Final ID: MDP617
Blood Pressure Lowering Effectiveness of Ultrasound Renal Denervation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background: Ultrasound Renal Denervation (uRDN) has emerged as an innovative therapeutic modality for resistant hypertension. However, there is uncertainty regarding the effectiveness of this procedure compared to other renal denervation techniques. We aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of uRDN especially on ambulatory and daytime blood pressure.
Objectives: given the need for clarity in treatment approaches, our study aimed to evaluate the impact of ultrasound renal denervation particularly on ambulatory and daytime blood pressure in patients with hypertension.
Methods: we conducted a systematic search of Embase, PubMed, and Cochrane Library databases up to March 2024 to identify randomized controlled trials (RCT) evaluating the effectiveness of uRDN. Statistical analyses were performed using RevMan 6.3 software, utilizing the mean and standard deviation method to calculate mean differences (MD) with a 95% confidence interval (CI).
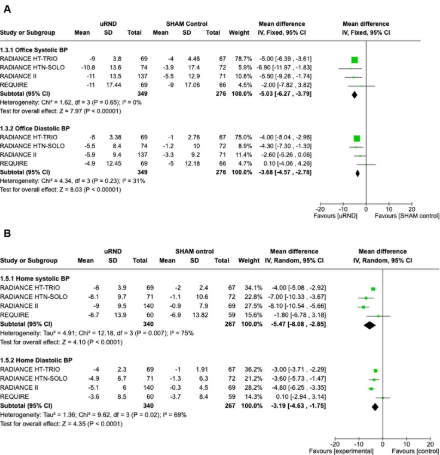
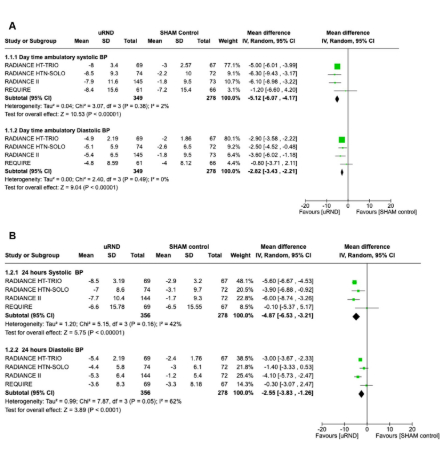
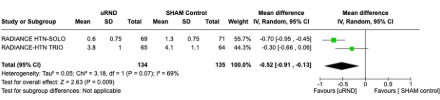
Results: four studies were included in the final analysis, involving 648 patients. Ultrasound renal denervation reduced daytime ambulatory SBP (5.12 mmHg; 95% CI -6.07 to -4.16, p = < 0.00001), 24 hours SBP (-4.87 mmHg; 95% CI 6.53 to -3.20, p = < 0.00001), office SBP (-5.03 mmHg; 95% CI -6.27 to -3.79, p = < 0.00001) at 2 months after the procedure and showed a decrease in patient medication at 6 months after the procedure.
Conclusions: the use of uRND decreases the blood pressure among patients within 2-3 months following the procedure. However, after 6-months of procedure, there is no further significant reduction in blood pressure, although there is a notable decrease in medication. With this data, it is reassuring to conclude that endovascular uRDN using upgraded catheter technologies with the refinement of contemporary procedural techniques has improved the BP-lowering efficacy and safety of RDN during a 3 to 6-month follow-up, with decrease short-term need in medications. The impact of uRDN on the long term deserves further investigation.
Background: Ultrasound Renal Denervation (uRDN) has emerged as an innovative therapeutic modality for resistant hypertension. However, there is uncertainty regarding the effectiveness of this procedure compared to other renal denervation techniques. We aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of uRDN especially on ambulatory and daytime blood pressure.
Objectives: given the need for clarity in treatment approaches, our study aimed to evaluate the impact of ultrasound renal denervation particularly on ambulatory and daytime blood pressure in patients with hypertension.
Methods: we conducted a systematic search of Embase, PubMed, and Cochrane Library databases up to March 2024 to identify randomized controlled trials (RCT) evaluating the effectiveness of uRDN. Statistical analyses were performed using RevMan 6.3 software, utilizing the mean and standard deviation method to calculate mean differences (MD) with a 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results: four studies were included in the final analysis, involving 648 patients. Ultrasound renal denervation reduced daytime ambulatory SBP (5.12 mmHg; 95% CI -6.07 to -4.16, p = < 0.00001), 24 hours SBP (-4.87 mmHg; 95% CI 6.53 to -3.20, p = < 0.00001), office SBP (-5.03 mmHg; 95% CI -6.27 to -3.79, p = < 0.00001) at 2 months after the procedure and showed a decrease in patient medication at 6 months after the procedure.
Conclusions: the use of uRND decreases the blood pressure among patients within 2-3 months following the procedure. However, after 6-months of procedure, there is no further significant reduction in blood pressure, although there is a notable decrease in medication. With this data, it is reassuring to conclude that endovascular uRDN using upgraded catheter technologies with the refinement of contemporary procedural techniques has improved the BP-lowering efficacy and safety of RDN during a 3 to 6-month follow-up, with decrease short-term need in medications. The impact of uRDN on the long term deserves further investigation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association Between Computed Tomography Perfusion Parameters and Functional Independence in Acute Ischemic Stroke Post-Endovascular Therapy: A Secondary Analysis from the SELECT Study
Narangoli Adeeb, Sila Cathy, Opaskar Amanda, Xiong Wei, Degeorgia Michael, Duncan Kelsey, Ray Abhishek, Hu Yin, Sunshine Jeffrey, Bambakidis Nicholas, Sarraj Amrou, Yaghmoor Bassam, Pujara Deep, Alshaibi Faisal, Saidi Yazid, Shafiq Ameena, Albedaiwi Mohammed, Al Mostaneer Alhassin, Sundararajan Sophia
A Comparative Study Of Social Determinants, Hypertension, And Life Essential Factors In Alabama And Colorado From The 2021 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance SystemChukwunyere Chibuike, Owuor Kevin