Final ID: 4113300
Targeting Liver Epsins Ameliorates Dyslipidemia in Atherosclerosis
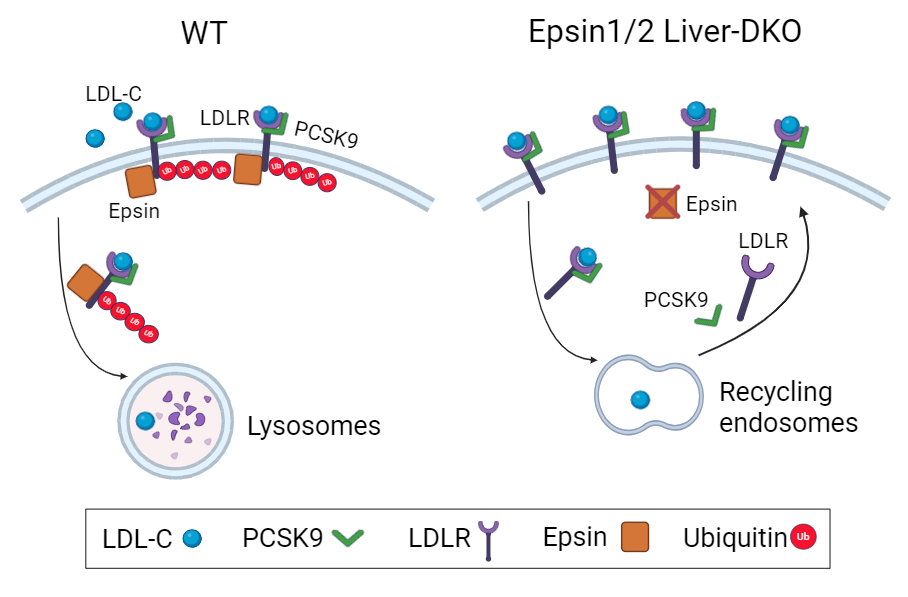
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Rationale: Low density cholesterol receptor (LDLR) in the liver is critical for the clearance of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in the blood. In atherogenic conditions, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9 (PCSK9) binds to LDLR on the surface of hepatocytes, preventing its recycling and enhancing its degradation in lysosomes, resulting in reduced LDL-C clearance. Our recent studies demonstrate that epsins, a family of ubiquitin-binding endocytic adaptors, are critical regulators of atherogenicity. Given the fundamental contribution of circulating LDL-C to atherosclerosis, we hypothesize that liver epsins promote atherosclerosis by controlling PCSK9-triggered LDLR endocytosis and degradation.
Objective: We will determine the role of liver epsins in promoting PCSK9-mediated LDLR degradation and hindering LDL-C clearance to propel atherosclerosis.
Methods and Results: We generated double knockout mice using albumin Cre in which both genes of epsin, namely, epsin 1 and epsin 2, are specifically deleted in the liver (Liver-DKO) on an ApoE -/- background. We discovered that western diet (WD)-induced atherogenesis was greatly inhibited, along with diminished blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Mechanistically, using scRNA-seq analysis on hepatocyte-derived data revealed elevated pathway involved in LDL particle clearance under WD treatment in ApoE-/- /Liver-DKO, which was coupled with diminished plasma LDL-C levels. Further analysis using the MEBOCOST algorithm revealed enhanced communication score between LDLR and cholesterol, suggesting elevated LDL-C clearance in the ApoE-/- Liver-DKO mice. In addition, we showed that loss of epsins in the liver upregulates of LDLR protein level. We further showed that epsins bind LDLR via the ubiquitin-interacting motif (UIM), and PCSK9-triggered LDLR degradation was abolished by depletion of epsins, preventing atheroma progression. Finally, our therapeutic strategy, which involved targeting liver epsins with nanoparticle-encapsulated siRNAs, was highly efficacious at inhibiting dyslipidemia and impeding atherosclerosis.
Conclusions: Liver epsins promote atherogenesis by mediating PCSK9-triggered degradation of LDLR, thus raising the circulating LDL-C levels. Targeting epsins in the liver may serve as a novel therapeutic strategy to treat atherosclerosis by suppression of PCSK9-mediated LDLR degradation.
Objective: We will determine the role of liver epsins in promoting PCSK9-mediated LDLR degradation and hindering LDL-C clearance to propel atherosclerosis.
Methods and Results: We generated double knockout mice using albumin Cre in which both genes of epsin, namely, epsin 1 and epsin 2, are specifically deleted in the liver (Liver-DKO) on an ApoE -/- background. We discovered that western diet (WD)-induced atherogenesis was greatly inhibited, along with diminished blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Mechanistically, using scRNA-seq analysis on hepatocyte-derived data revealed elevated pathway involved in LDL particle clearance under WD treatment in ApoE-/- /Liver-DKO, which was coupled with diminished plasma LDL-C levels. Further analysis using the MEBOCOST algorithm revealed enhanced communication score between LDLR and cholesterol, suggesting elevated LDL-C clearance in the ApoE-/- Liver-DKO mice. In addition, we showed that loss of epsins in the liver upregulates of LDLR protein level. We further showed that epsins bind LDLR via the ubiquitin-interacting motif (UIM), and PCSK9-triggered LDLR degradation was abolished by depletion of epsins, preventing atheroma progression. Finally, our therapeutic strategy, which involved targeting liver epsins with nanoparticle-encapsulated siRNAs, was highly efficacious at inhibiting dyslipidemia and impeding atherosclerosis.
Conclusions: Liver epsins promote atherogenesis by mediating PCSK9-triggered degradation of LDLR, thus raising the circulating LDL-C levels. Targeting epsins in the liver may serve as a novel therapeutic strategy to treat atherosclerosis by suppression of PCSK9-mediated LDLR degradation.
More abstracts on this topic:
4-Phenylbutyric Acid Reduces Endoplasmic Reticulum Retention and Partially Restores Function of LDLR p.D622N Mutation In Vitro: A Potential Therapy for Hypercholesterolemia
Wang Yongxiang, Zhang Piyi, Bai Ming, Zhang Zheng
A Case of Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Systemic Thromboembolism in a Young Patient on Testosterone Replacement TherapySabri Muhammad, Ijaz Naila, Nadeem Ramsha, Checchio Lucy, Riaz Faiza