Final ID:
Mitigating Sex-Specific Thrombotic Risk by Personalizing Thromboprophylaxis
Abstract Body: Background: Despite advances in endovascular revascularization techniques for peripheral arterial disease (PAD), thrombotic complications remain a significant cause of morbidity namely amputation. Women, despite having lower risk factors, are at increased risk for arterial thrombotic events and amputation. This is partially due to the fact that standard of care thromboprophylaxis is administered in a “one size fits all “ approach that may inadequarely treat women. The aim of this study is to evaluate the impact of using a novel personalized approach to thromboprophylaxis to achieve therapeutic antiplatelet levels in women.
Methods: We developed a novel approach to thromboprophylaxis called Thromboprophylaxis for Arterial Revascularization to Guide Elderly Therapy (TARGET) that uses objective viscoelastic testing, namely thromboelastrography (TEG), to guide anticoagulation. We implemented this protocol in a cohort of patients and compared thrombotic outcomes to those of patients who received the “one size fits all” standard of care.
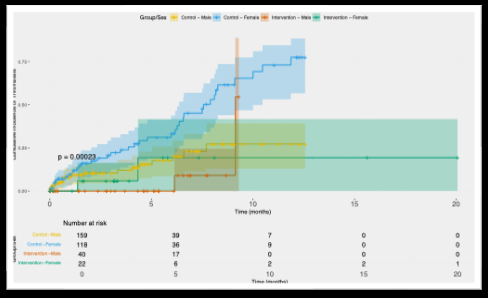
We studied 339 patients (277 control: 159 male vs. 118 female; 62 intervention: 40 male vs. 22 female) over 20 months. The control group received standard dual antiplatelet therapy, while the intervention group received TEG-PM-guided antiplatelet adjustment. Primary endpoint was time to first imaging-confirmed thrombotic event, analyzed using Cox proportional hazards and Kaplan-Meier estimation, with Male-Control as reference.
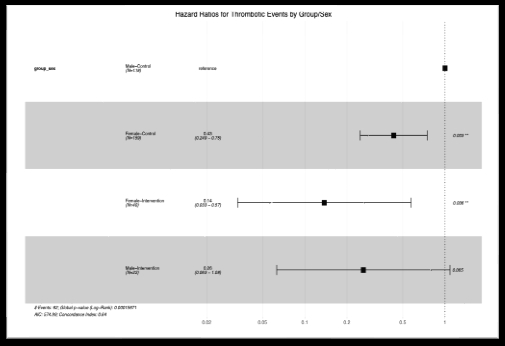
Results: The TEG-PM-guided intervention demonstrated significant sex-specific effects on thrombosis prevention. Control females exhibited the highest baseline thrombotic risk, with cumulative incidence reaching 75% during follow-up. Females showed the greatest benefit from TARGET intervention with an 86% risk reduction (HR 0.14, 95% CI 0.033-0.57, p=0.006) compared to male controls. Males demonstrated a trend toward benefit with a 74% risk reduction (HR 0.26, 95% CI 0.063-1.08, p=0.065). The cumulative incidence of thrombotic events differed significantly between groups (global p<0.00023), with lower event rates in the intervention groups.
Conclusion: Females showed the highest baseline thrombotic risk in PAD but gained most from TEG-PM-guided thromboprophylaxis. While males showed less improvement, the results suggest individualized TEG-PM-guided thromboprophylaxis may be especially important for female PAD patients.
Methods: We developed a novel approach to thromboprophylaxis called Thromboprophylaxis for Arterial Revascularization to Guide Elderly Therapy (TARGET) that uses objective viscoelastic testing, namely thromboelastrography (TEG), to guide anticoagulation. We implemented this protocol in a cohort of patients and compared thrombotic outcomes to those of patients who received the “one size fits all” standard of care.
We studied 339 patients (277 control: 159 male vs. 118 female; 62 intervention: 40 male vs. 22 female) over 20 months. The control group received standard dual antiplatelet therapy, while the intervention group received TEG-PM-guided antiplatelet adjustment. Primary endpoint was time to first imaging-confirmed thrombotic event, analyzed using Cox proportional hazards and Kaplan-Meier estimation, with Male-Control as reference.
Results: The TEG-PM-guided intervention demonstrated significant sex-specific effects on thrombosis prevention. Control females exhibited the highest baseline thrombotic risk, with cumulative incidence reaching 75% during follow-up. Females showed the greatest benefit from TARGET intervention with an 86% risk reduction (HR 0.14, 95% CI 0.033-0.57, p=0.006) compared to male controls. Males demonstrated a trend toward benefit with a 74% risk reduction (HR 0.26, 95% CI 0.063-1.08, p=0.065). The cumulative incidence of thrombotic events differed significantly between groups (global p<0.00023), with lower event rates in the intervention groups.
Conclusion: Females showed the highest baseline thrombotic risk in PAD but gained most from TEG-PM-guided thromboprophylaxis. While males showed less improvement, the results suggest individualized TEG-PM-guided thromboprophylaxis may be especially important for female PAD patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
Accelerometer-Measured Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior and Risks of All-Cause and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Among Postmenopausal Cancer Survivors: The Women’s Health Accelerometry Collaboration
Hyde Eric, Stefanick Marcia, Skiba Meghan, Crane Tracy, Lee I-min, Lacroix Andrea, Bandoli Gretchen, Zou Jingjing, Crespo Noe, Parada Humberto, Evenson Kelly, Lamonte Michael, Nguyen Steve, Howard Annie Green
CC-Chemokine Receptor 2 Inhibition Prevents Monocyte/Macrophages Recruitment in Abdominal Aortic AneurysmsElizondo Benedetto Santiago, Zaghloul Mohamed, Arif Batool, Bredemeyer Andrea, Lavine Kory, Gropler Robert, Liu Yongjian, Zayed Mohamed