Final ID: MDP1481
Pericoronary Adipose Tissue Inflammation as a Marker of Increased Coronary Plaque Burden in Patients With Chronic Coronary Artery Disease With Zero Calcium Score
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Dysfunctional or excess adiposity plays pivotal role in the development of coronary atherosclerosis. It remains unclear whether pericoroanry adipose tissue (PCAT) inflammation is associated with increased coronary plaque burden in its early stage of atherosclerosis, independent of traditional coronary risks or cardiovascular-kidney metabolic health.
Purpose: To investigate the association of PCAT inflammation with coronary plaque burden in patients with newly suspected with chronic coronary artery disease (CAD) and zero calcium score who underwent coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA).
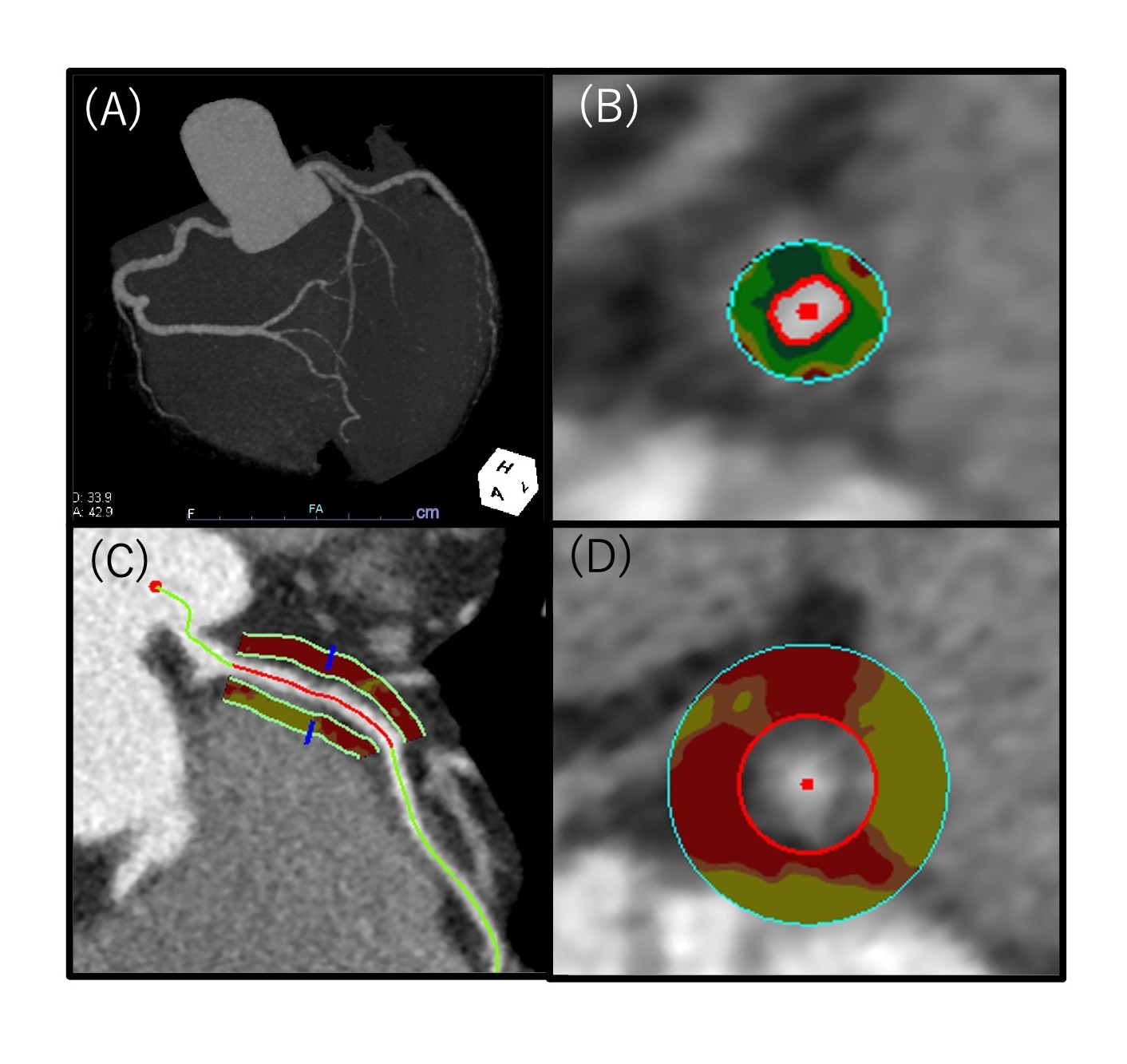
Methods: This retrospective CCTA study consists of 294 chronic CAD patients with zero calcium score (59 years, male 51 %). Chronic CAD was defined as stable condition with presence of increased non-calcified plaque burden on CCTA (Figure 1A-D). PCAT attenuation (PCATA) was assessed by fat attenuation index in the major three coronary arteries (right coronary artery, RCA; left anterior descending artery; LAD, and left circumflex coronary artery, LCX)(Figure 1C and D). Multivariable analysis using linear regression model was performed to determine independent predictors of increased %PV by adjusting for traditional coronary risks, metabolic risks, and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Hisayama Risk Score (HRS) was calculated to estimate 10-year cardiovascular risks.
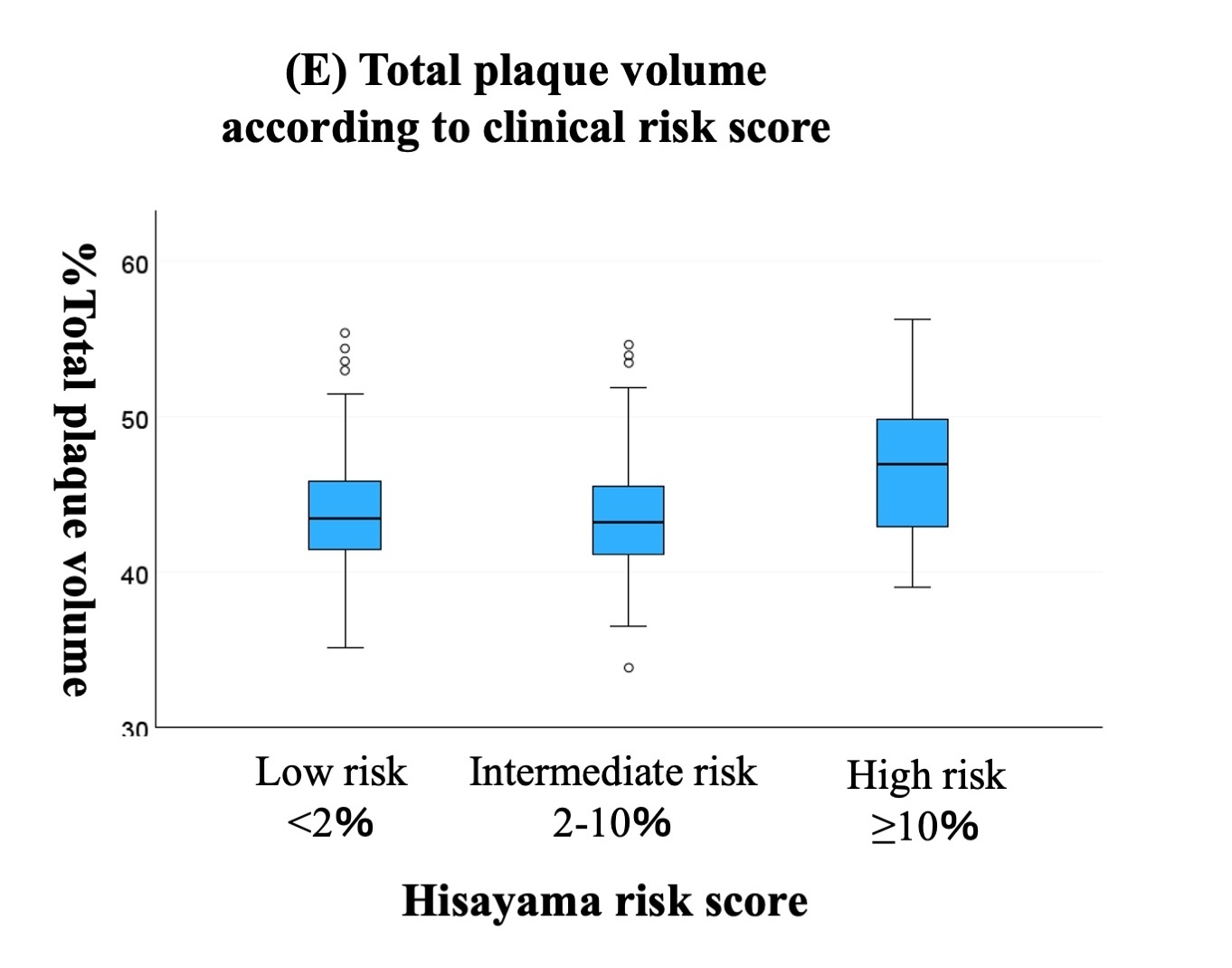
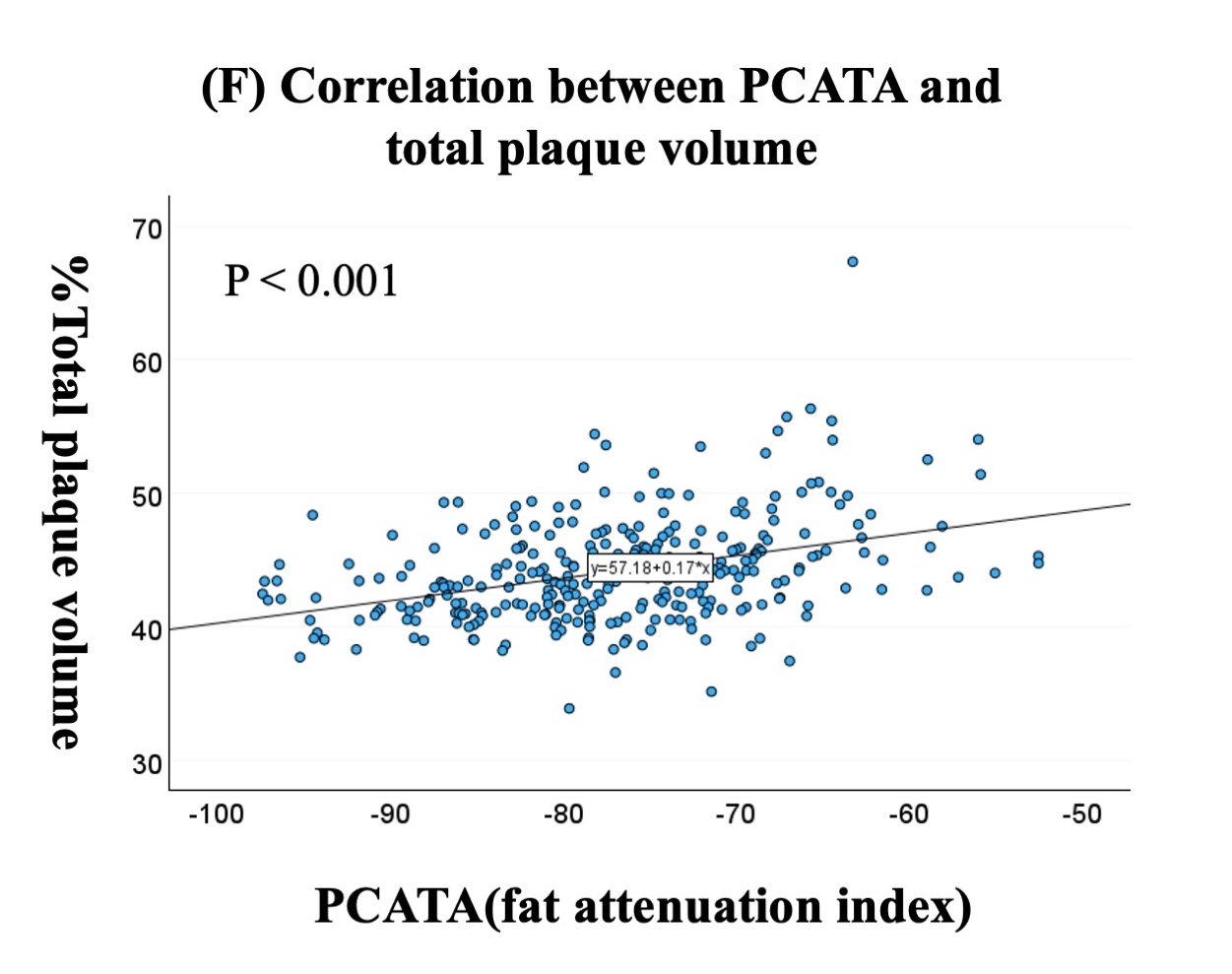
Results: Mean %plaque volume (PV) and PCATA-RCA was 44±4.0% and -77±8.8 HU. %PV was correlated with age (p<0.05), systolic blood pressure (p<0.05), non-HDL cholesterol (p<0.05), Hisayama risk score (p<0.05, Figure 2), PCATA-RCA (p<0.001, Figure 3), PCATA-LAD (p<0.001), and LCX-PCATA (p<0.001). In a multivariable linear regression model adjusting for age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and current smoking (model 1), PCATA-RCA was independently associated with %PV [beta, 0.17; 95% confidential interval (CI) 0.115-0.217, p < 0.001]. In a model adjusting for age, sex, metabolic syndrome, body mass index ≥23kg/mm2, and CKD (model 2), PCATA-RCA (beta, 0.18; 95% CI 0.128-0.232, p<0.001) and high-risk HRS (beta, 3.1; 95% CI 1.35−4.87, p<0.001) were independently associated with %PV. Similarly, independent associations of PCATA in LAD and LCX with %PV was observed.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that PCATA is a robust marker related to increased burden of coronary atherosclerosis even in the early stage of atherosclerosis as defined by zero coronary artery calcium score.
Purpose: To investigate the association of PCAT inflammation with coronary plaque burden in patients with newly suspected with chronic coronary artery disease (CAD) and zero calcium score who underwent coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA).
Methods: This retrospective CCTA study consists of 294 chronic CAD patients with zero calcium score (59 years, male 51 %). Chronic CAD was defined as stable condition with presence of increased non-calcified plaque burden on CCTA (Figure 1A-D). PCAT attenuation (PCATA) was assessed by fat attenuation index in the major three coronary arteries (right coronary artery, RCA; left anterior descending artery; LAD, and left circumflex coronary artery, LCX)(Figure 1C and D). Multivariable analysis using linear regression model was performed to determine independent predictors of increased %PV by adjusting for traditional coronary risks, metabolic risks, and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Hisayama Risk Score (HRS) was calculated to estimate 10-year cardiovascular risks.
Results: Mean %plaque volume (PV) and PCATA-RCA was 44±4.0% and -77±8.8 HU. %PV was correlated with age (p<0.05), systolic blood pressure (p<0.05), non-HDL cholesterol (p<0.05), Hisayama risk score (p<0.05, Figure 2), PCATA-RCA (p<0.001, Figure 3), PCATA-LAD (p<0.001), and LCX-PCATA (p<0.001). In a multivariable linear regression model adjusting for age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and current smoking (model 1), PCATA-RCA was independently associated with %PV [beta, 0.17; 95% confidential interval (CI) 0.115-0.217, p < 0.001]. In a model adjusting for age, sex, metabolic syndrome, body mass index ≥23kg/mm2, and CKD (model 2), PCATA-RCA (beta, 0.18; 95% CI 0.128-0.232, p<0.001) and high-risk HRS (beta, 3.1; 95% CI 1.35−4.87, p<0.001) were independently associated with %PV. Similarly, independent associations of PCATA in LAD and LCX with %PV was observed.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that PCATA is a robust marker related to increased burden of coronary atherosclerosis even in the early stage of atherosclerosis as defined by zero coronary artery calcium score.
More abstracts on this topic:
Analysis of C-reactive protein omics-measures associates methylation risk score with obstructive sleep apnea-related measures
Wang Ziqing, Hou Lifang, Ramos Alberto, Kaur Sonya, Durda Peter, Gonzalez Hector, Fornage Myriam, Redline Susan, Isasi Carmen, Sofer Tamar, Wallace Danielle, Spitzer Brian, Huang Tianyi, Taylor Kent, Rotter Jerome, Rich Stephen, Liu Peter, Daviglus Martha
Aging Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction is Mediated by Noncoding RNAsChakraborty Sankalpa, Dickerson Bryce, Bounds Curren, Lemus Sophia, Hickman Caleb, Rajagopalan Viswanathan