 and 2020, this study enrolled 175 patients (82% implanted CRT with a defibrillator) without a previous history of VA (sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) of ventricular fibrillation (VF)). We studied the impact of serum chloride levels before CRT implantation. The primary endpoint was defined as VA, VA with ICD therapy and sudden cardiac death. The secondary endpoint was all-cause mortality.
Results: During median follow-up of 35 months, 53 patients (30%) experienced VA. Patients with VA had a tendency toward high LVESV (172ml vs. 150ml, p<0.09) and low left ventricular ejection fraction (26 vs. 29, p<0.09), and significantly reduced rate of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (30% vs. 70%, p<0.05) at the time of CRT implantation. The rate of CRT responders was significantly higher in patients without VA than with VA (59% vs. 40%, p<0.05). The cut-off value of chloride for VA was determined to be 102mEq/l using receiver operating characteristic analysis. The patients with chloride ≤102mEq/l had significantly higher rates of VA (41% vs. 25%, log-rank p<0.05) and mortality (33% vs. 18%, log-rank p<0.05) (Figure). By multivariate cox analysis, the level of chloride had an independent predictive value of VA in patients with CRT (hazard ratio [HR] 1.08 per 1mEq/l decrease, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.00-1.16, p<0.05) (Table).
Conclusions: The chloride level had a predictive value for VA after CRT implantation in HF patients without previous VA. The management of electrolytes, including chloride, might be important for preventing fatal arrhythmia in patients with HF undergoing CRT implantation.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Concomitant Wild-Type Transthyretin and Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis Involving Separate Organs
Chiu Leonard, Afrough Aimaz, Nadeem Urooba, Jebakumar Deborah, Grodin Justin
A Bridge from Sweet to Sour: A Case of Recurrent Myocardial Stunning in Diabetic KetoacidosisSatish Vikyath, Pargaonkar Sumant, Slipczuk Leandro, Schenone Aldo, Maliha Maisha, Chi Kuan Yu, Sunil Kumar Sriram, Borkowski Pawel, Vyas Rhea, Rodriguez Szaszdi David Jose Javier, Kharawala Amrin, Seo Jiyoung