Final ID:
SURF4-containing Classical Vesicles Mediate Apolipoprotein(a)-ApolipoproteinB Secretory Trafficking
Abstract Body: Introduction: Elevated plasma levels of Lp(a) are an independent, causal risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Plasma Lp(a) concentration depends mainly on Lp(a) production rate in hepatocytes, which is mediated by intracellular non-covalent complexes between weak lysine binding sites in apo(a) kringles IV types 7 and 8 (LBS7,8) with apoB. Lp(a) is smaller, denser and more cholesterol-rich than VLDL, and Lp(a)-apoB is secreted at a lower rate than VLDL-apoB. Thus, Lp(a) and VLDL may follow different intracellular assembly and trafficking pathways. VLDL secretory trafficking has been reported to involve SURF4-containing, TANGO1-dependent, expanded COPII VLDL transport vesicles (VTV). However, the mechanisms causing differences in lipidation and apolipoprotein composition of Lp(a) compared to VLDL remain unclear.
Hypothesis: The intracellular interaction between apo(a) and apoB diverts nascent Lp(a) from VTVs and hence impacts its secretion rate and lipidation.
Methods: HuH7 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding either 17K (wild-type) or 17K△LBS7,8 apo(a) and incubated with oleic acid to stimulate lipoprotein assembly. Lp(a) secretion was assessed by immunoblot of medium from cells also transfected with siRNAs targeting expression of the VLDL-associated proteins SURF4, TM6SF2, FITM2, MTP or TANGO1. Interactions between apo(a), apoB and the VLDL ER cargo receptor, SURF4 were studied by pulldown assays. Confocal and super resolution radial fluctuation (SRRF) microscopy were used to assess apo(a)-apoB intracellular colocalization.
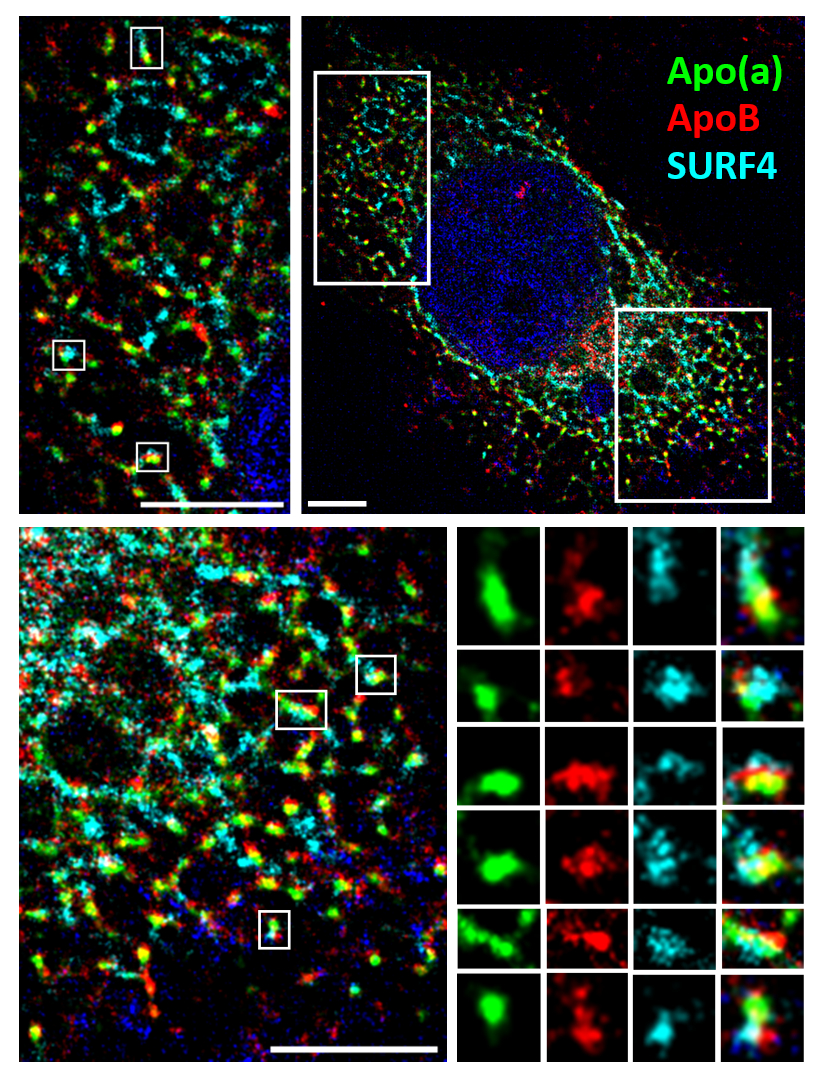
Results: Knockdown of SURF4, TM6SF2, FITM2, and MTP using siRNA reduced apo(a) and apoB secretion. The reduction in apo(a) secretion was dependent upon the weak lysine binding sites present in apo(a) KIV types 7 and 8 in the case of siRNAs against TM6SF2 and MTP but not SURF4. Surprisingly, TANGO1 siRNA reduced apoB secretion, but increased apo(a) secretion. Pulldowns showed that apo(a) transfection reduced SURF4-apoB binding; this decrease was dependent on apo(a)-apoB interactions. Using SRRF microscopy, colocalization of apo(a), apoB and SURF4 was observed.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest a role for several new players in the apo(a)-apoB secretion pathway and highlight the difference in secretory trafficking mechanisms between Lp(a) and VLDL. SURF4 may act as an ER-cargo receptor for apo(a) secretory trafficking, albeit potentially independent of the apo(a)-apoB interaction.
Hypothesis: The intracellular interaction between apo(a) and apoB diverts nascent Lp(a) from VTVs and hence impacts its secretion rate and lipidation.
Methods: HuH7 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding either 17K (wild-type) or 17K△LBS7,8 apo(a) and incubated with oleic acid to stimulate lipoprotein assembly. Lp(a) secretion was assessed by immunoblot of medium from cells also transfected with siRNAs targeting expression of the VLDL-associated proteins SURF4, TM6SF2, FITM2, MTP or TANGO1. Interactions between apo(a), apoB and the VLDL ER cargo receptor, SURF4 were studied by pulldown assays. Confocal and super resolution radial fluctuation (SRRF) microscopy were used to assess apo(a)-apoB intracellular colocalization.
Results: Knockdown of SURF4, TM6SF2, FITM2, and MTP using siRNA reduced apo(a) and apoB secretion. The reduction in apo(a) secretion was dependent upon the weak lysine binding sites present in apo(a) KIV types 7 and 8 in the case of siRNAs against TM6SF2 and MTP but not SURF4. Surprisingly, TANGO1 siRNA reduced apoB secretion, but increased apo(a) secretion. Pulldowns showed that apo(a) transfection reduced SURF4-apoB binding; this decrease was dependent on apo(a)-apoB interactions. Using SRRF microscopy, colocalization of apo(a), apoB and SURF4 was observed.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest a role for several new players in the apo(a)-apoB secretion pathway and highlight the difference in secretory trafficking mechanisms between Lp(a) and VLDL. SURF4 may act as an ER-cargo receptor for apo(a) secretory trafficking, albeit potentially independent of the apo(a)-apoB interaction.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Role for Lipoprotein(a) in Potentiating Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation
Mouawad Sahar, Boffa Michael, Koschinsky Marlys
A Mechanistic Insight Into The Connection Between Metabolism And Differentiation In ACTA2 P. R179 Smooth Muscle CellsEsparza Pinelo Jose, Krenz Hannah, Chen Jessica, Kaw Anita, Milewicz Dianna, Kwartler Callie